
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
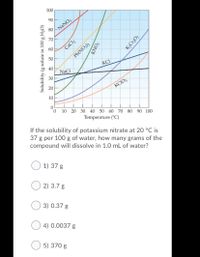
Transcribed Image Text:100
90
NANO3
80
70
60
CaCl2
50
Pb(NO3)2
40
KCI
NaCl
30
20
KCIO3
10
10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80
90 100
Temperature (°C)
If the solubility of potassium nitrate at 20 °C is
37 g per 100 g of water, how many grams of the
compound will dissolve in 1.0 mL of water?
1) 37 g
2) 3.7 g
3) 0.37 g
4) 0.0037 g
O 5) 370 g
Solubility (g solute in 100 g H2O)
KNO3
ONY
K,Cr2O7
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- "Question 6: List below are solubility versus temperature data for an organic substance A dissolved in water. Temperature (°C) 0 20 Solubility of A in 100 mL of Water (g) 1.5 3.0 6.5 60 11.0 80 17.0 a. Suppose 0.1 g of A and 1.0 mL of water were mixed and heated to 80°C. Would all of the substance A dissolve? b. The solution prepared in (a) is cooled. At what temperature will crystals of A appear? around 20°C c. Suppose the cooling described in (b) was continued to 0°C. How many grams of A would come out of the solution? Explain how you obtained your answer. 40arrow_forwardSolve correctly please. (Gpt/ai wrong answer not allowed)arrow_forwardOxygen is soluble in water, much to the benefit of aquatic life forms. At 25 °C, the solubility of oxygen is about 7×10–6 g/cm3, and the pressure of O2 is about 20% of the atmospheric pressure. Could the oxygen dissolved in water affect your experimental results significantly?arrow_forward
- 1. CL was tasked to identify the white solid inorganic salt that Dr. Yang gave her. From her preliminary tests, the possible identities were narrowed down to the following: Zn(CN)₂ Ksp (30°C) = 7.30 x 1012 AgSCN Ksp (30°C) = 5.90 × 10 11 CL chose to investigate the solubility equilibrium of this salt and determine its identity. To a 100.0 mL distilled water at room temperature, CL added the unknown reagent until it no longer dissolves. After letting the mixture stand for 15 mins, she filtered and collected the filtrate in another beaker. From this, a 20.00 mL aliquot was drawn and was titrated with 10.20 mL of 5.00 x 10 M HCI to reach the phenolphthalein endpoint. A. Let X be the titratable species from the dissolved salt. Determine the concentration of X from the titration data. B. Based on the results of CL's experiment and the provided constants, what is the likely identity of the unknown salt? Show complete solutions to support your answer. When she submitted her report to Dr.…arrow_forward1/T (K-¹) 2 N₂O5(g) → 4NO2(g) + O₂(g) K(S-¹) 4.87 x 10-3 1.50 x 10-³ 4.98 x 10-4 1.35 x 10-4 3.46 x 10-5 7.87 x 10-7 T (K) 338 0.0030 328 0.0030 318 0.0031 308 0.0032 298 0.0034 273 6.0037 The data in the table above provide the temperature dependence of the rate constant for the reaction shown. Complete the table with required information to 2 significant figures each. - a=-12571.42 In K, no units 5.3 - 6.5 7.6 8.9 Carefully construct a neat and well labelled graph/plot of In K (y-axis) versus 1/T (x-axis) in the appropriate quadrant (s), using EXCEL or the template below; then determine the slope and activation energy, Ea for the given reaction. Recall that the Arrhenius Equation is represented in a more useful form as In K= In A- (Ea/RT) & R= 8.31 x 10-³ kJ/mol-K. Determine by calculation, the value of Ea in kj/mole given that, slope = -E/R slope: - Ca = slope & - Ga= €ag Ea=-(-12571.42) x (8.3) x 10 Rg/mol-K) Ea=104.47 kj/md 10.3 - 14.1 Y = (-14.1)-(-5.3) = -8.8 x = (0.0037) -…arrow_forwardSolubility Curves of Selected Compounds 150 140 130 120 110 100 NaNO 90 3 80 70 60 NHC 50 40 Naci 30 20 KCIÓ, 10 Ce(sO 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 Temperature (C) At one point, ammonia and potassium nitrate have the same solubility. At that point the solubility of the compounds is: O 77 g/100 g water O 44 g /100 g water O 40 g/ 100 g water O 25 g/100 g water 1 4 8. 9 DELL %23 Grams of solutearrow_forward
- SUBJECT : GENERAL CHEMISTRY 2 TOPIC : THE SOLUTION PROCESS AND FACTORS AFFECTING SOLUBILITYarrow_forwardWhat is the solubility of Ca3(PO4)2 Ksp = 1.3 x 10-32 in a 0.048 M Ca(NO3)2 solution? 5.4 x 10-15M , 1.1 x 10-14 M, 2.6 x 10-16 M, 2.9 x 10-29 Marrow_forwardPseudogoutis caused by the formation of calcium diphosphate (Ca2P2O7) crystals in tendons, cartilage and ligaments, usually occurring if diphosphate levels in blood plasma 7 become very If the [Ca2+] in blood plasma is 9.2 mg/dL and Ksp for Ca2P2O7 is 8.64 x 10-13, what is the minimum concentration of diphosphate P2O 4- necessary for precipitation?arrow_forward
- An impure sample of 250 mg of adipic acid was recrystallized from 2.0 mL of boiling water. The solution was cooled to room temperature slowly and further cooled in an ice bath. What is the maximum amount of recoverable adipic acid at 0 oC? Solubility of adipic acid at 0 oC is 0.3 g/ 100 mL Group of answer choices 6 mg 249 mg 244 mg 250 mgarrow_forwardConsider the solubilities of a particular solute at two different temperatures. Temperature (C) Solubility (g/100 g H,O) 20.0 41.3 30.0 71.3 Suppose a saturated solution of this solute was made using 77.0 g H,O at 20.0 °C. How much more solute can be added if the temperature is increased to 30.0 °C? mass: g * TOOLS x10arrow_forwardAt 90°C, if 51 g of potassium chloride are completely dissolved, the solution is considered to be SOLUBILITY CURVES KI 140 130 120 100 NONO, KNO3 90. HCI, 70 NH CI 60 KCI 50 40 Naci KCIO, 30 20 10 O 10 20 30 40 50 do 70 80 9o 100 TEMPERATURE °C A. supersaturated B. saturated C. uncool GRAMS OF SOLUTE /100g H,0arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY