
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
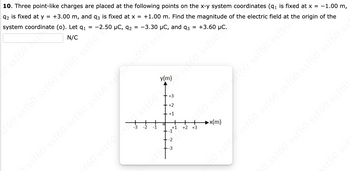
Transcribed Image Text:10. Three point-like charges are placed at the following points on the x-y system coordinates (q₁ is fixed
92 is fixed at y = +3.00 m, and q3 is fixed at x = +1.00 m. Find the magnitude of the electric field at
system coordinate
(0). Let q₁
-2.50 µC, 92 = -3.30
N/C
ssf60 ssf60 ssf60 ssf60 ss 50 ssf60 ssio and q3 = +3.60 µC.
ssf60 st
f60 ssf60 ssf60 ssf60 ssf60?
-2
+2
+ +1
O
ssf6
+1
-1
+
-3
f6
08 09 09 098 09
x(m)
at x =
the origin
ssf60°t the
09588 0915 09588 091
-1.00 m,
of the
$60 ssf ssf60 ssf60 ssf60 ssf60 ssf60 ss
sf60 sst
50 ssf60 ssf60 ssf60 ssf60
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
According to question we need to find resultant electric field at point O.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- of 15 > Two charges are placed on the x-axis, +3.00 µC at the origin and -10.0 µC at x = 10.0 cm. Define the positive direction as the +x-direction. #3 Find the electric field E on the x-axis at x = 6.00 cm. At what point(s) xo on the x-axis is the electric field zero? If there are multiple points, enter the x-coordinates as a comma-separated list. E D C $ 4 * R F 67 5 5 V 7 T G ^ 6 B MacBook Pro Y H & 7 N U J * 8 M - E = Xo = ( 9 K O < ) 0 J P A - لالہ [ ? Question + 11 } 1 m N/C deletearrow_forwardTwo point charges are arranged on the x-y coordinate system as follows: q1 = 3.0x10-9 C at (0, 3m) and q2 = -9.0x10-9C at (4.5m, 0). Find the electric field at origin (0,0)arrow_forwardTwo uncharged spheres are separated by 2.50 m. If 2.20 ✕ 1012 electrons are removed from one sphere and placed on the other, determine the magnitude of the Coulomb force (in N) on one of the spheres, treating the spheres as point charges.arrow_forward
- An electron and a proton are each placed at rest in a uniform electric field of magnitude 518 N/C. Calculate the speed of each particle 47.6 ns after being released.arrow_forwardA particle of charge q is fixed at point P, and a second particle of mass m and the same charge q is initially held a distance ri from P. The second particle is then released. Determine its = 0.90 mm, and r2 = 2.5 mm. 2. speed when it is a distance r2 from P. Let q = 3.1 µC, m 20 mg, riarrow_forwardPoint charges q₁ =92 = 3.2 x 10-6 C are fixed on the x-axis at x = -3.8 m and x = 3.8 m. What charge q (in C) must be placed at the origin so that the electric field vanishes at x = 0, y = 3.8 m? C + Additional Materials Readingarrow_forward
- Consider the electric dipole shown in the figure. (a) Show that the electric field at a distant point on the x-axis is Ex = 4kqa/x3 (b) Where do you think you might find the expression of electric field from a dipole useful?arrow_forwardFour identical metallic objects carry the following charges: +1.80, +6.84, -4.87, and -9.09 C. The objects are brought simultaneously into contact, so that each touches the others. Then they are separated. (a) What is the final charge on each object? (b) How many electrons (or protons) make up the final charge on each object? I've tried -1.33 for A and it's incorrect.arrow_forward9. In a certain region of space, a uniform electric field has a magnitude of 4.6 x 104 N/C and points in the positive x direction. Find the magnitude and direction of the force this field exerts on a charge of -9.30 uc. A uniform electric field is established by connecting the plates of a para If the plates are separated by 0.75 cm, warrow_forward
- Four identical metallic objects carry the following charges: +1.23, +6.89, -4.44, and -9.28 μC. The objects are brought simultaneously into contact, so that each touches the others. Then they are separated. (a) What is the final charge on each object? (b) How many electrons (or protons) make up the final charge on each object? (a) Number i (b) Number IN Units Unitsarrow_forwardThe figure shows an electric dipole. What is the magnitude of the dipole's electric field at point P? Assume that q = 1.34 x 10-6 c, d = 8.65 x 10-6 m, and r = 7.81 cm. +q L. P Number MI d/2 F d/2 Units <arrow_forwardTwo uncharged spheres are separated by 3.50 m. If 1.40 ✕ 1012 electrons are removed from one sphere and placed on the other, determine the magnitude of the Coulomb force (in N) on one of the spheres, treating the spheres as point charges.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON