
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
A parallel plate capacitor has a surface charge density of σ = 0.0046 C/m2 on one plate. A small sphere charged to Q = 5.2E-06 C is moved a distance d = 0.17 m between the plates. Refer to the figure, which is not drawn to scale.
Enter an expression for the electric field vector within the capacitor, E, using given quantities and the unit vectors i and j.
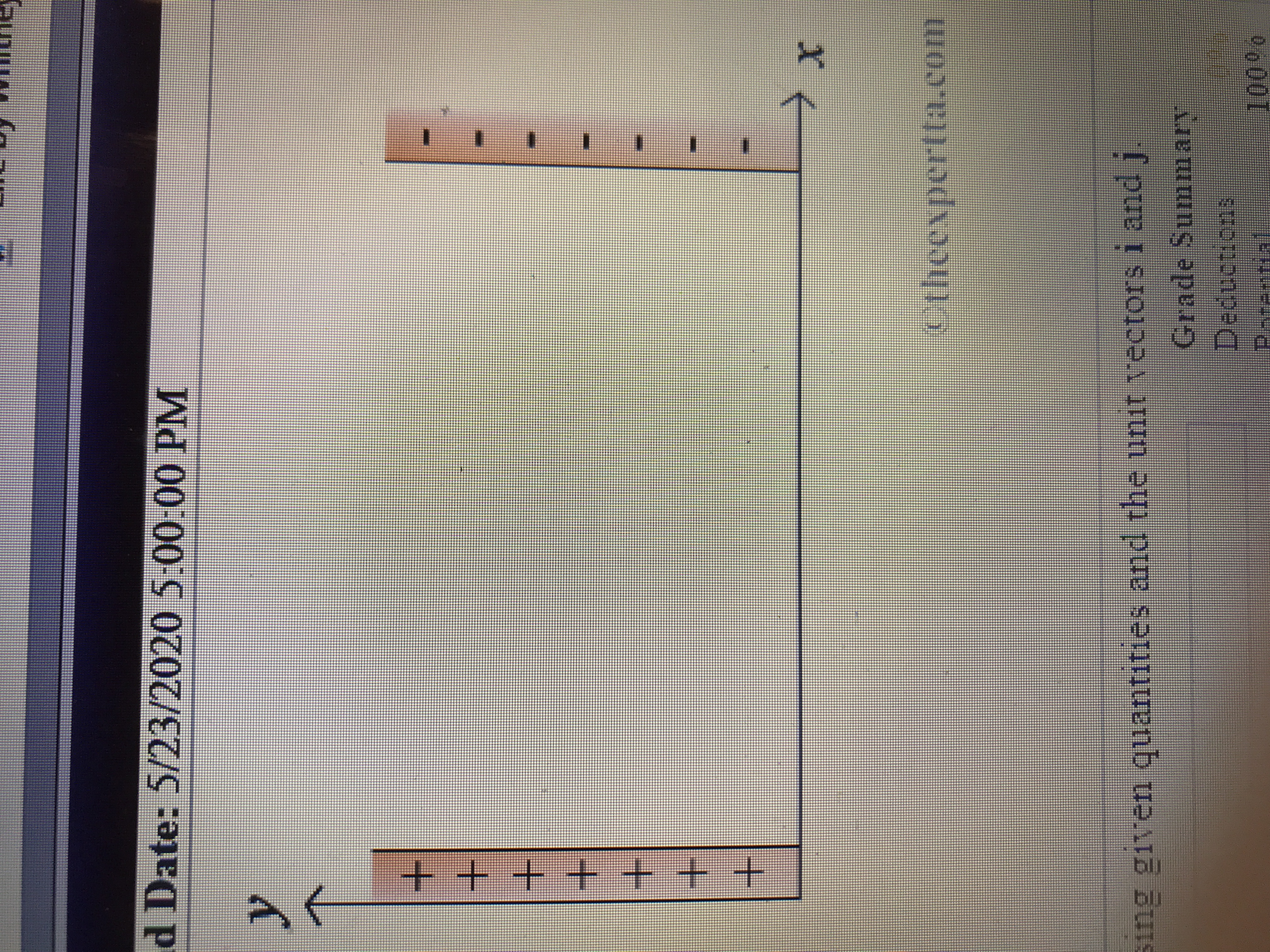
Transcribed Image Text:d Date: 5/23/2020 5:00:00 PM
etheexpertta.com
Sing given quantities and the unit ectors i andj.
Grade Summary
Deductions
Parential
1000 0
+++++ + +
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- can you please ans (k) & ( l)?arrow_forwardThree charges are at the corners of a square. q1 is located at the origin, q2 is located at (1, 0),and q3 is located at (1,1) (the position coordinates are in millimeters). The charges are all equalin magnitude; 1.5x10-6 C. Calculate the electric field at the point (0,1).arrow_forwardIn a rectangular coordinate system a positive point charge q = 6.00 x 10-9 C is placed at the point x = +0.150m, y = 0, and an identical point charge is placed at x = -0.150m, y = 0. Find the x- and y-components, the magnitude, and the direction of the electric field at x = 0.300 m, y = 0. (with precise solution please) A. Ex = 129N/C and Ey = -510N/C with direction of 284 degrees counterclockwise from +x axis B. Ex = 2663.1 N/C and Ey = 0 to the +x direction C. Ex = 0 and Ey = 0 D. none of the abovearrow_forward
- A circular ring of radius 27 cm and total charge 600 μC is centered at the origin as shown in the figure below. If the charge is distributed uniformly around the ring, what is the electric field at the origin? (Enter the magnitude of the electric field.) N/C y B xarrow_forwardA charge distribution creates the following electric field throughout all space: E(r, 0, q) = (3/r) (r hat) + 2 sin cos sin 0(theta hat) + sin cos p (phi hat). Given this electric field, calculate the charge density at location (r, 0, p) = (ab.c).arrow_forwardConsider two thin disks, of negligible thickness, of radius R oriented perpendicular to the x axis such that the x axis runs through the center of each disk. The disk centered at x=0 has positive charge density η, and the disk centered at x=a has negative charge density −η, where the charge density is charge per unit area. What is the magnitude E of the electric field at the point on the x axis with x coordinate a/2? Express your answer in terms of η, R, a, and the permittivity of free space ϵ0.arrow_forward
- E ↑ Απεργια This problem checks your understanding of the term in the equation for the electric field due to a point charge, Consider a charged particle at a point S whose coordinates are (4 m, 2 m, 6 m). We would like to find the electric field vector at a point P whose coordinates are (7 m, 8 m, 1 m). The "unit vector" is a vector that points from S to P that has length of 1 (or "unity"). What is its y component, in meters? (Report your answer to one decimal place.)arrow_forward|K1|K2 EEE =0 OM OR The figure shows three parallel plates. The two spaces between the plates are filled with different dielectric materials with different constants (K, and K2). The electric field in both dielectric media turns out be equal; E is the rightward component of the electric field in those two regions. The field on the right of the rightmost plate is observed to be 0. Based on these, find the surface charge densities on the middle plate, oM, and the rightmost plate, or. Note: Gauss' law in the presence of dielectric materials: feẼ - dà = Qene: OM OR =arrow_forwardThe surface charge density (eta) h of an infinite charged plane is -2.0 x 10-6 C/m2. A proton is shot straight away from the plane at 2.0 x 106 m/s. Make a sketch of the situation. How far does the proton travel before reaching its turning point?arrow_forward
- A cylindrical distribution of charge ρ = α /√ r where α = 2 µC/m 5/2 extends from 0 cm to 9.3 cm . Concentric with this is a dielectric shell with 5.44 of inner radius 16.6 cm and outer radius 24.9 cm . What is the electric field at 3.53 cm ?arrow_forwardesc The nucleus of a 125 Xe atom (an isotope of the element xenon with mass 125 u) is 6.0 fm in diameter. It has 54 protons and charge q = +54e. R 2 R F2 W # 3 80 E $ 4 R Part A What is the electric force on a proton 2.6 fm from the surface of the nucleus? Hint: Treat the spherical nucleus as a point charge. Express your answer with the appropriate units. F= 8.64 Part B μà 1 Submit Previous Answers Request Answer % 5 X Incorrect; Try Again; 4 attempts remaining F5 What is the proton's acceleration? Express your answer with the appropriate units. Value T → HA N 6 C FIC ? Units MacBook Air Y & 7 U * 8 FB ( 9 F9 0 0 P + Reviewarrow_forwardA hemispherical surface of radius b = 94.5 m is fixed in a uniform electric field of magnitude Eo = 5.12 V/m, as shown in the figure. The x axis points out of the screen. azimuthal angle. Use as your outward-pointing unit normal vector. ↑ Enter the general expression for an infinitesimal area element, dÃ, in spherical coordinates (r, 0, 4), where is the polar angle and is the Calculate the electric flux, in volt meters, through the hemisphere. note: Ē=Ekarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON