
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
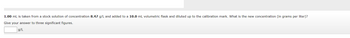
Transcribed Image Text:1.00 mL is taken from a stock solution of concentration 8.47 g/L and added to a 10.0 mL volumetric flask and diluted up to the calibration mark. What is the new concentration (in grams per liter)?
Give your answer to three significant figures.
g/L
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A chemistry student weighs out 0.170 g of citric acid (H₂CH₂O₂), a triprotic acid, into a 250. mL volumetric flask and dilutes to the mark with distilled water. He plans to titrate the acid with 0.1700 M NaOH solution. Calculate the volume of NaOH solution the student will need to add to reach the final equivalence point. Be sure your answer has the correct number of significant digits. 0mL x10 Xarrow_forwardMeasurement and Matter Adding or subtracting and multiplying or dividing measurements 1/3 B A chemistry student must write down in her lab notebook the concentration of a solution of sodium hydroxide. The concentration of a solution equals the mass of what's dissolved divided by the total volume of the solution. Here's how the student prepared the solution: The label on the graduated cylinder says: empty weight: 7.2 g . She put some solid sodium hydroxide into the graduated cylinder and weighed it. With the sodium hydroxide added, the cylinder weighed 63.517 g. . She added water to the graduated cylinder and dissolved the sodium hydroxide completely. Then she read the total volume of the solution from the markings on the graduated cylinder. The total volume of the solution was 91.0 mL. What concentration should the student write down in her lab notebook? Be sure your answer has the correct number of significant digits. g-mL Garrow_forwardA chemistry student weighs out 0.113 g of acetic acid (HCH3CO₂) into a 250. mL volumetric flask and dilutes to the mark with distilled water. He plans to titrate the acid with 0.1100 M NaOH solution. Calculate the volume of NaOH solution the student will need to add to reach the equivalence point. Round your answer to 3 significant digits. 0 mL $ ? x10 Xarrow_forward
- Please use the corrrect significant digits (3), if needed use scientific notation.arrow_forward2.93 g Measured Volume of Water: 100.0 mL each question with correct significant figures and units. You must show calculations for determining each quantity. If necessary, use the molar mass of NaCI = 58.44 g/mol. You will be asked to show your work for each question. A.Determine the number of moles of NaCI in the solution B.Determine the number of moles of all solutes (both cations and anions) from the number of moles of NaCI that you determined above. C. Determine the mass (in kg) of solvent (assume that the density of water is 1.000 g/mL). D. the molality of all solutes.arrow_forwardCalculate the molarity of each of the following solutions. Round each of your answers to 3 significant digits. Part 1 of 3 6.59 g of methanol (CH3OH) in 1.50 × 10² mL of solution. Part 2 of 3 M Part 3 of 3 M x10 8.37 g of calcium chloride (CaCl₂) in 2.20 × 10² mL of solution. X M x10 X 7.02 g of naphthalene (C₁0Hg) in 85.2 mL of benzene solution. ☐ Ś x10 X S Śarrow_forward
- Explain the results obtained in this experimentarrow_forwardA chemistry student weighs out 0.0176 g of formic acid (HCHO2)into a 250. mL volumetric flask and dilutes to the mark with distilled water. He plans to titrate the acid with 0.1300 M(molarity) NaOH solution. Calculate the volume of NaOH solution the student will need to add to reach the equivalence point. Round your answer to 3 significant digits.arrow_forwardA chemistry student weighs out 0.0960 g of phosphoric acid (H,PO4), a triprotic acid, into a 250. mL volumetric flask and dilutes to the mark with distilled water. He plans to titrate the acid with 0.1100 M NaOH solution. Calculate the volume of NaOH solution the student will need to add to reach the final equivalence point. Round your answer to 3 significant digits. |mL ola х10 Ararrow_forward
- A A chemistry student weighs out 0.130 g of phosphoric acid (H,PO,), a triprotic acid, into a 250. mL volumetric flask and dilutes to the mark with distilled water. He plans to titrate the acid with 0.1200 M NaOH solution. Calculate the volume of NaOH solution the student will need to add to reach the final equivalence point. Round your answer to 3 significant digits. mL x10arrow_forwardAn analytical chemist weighs out 0.264 g of an unknown diprotic acid into a 250 mL volumetric flask and dilutes to the mark with distilled water. He then titrates this solution with 0.1900M NAOH solution. When the titration reaches the equivalence point, the chemist finds he has added 18.5 mL of NaOH solution. Calculate the molar mass of the unknown acid. Round your answer to 3 significant digits. x10 molarrow_forwardPlease helparrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY