
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780134580999
Author: Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Yarrowia lipolytica(Yl) is a non-conventional yeast that diverged from baker’s yeast, Saccharomyces cerevisiae(Sc), early in evolutionary history. The regulation of glycolytic enzymes in Yl differs from that of Sc. The figures below show how PFK activity is affected by fructose-2,6-bisphosphate and phosphoenolpyruvate. Based on these data, which molecule is the major regulator of PFK activity in each species?
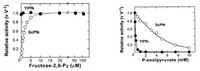
Transcribed Image Text:### Enzyme Activity: Effect of Fructose-2,6-P2 and P-enolpyruvate
#### Graph 1: Effect of Fructose-2,6-P2 on Enzyme Activity
The graph on the left illustrates the relationship between relative enzyme activity (v/V-1) and concentrations of Fructose-2,6-P2 (µM). It compares two different enzymes: YlPfk (represented by closed circles) and ScPfk (represented by open circles).
- **X-axis (horizontal)**: Fructose-2,6-P₂ concentration in micromolars (µM)
- **Y-axis (vertical)**: Relative activity of the enzyme (v/V-1)
**Key Observations**:
1. **YlPfk** shows a consistent relative activity near 1.0 across all concentrations of Fructose-2,6-P₂.
2. **ScPfk**, on the other hand, demonstrates increasing relative activity as Fructose-2,6-P₂ concentration increases, plateauing around a relative activity of 1.0 at approximately 50 µM.
#### Graph 2: Effect of P-enolpyruvate on Enzyme Activity
The graph on the right shows the effect of varying concentrations of P-enolpyruvate (mM) on the relative activity (v/V-1) of two different enzymes: YlPfk (represented by closed circles) and ScPfk (represented by open circles).
- **X-axis (horizontal)**: P-enolpyruvate concentration in millimolars (mM)
- **Y-axis (vertical)**: Relative activity of the enzyme (v/V-1)
**Key Observations**:
1. **ScPfk** exhibits a gradual decline in relative activity as P-enolpyruvate concentration increases, dropping from 1.0 to about 0.2 as the concentration approaches 10 mM.
2. **YlPfk** shows a steep decline in relative activity at low concentrations, with activity near 0.1 at around 1-2 mM and staying low as the concentration increases.
### Conclusion
These graphs collectively reveal that:
- **YlPfk** maintains high activity regardless of Fructose-2,6-P₂ levels but is highly sensitive to low levels of P-enolpyruvate.
- **ScPfk
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Researchers isolated a yeast phosphofructokinase (PFK) mutant in which a serine at the fructose-2,6-bisphosphate binding site was replaced with an aspartate residue. The amino acid substitution completely abolished the binding of fructose-2,6-bisphosphate to PFK. There was a dramatic decline in glucose consumption and ethanol production in the mutant compared to control yeast. Why can't the mutant PFK bind with fructose-2,6-bisphosphate?arrow_forwardWhich of the following coenzymes are required for the metabolic reactions that convert glycerol intoglucose? NAD+ Biotin Both A and B Neither A nor B Assume that the gene for glycogen phosphorylase kinase is mutated and the mutated enzyme cannotbe phosphorylated. Which of the following statements applies to individuals carrying such a genemutation? -Glycogen phosphorylase becomes less active -More glycogen phosphorylase b is converted to glycogen phosphorylase a - Both A and B - Neither A nor Barrow_forwardInsulin resistance, as occurs in type 2 diabetes, may lead to increased ketone production and release into blood. Describe the biochemistry that links insulin resistance and ketone production. Compare the cellular energy (e.g. ATP) required and produced when glycogen is synthesize and hydrolyzed, respectively. Compare and contrast the mechanism of fatty acid synthase with translation. When young rats are placed on a totally fat acid free diet, they grow poorly, develop a scaly dermatitis, lose hair, and soon die these symptoms that can be prevented if plant material is included in the diet. Why?arrow_forward
- Consider the malate dehydrogenase reaction, part of tricarboxylic acid cycle, shown below. malate + NAD+ oxaloacetate + NADH + H+ ΔGo ’ = 29.7 kJ/mol. It has been reported that the concentrations of NAD+ and NADH in yeast mitochondria were 20 mM and 0.3 mM, respectively. If we performed similar measurements and also determined that the concentration of malate in yeast mitochondria was 0.5 mM and that of oxaloacetate was 0.1 µM at pH 7.0 at 37˚C, use this information to calculate the free energy of the reaction of yeast in mitochondria.arrow_forwardCorticosteroids (a type of hormone), and Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs) are non-narcotic pain relievers. Both medications are prescribed to reduce inflammation in the body. NSAIDs such as aspirin, acetaminophen, and ibuprofen are able to reduce pain, fever, and inflammation by blocking the action of the cyclooxygenase enzyme (COX) that catalyzes the conversion of arachidonic acid into prostaglandins. Common corticosteroids include prednisone, cortisone, and methylprednisolone. Choose one of these three corticosteroids. The corticosteroid that you choose and then explain how the drug works to reduce inflammation.arrow_forwardConsider the malate dehydrogenase reaction, part of tricarboxylic acid cycle, shown below. malate + NAD+ oxaloacetate + NADH + H+ ΔGo ’ = 29.7 kJ/mol. It has been reported that the concentrations of NAD+ and NADH in yeast mitochondria were 20 mM and 0.3 mM, respectively. If we performed similar measurements and also determined that the concentration of malate in yeast mitochondria was 0.5 mM and that of oxaloacetate was 0.1 µM at pH 7.0 at 37˚C, use this information to calculate the equilibrium constant for the given reaction.arrow_forward
- Strategies for regulating the central pathways in carbohydrate metabolism vary among different cells in one organism and among organisms. Slight changes in the regulation of enzymes in central metabolism can effectively re-route metabolite traffic through these pathways, just like a small mutation in PFK-1 can convert a healthy cell into a cancerous one. For instance, Gillaspera mold uses an alternative strategy for regulation the TCA and glycolysis. Gillaspera contains a unique isocitrate dehydrogenase that has an allosteric site for citrate. High citrate inhibits isocitrate dehydrogenase in this organism. Gillaspera also lacks a citrate binding site on PFK-1, so this variant of the enzyme is not affected by citrate concentrations at all. Gillaspera lacks the enzymes ethanol dehydrogenase and lactate dehydrogenase and no carbons are lost in its unique fermentation product. Would high glucose in these organisms lead to production of carbon dioxide from glucose catabolism?…arrow_forwardCan you please pick the right answer in each parentheses? The pentose phosphate pathway provides a number of critical functions including ["production of ribose-5-phosphate", "production of NADH"] that is vital for ["synthesis of nucleotides and coenzymes", "oxidative phosphorylation"] . This pathway is divided into oxidative and non-oxidative steps. The latter steps ["are involved in the conversion of various sugar phopshates, so called ["carbon shuffle reactions"", "are directly involved in NADPH production"] . If ["NADP+", "NAD+"] levels are high, flux through the pentose phosphate pathway is promoted by allosteric regulation of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase. If reducing equivalents derived form the pentose phosphate pathway are high, glucose-6-phosphate is directed toward ["a phosphatase and then export from the cell", "glycolysis"] .arrow_forwardMalate dehydrogenase is an enzyme that converts malate to oxaloacetate in the last stage of the TCA Cycle (citric acid cycle/Krebs cyde), represented by the following equation: NAD+ Malate Oxaloacetate NADH A group of students carried out an experiment to determine the optimum temperature for the activity of a commercially produced malate dehydrogenase (from yeast) at several different temperatures. A series of test tubes was set up containing 2.0 cm of phosphate buffer with a pH of 7.5, 0.1 cm? of NADH, 0.1 cm of malate dehydrogenase and 0.7 cm3 of water. The tubes were incubated in water baths at the various temperatures for 5 minutes. At certain time intervals each tube was placed in a colorimeter, set at an absorbance value of 1.0. The reaction was then started by adding 0.1 cm? of oxaloacetic acid to the tube. Enzyme activity was measured by following the decrease in absorbance for 120 seconds. The experiment was repeated to give duplicate results. Enzyme activity was then…arrow_forward
- A solution of [U 14C] glucose-1-phosphate (specific activity = 16,000 cpm/mmole) was incubated with glycogen and glycogen phosphorylase, an enzyme which adds glucose units on to glycogen. Radioactivity was incorporated into the glycogen primer at a rate = 2550 cpm/min. The rate of the enzymatic reaction in units of mmole glucose incorporated per minute is: (a) 0.016 mmol/min (b) 0.57 mmol/min (c) 0.16 mmol/min (d) 5.7 mmol/minarrow_forwardATP synthase is a protein that catalyzes the formation of the energy storage molecule adenosine triphosphate using adenosine diphosphate and inorganic phosphate. Which of the following are true for the protein, ATP synthase? Select all apply A mutation of Asp61 to glutamic acid would have less of a deleterious effect on its ability to synthesize ATP than a mutation of Asp61 to alanine A mutation of Asp61 to alanine would have less of a deleterious effect on its ability to synthesize ATP than a mutation of Asp61 to glutamic acid The F1 subunit is primarily responsible for translocating H+ ions across the inner mitochondrial membrane during ATP synthesis The FO subunit is primarily responsible for translocating H+ ions across the inner mitochondrial membrane during ATP synthesisarrow_forwardExplain the purpose of the glycerol 3 phosphate shuttle (Don’t worry about the mechanism, just the purpose of the shuttle. Just one sentence here!). Suppose a cell could only rely on the glycerol 3 phosphate shuttle and not the malate-aspartate shuttle, how would that affect the amount of ATP that could be generated from the complete oxidation of 1 molecule of glucose in that cell? How would this change the amount of ATP that could be generated from the complete oxidation of 1 molecule of palmitate in this cell?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781259398629
Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780815344322
Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781260159363
Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9781260231700
Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:McGraw Hill Education