
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Transcribed Image Text:Knowledge Check
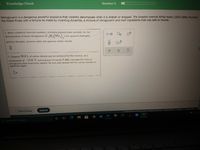
Question 3
Nitroglycerin is a dangerous powerful explosive that violently decomposes when it is shaken or dropped. The Swedish chemist Alfred Nobel (1833-1896) founded
the Nobel Prizes with a fortune he made by inventing dynamite, a mixture of nitroglycerin and inert ingredients that was safe to handle.
1. Write a balanced chemical equation, including physical state symbols, for the
decomposition of liquid nitroglycerin (C,H,(NO,)) into gaseous dinitrogen,
gaseous dioxygen, gaseous water and gaseous carbon dioxide.
2. Suppose 30.0 L of carbon dioxide gas are produced by this reaction, at a
15.0 °C and pressure of exactly 1 atm. Calculate the mass of
temperature of
nitroglycerirn that must have reacted. Be sure your answer has the correct number of
significant digits.
I Don't Know
Submit
O2020 McGraw-Hill Education. All Rights Reserved.
Terms of Use Privacy Accessibility
O Type here to search
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 6 steps with 6 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Calculate the red part given the dataarrow_forwardAssuming constant pressure, a gas has a final volume of 15 L. If the temperature increases from 330 K to 450 K, find the initial volume. Show all work in the space provided, and then write your final answer on the short line.arrow_forwardMagnesium will burn in air to form both Mg3N2 and MgO. What mass of each product would be found if burning a 3.55 g sample of magnesium to completion produces a combined total of 5.09 g of the two products? g Mg3N2 g MgOarrow_forward
- 21 Consider the combustion of in oxygen gas to produce carbon dioxide gas and water vapor. In an experiment, 0.1063 g of C₅H₈ is combusted to produce enough heat to raise the temperature of 150.0 g of water by 7.632 °C. C₅H₈ (l) + 7 O₂ (g) → 5 CO₂ (g) + 4 H₂O (g) d If 4790 J of heat were absorbed by the water, then how much heat, in J, was produced by the combustion of C₅H₈? (include the appropriate sign)arrow_forwardMagnesium will burn in air to form both Mg3N2 and MgO. What mass of each product would be found if burning a 3.28 g sample of magnesium to completion produces a combined total of 5.09 g of the two products? g Mg3N2 g MgOarrow_forwardAncient Romans built often out of bricks and mortar. A key ingredient in their mortar was quicklime (calcium oxide), which they produced by roasting limestone (calcium carbonate). 1. Write a balanced chemical equation, including physical state symbols, for the decomposition of solid calcium carbonate (CaCO3) into solid calcium oxide and gaseous carbon dioxide. x10 2. ose 20.0 L of carbon dioxide gas produced by this reaction, at a temperature of 370.0 °C and pressure of exactly 1 atm. Calculate the mass of calcium carbonate that must have reacted. Round your answer to 3 significant digits.arrow_forward
- Ancient Romans built often out of bricks and mortar. A key ingredient in their mortar was quicklime (calcium oxide), which they produced by roasting limestone (calcium carbonate). 1. Write a balanced chemical equation, including physical state symbols, for the decomposition of solid calcium carbonate (CaCO,) into solid calcium oxide and gaseous carbon dioxide. ? 2. Suppose 11.0 L of carbon dioxide gas are produced by this reaction, at a temperature of 360.0 °C and pressure of exactly 1 atm. Calculate the mass of calcium carbonate that must have reacted. Round your answer to 3 significant digits.arrow_forwardAncient Romans built often out of bricks and mortar. A key ingredient in their mortar was quicklime (calcium oxide), which they produced by roasting limestone (calcium carbonate). 1. Write a balanced chemical equation, including physical state symbols, for the decomposition of solid calcium carbonate (CaCO2) into solid calcium oxide and gaseous carbon dioxide. C 2. Suppose 86.0 L of carbon dioxide gas are produced by this reaction, at a temperature of 260.0 °C and pressure of exactly 1 atm. Calculate the mass of calcium carbonate that must have reacted. Round your answer to 3 significant digits.arrow_forwardWhen answering this problem, report the answer with the appropriate number of significant figures. When entering units, use proper abbreviated units with proper capitalization. A student followed the procedure in this experiment, using 50.00 mL of 2.00 molar HCl and 51.00 mL of 2.00 molar NaOH both solutions having an initial temperature of 22.7 oC. After mixing, a maximum temperature of 32.2 oC is measured. The final mass of the mixture was found to be 107.87 grams. For this problem, assume the specific heat of the solution is 4.18 J/g oC. Report all answers with the proper number of significant figures. What is the heat transferred by this reaction, in Joules?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY