
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
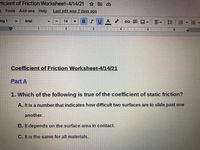
Transcribed Image Text:ficient of Friction Worksheet-4/14/21 D
t Tools Add-ons Help
Last edit was 2 days ago
ing 1
Arial
14
IUA
三三
12 1
6.
Coefficient of Friction Worksheet-4/14/21
Part A
1. Which of the following is true of the coefficient of static friction?
A. It is a number that indicates how difficult two surfaces are to slide past one
another.
B. It depends on the surface area in contact.
C. It is the same for all materials.
!!!
lilı
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 13. Blocks A and B are connected by a cable that passes through two pulleys of negligible mass, as shown in the figure. The kinetic coefficient of friction between the inclined plane and block A is 0.4. If the initial velocity of A is 8 ft/s down the plane, determine how far A travels and how much time it takes to stop. P=0.4 20° 8 pies/s A 10 lb B 6lbarrow_forward1. You are working as a letter sorter in the Post Office. Postal regulations require that employees' footwear must have a minimum coefficient of static friction of 0.5 on a specified tile surface. You are wearing athletic shoes for which you do not know the coefficient of static friction. In order to determine the coefficient, you imagine that there is an emergency and start running across the room. You have a co-worker time you, and find that you can begin at rest and move 4.23 m in 1.20 s. If you try to move faster than this, your feet slip. Assuming your acceleration is constant, does your footwear qualify for the postal regulation? 7arrow_forward2. A 110 g hockey puck sent sliding over ice is stopped in 15 m by the frictional force on it from the ice. (a) If its initial speed is 6.0 m/s, what is the magnitude of the frictional force? (b) What is the coefficient of friction between the puck and the ice?arrow_forward
- 21. Cooking an omelet on a boat is tricky because the tilting of the boat can cause the omelet to slip off the flat griddle. If the coefficient of static friction between the omelet and the griddle is 0.05, what is the largest angle (measured from the horizontal) that the griddle can tilt before the omelet starts to slide? A) 3° B) 6° C) 9° D) 12° E) 15°arrow_forward1. Two blocks are positioned on surfaces, each inclined at the same angle of 42.8 degrees with respect to the horizontal. The blocks are connected by a rope which rests on a frictionless pulley at the top of the inclines as shown, so the blocks can slide together. The mass of the black block is 2.07 kg, and the coefficient of kinetic friction for both blocks and inclines is 0.510. Assume static friction has been overcome and that everything can slide. What is must be the mass of the white block if both blocks are to slide to the LEFT at an acceleration of 1.5 m/s^2? 2. Two blocks are positioned on surfaces, each inclined at the same angle of 49.5 degrees with respect to the horizontal. The blocks are connected by a rope which rests on a frictionless pulley at the top of the inclines as shown, so the blocks can slide together. The mass of the black block is 2.24 kg, and this time there is NO friction. What is must be the mass of the white block if both blocks are to slide to the LEFT at…arrow_forward5) A box with mass m=1.25 kg rests on the top of a bar. The coefficient of static friction between the box and the bar is μs=0.73 and the coefficient of kinetic friction is μk=0.39. a) Write an expression for Fm the minimum force required to produce movement of the box on the top of the bar. b) Solve numerically for the magnitude of the force Fm in Newtons. c) Write an expression for a, the box's acceleration, after it begins moving. (Assume the minimum force, Fm, continues to be applied.) d) Solve numerically for the acceleration, a in m/s².arrow_forward
- 2. A block of mass 3.00 kg is pushed up against a wall by a force P that makes a 50.0° angle with the horizontal as shown in the figure. The coefficient of static friction between the block and the wall is 0.250. Determine the possible values for the magnitude of P that allow the block to remain stationary 50.0° Parrow_forwardsonia- m pject Pool partment... 7 1 1329 2 S X 7. A 7.50 kg block is pressed against a vertical wall by a force (F), as shown in the figure below. The coefficient of static friction between the block and the wall is 0.41 and the directional angle 8 for the force is 50.0°. Determine the magnitude of the force (F) when the block is about to slide down the wall. N 3 E D 80 F C $ 4 R F % 5 V T G (2991109 911 6 ccito coi16 MacBook Air 6: B S Y H & 7 S 63 91129 911539115 91109 91103 911931 92 U N 6 ceiloo cc 16 ecil6 ceiló ccrl6 cc 16. c 8 J ció ecil6 ceil D-Il ER 1 M ( 9 K MOSISO O O 4 19 Parrow_forward4. The 100-kg crate is subjected to the forces shown. If it is originally at rest, determine the distance it slides in order to attain a speed of v= 6 m/s. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the crate and the surface is Hk = 0.2. 500 N 400 N 30° 45°arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON