
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question

Transcribed Image Text:Industry Print Exercise 23-2
Refer to print PR 23-2. The sequence of operations for this print is given below. Answer the questions
following the sequence of operations.
Sequence of Operations
descends at a controlled rate, slowly compacting the explosive charge to avoid detonation due to a sudden
Description: This is a system to control a 90-ton hydraulic, explosive-compaction press. The press ram
shock.
1. The cycle is started by energizing solenoid A, which shifts control valve 3 and supplies pressure to the
head end of the hydraulic cylinder (7). This operates the ram.
2. The cylinder (7) extends at a slow rate controlled by the fluid in the rod end of the cylinder, which is
vented through the flow control valve (5).
the
1. When
de-energizes solenoid A and energizes solenoid B. This shifts control valve 3 to retract the cylinder (7).
de rol valve 5 has an integral check valve that permits the free flow of fluid in the opposite direction,
causing the cylinder (7) to rapidly retra
retract.
4. The retraction of the cylinder (7) actuates the limit switch (8), which de-energizes solenoid B. Control
valve 3 returns to the neutral position. This completes the cycle. This circuit has safety features.
On electrical power outage, both solenoid A and solenoid B are de-energized. This allows valve 3 to
return to the center position, thus stopping ram travel. Also, valve 4 provides low-pressure relief on the
ram upstroke, and valve 2 provides high-pressure relief on the ram downstroke.
Questions
1. What is the name of the circuit?
2. How many reservoir symbols are shown, and how many reservoirs are there?
3. What starts the sequence of operations?
4. When valve 3 shifts on due to the energizing of solenoid A, to which end of the cylinder (7) is pressure
supplied?
5. What causes the ram to extend at a slow, controlled rate?
6. What causes the ram to retract?
7. Why does the cylinder (7) retract rapidly?
514
Section 5 Specialized Parts and Prints
8. What completes the cycle?
9. What happens in the event of electrical power outage?
10. Give the function of valves 2 and 4.
513
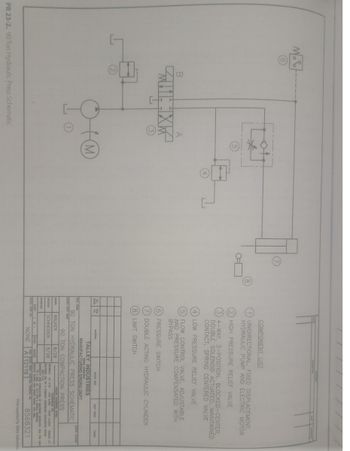
Transcribed Image Text:B
XK
PR 23-2. 90 Ton Hydraulic Press Schematic
5
(M)
(2) HIGH PRESSURE RELIEF VALVE
(3) 4-WAY, 3-POSITION, BLOCKED-CENTER,
DOUBLE SOLENOID ACTUATED, MAINTAINED
CONTACT, SPRING CENTERED VALVE
(4) LOW PRESSURE RELIEF VALVE
FLOW CONTROL VALVE, ADJUSTABLE
AND PRESSURE COMPENSATED WITH
BYPASS
6) PRESSURE SWITCH
(7) DOUBLE ACTING HYDRAULIC CYLINDER
(8) LIMIT SWITCH
REDD NEM
CHECKED
TOOL NAME
COMPONENT LIST
UNIDIRECTIONAL, FIXED DISPLACEMENT,
HYDRAULIC PUMP AND ELECTRIC MOTOR
APPROVED
SHEET
MATERIAL
STOCK SIZE
TALLEY INDUSTRIES
MESA, ARIZONA
MANUFACTURING ENGRG DEPT
90 TON HYDRAULIC PRESS SCHEMATIC
90 TON COMPACTION PRESS
8/28
8/28
WALKER
SCHNEIDER
SCALE NONE
NONE A 12116
200 300 002 000 0002 ANGLES at
COMMON CONTORNE CONCENTRIC whos
REMOVE BURS NO SAP EDES 230 MAK
8568321
Print supplied by Talley Industries
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A domestic refrigerator is placed in an insulated closed room. If the unit operates with the door open which of the following statements are true for the case. There may be greater then one correct answer. Select one or more: O a. The temperature of the room will rise. O b. None of the statements are true for such a case. O c. The temperature of the room will fall. O d. The internal energy of the room will increase.arrow_forwardQuestion 7 What is vacuum pressure? "It is the pressure above the atmospheric pressure, measured using a gauge." "It is the pressure below the atmospheric pressure, measured using a gauge." It is the sum of the atmospheric and gauge pressures. It is the pressure of the atmosphere.arrow_forwardQuestion Two: The crank shaft of an engine runs at 2400 rpm. If it takes 0.002 second after ignition for the charge to gain maximum pressure, what should the crank angle be when spark occurs. If the inlet valve opens 12° before T.D.C. and closes 43° after B.D.C. for how long is it open during one cycle?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY