
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
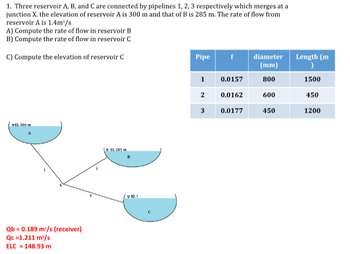
Transcribed Image Text:1. Three reservoir A, B, and C are connected by pipelines 1, 2, 3 respectively which merges at a
junction X. the elevation of reservoir A is 300 m and that of B is 285 m. The rate of flow from
reservoir A is 1.4m³/s
A) Compute the rate of flow in reservoir B
B) Compute the rate of flow in reservoir C
C) Compute the elevation of reservoir C
EL 300 m
Qb = 0.189 m³/s (receiver)
Qc =1.211 m/s
ELC = 148.93 m
EL 285 m.
VEL?
Pipe
1
2
3
f
0.0157
0.0162
0.0177
diameter
(mm)
800
600
450
Length (m
)
1500
450
1200
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 8 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Example 8 (Page 271): Ο = If oil (viscosity: v reservoir at a rate of 0.028 m3/s in the 15 cm (diameter) smooth pipe. What is the elevation of the oil surface in the upper reservoir. Elevation = ? D 60 m LV2 -ΣΗΣ + D 2g pipe 1 × 10-6 m2/s , SG = 0.9) flows from the upper to the lower 7 m ht 130 m = component V2 2g Elevation = 130 marrow_forwardA single pumping well exists in an ideal confined aquifer. The aquifer has a transmissivity of 4700 ft2/d and storage coefficient of 0.00025. The well is 85 ft west of a no-flow boundary that runs north-south. The pumping well has an effective radius of 0.50 ft, and pumps at a flow rate of 200 gpm. No flow Determine: 85 ft 1. The total drawdown in ft at the pumping well at 6.0 hours after the well was turned on, ignoring characteristic well losses.arrow_forwardA pump is installed in the pipeline between reservoirs A and E as shown in the figure below. Water surface elevations for Reservoirs A and E are 25 ft and 40 ft, respectively. The diameters and lengths of pipes are shown in the figure. The Hazen-Williams coefficients for all pipes are 120. Entrance loss from reservoir A is 0.5 and exit loss from reservoir E is 1.0. The discharge for the pipeline is 10 cfs. The efficiency of the pump is 0.85. Determine the horsepower required for the pump.arrow_forward
- 2.Water exits a reservoir through a 1-Km long D=?mm diameter horizontal Tunnel as shown below. The entrance is sharp-edged, and the discharge is to the lower reservoir. If the flow rate is 2 CMS, What tunnel diameter is required to achieve the desired flow rate if local losses are neglected? Upper reservoir Tunnel = 1 km 23 m Lower reservoirarrow_forwardConsider a flocculation basin consisting of 3 tanks in series. Each tank is of the same dimension (4.2 deep x 4.2 m long x 3.8 m wide) and is mixed by a paddle wheel. The paddle wheel for the first tank has a 185 W power input, the second wheel 30 W input, and the third wheel 7.6 W power. Given a water temperature of 15 C and a flow rate of 4.2 MGD, calculatea. The mixing intensity of each of the tanksb. Calculate the ratio of No/N for tank 1 given a particle diameter of 20 μm and a number concentration 200,000 particles/mL (this ratio the number of particles that have aggregated to form a bigger particle).arrow_forwardProblem 1: A pipeline 300 m long discharge freely at a point 50 m lower than the water surface at intake (Figure 1). The pipe intake projects into the reservoir. The first 200 m is of 350 mm diameter and the remaining 100 m is of 250 mm diameter. (a) Find the rate of discharge assuming f= 0.06. If the junction point C of the two sizes of pipe is 40 m below the intake water surface level, find the pressure head. L₁, D₁, f AZ1 C L2, D2, f T 122 -V₁arrow_forward
- A 300 mm diameter test well penetrates 27 m below the static water table. After 24 hours of pumping at 69 liters/sec, the water level in an observation well at a distance of 98 m from the test well is lowered 0.56 m. The other observation well at a distance of 34.5 m from the test well has a drawdown of 1.10 m. What is the rate of flow in m³/day? O 6691.5 m³/day O 6591.6 m/day 5961.6 m³/day O 5691.6 m3/dayarrow_forwardA hydraulic jump is formed in a 4 m wide rectangular open channel at a short distance downstream of a control gate. The flow depth just downstream of the gate is 1.8 m and the outlet discharge is 134 m3 /s. The density of water is 1000 kg/m3 . Determine the flow depth downstream of the jump and the headloss in the jump. Express the headloss in kW per metre width. i need ansswer in 30 minutes thank uarrow_forwardI need the answer as soon as possiblearrow_forward
- Water at 20°C is pumped at a rate of 15 L/s into a reservoir as shown in the Figure below. Between the pump and the reservoir is 150 m of 100 mm diameter PVC pipe, and the water surface elevation in the reservoir is 8 m above the centerline of the inflow pipe. The roughness height of the PVC pipe can be assumed to be negligibly small. Estimate the gauge pressure (kPa) on the downstream side of the pump. 15 L/s 133 120 111.7 131.5 Pump P - 150 m. 100 mm Reservoir 8marrow_forwardReservoirs A, B and C are connected by pipelines 1, 2 and 3 respectively which meets at the junction D. The elevation of reservoir A s 300 m, while that of C Is 277 m. Reservoir B is higher than reservoir A. The rate of flow out of reservoir B is 560 liters/sec. Compute the elevation of Reservoir B in m Pipe 1 (D=900 mm; L=1500 m; f=0.0208) Pipe 2 (D=600 mm; L=450 m; f=0.0168) Pipe 3 (D=450 mm; L=1200 m; f=0.0175) Round your answer to 3 decimal places.arrow_forward(a) Using the Pipe flow graph (Appendix 2), obtain the discharge through the pipeline joining the two reservoirs as shown below. Pipe diameter (D) = 450 mm Pipe length (from A to B) L = 4600 m In addition, also calculate the pressure in the pipeline at Point C, which is 2600 m from reservoir A. A 7.25m C B ALI 3.55marrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning