
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
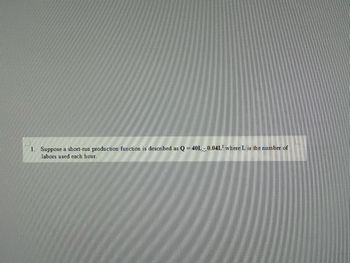
Transcribed Image Text:1. Suppose a short-run production function is described as Q40L 0.04L2 where L is the number of
labors used each hour.

Transcribed Image Text:a.
Derive the equation for Marginal Product of labor (MPL):
b.
Determine the amount of labor (L) at which total output is maximized (Qmax).
C.
If each unit of output (Q) has a marginal revenue (price) of $5 and the marginal cost of
labor (MCL) is $28 per L, what is the optimal amount of labor (L) or this firm to employ?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- I need this in words Not handwritten or no picarrow_forward1. The following production function is used to produce wheat, q, from capi- tal, K, and labour, L: q = f(K, L) = «³K/3 + B³L/3 a) Describe the role of a and B in this production function. b) Derive the slope of an isoquant for this production function and in- terpret your result. Draw the isoquant in (K L) space, labeling where appropriate. The drawing does not need to be exact, but the curvature needs to be approximately correct. Explain why under- standing the curvature is so important. | c) Does this production function follow the "Law of Diminishing Marginal Returns"? Show your work and explain your answer.arrow_forwardConsider a production function Q = (K.5 + L.5) 2 Does this production function exhibit Increasing, Constant, or Decreasing returns to scale?arrow_forward
- 2. A firm has a production function given by the following table: Units of Labor 1 2 3 4 5 K=1 3 8 12 15 17 K=2 10 15 19 22 24 K=3 16 21 25 28 30 K=4 20 25 28 30 31 (1) Suppose that K is fixed at 2. Does this production function exhibit diminishing marginal returns? (ii) Does this production function exhibit constant returns to scale for all values of K and L?arrow_forwardConsider the production function from earlier: Quantity of Haircuts 20 15 10 0+0 0 N 2 8 14 O Increasing marginal productivity O Constant marginal productivity O Decreasing marginal productivity 3 19 23 Labor (hours) 27 26 Total Product Curve From 1 labor hour up to 7 labor hours, what sort of marginal productivity does this production function have?arrow_forwardGiven the following production function: q = 10KL. Assume that w = 25, r = 75 and C = 1200. (a) Mathematically find the minimum cost combination of capital and labour to produce a given level of output.b) Does the production function in part (a) show increasing returns to scale, decreasing returns to scale, or constant returns to scale? Explain. (c) Using isoquants and isocosts, graphically illustrate the effect of an increase in the wage rate, assuming the firm is producing at the same level of output.arrow_forward
- 5. Selpats produces pens with the production function f(k, l) = 200vkl. The price of capital is wk = 40 and the price of labor is wL = 10. (i) Determine the optimal input bundle for producing y pens in the long run and find the long-run cost function. (ii) Determine the optimal input bundle for producing y = 10,000 pens in the long run. (iii) Now suppose that capital is fixed at k = 25 in the short run. Find the short-run total cost function and the short-run marginal cost function. Explain the relationship between the short-run and long-run marginal costs when y = 10,000. (iv) Suppose that the price of output is p. Which value of y maximizes short-run profit? р.arrow_forwardSuppose a firm's production function is Q=200L +5L2-0.08L³. Which of the following is the Average Production of Labor (APL)? Oa. 200+10L-0.24L² Ob. 10L-0.24L² Oc. 5L-0.08L² Od. 200+5L-0.08L²arrow_forwardPlease answer fast please arjent help please ASAP pls answer fastarrow_forward
- Suppose the production function for T-shirts can be represented as q = L0.25 K0.75. Show that the production function has constant returns to scale.arrow_forwardA firm estimates its long-run production function to be Q = -0.0050 K³L³ + 15 K²L² Suppose the firm employs 10 units of capital. At product of labor begins to diminish. A) 150 B) 66.67 C) 1000 D) 100 E) 200 I units of labor, marginalarrow_forwardIn the short run, a firm which has production function f(L, M) = 4L1/2M1/2 must use 4 machines. If the cost of labor is £4 per unit and the cost of machines is £4 per unit, what is the short-run total cost of producing 48 units of output? Use Lagrangearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education