
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Course List)
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781337705028
Author: Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
I need detailed help solving this exercise from Foundation Engineering.
Step by step, please.
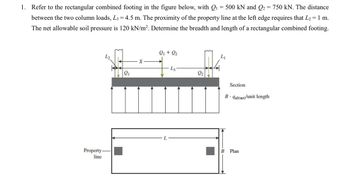
Transcribed Image Text:1. Refer to the rectangular combined footing in the figure below, with Q₁ = 500 kN and Q2 = 750 kN. The distance
between the two column loads, L3 = 4.5 m. The proximity of the property line at the left edge requires that L₂ = 1 m.
The net allowable soil pressure is 120 kN/m². Determine the breadth and length of a rectangular combined footing.
Property-
line
X
Q1 + Q₂
L3
Section
B⚫ qall(net)/unit length
L
B Plan
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- The allowable settlement for the shown square footing is 2.5 cm. the footing is placed on clay soil with the following properties. Use 4 layers to calculate the consolidation settlement and see if it satisfies the criterion. (footing weight is negligible) Hint: use the following eqation for Aoz (Boussinesq equations) For square foundations: 0.5 Δσ. = P1=1000 KN 2.0 - 1 + 1.5 1 B (2) 1.76 (q - o:) YSat = 20 KN/m³ Y = 18 KN/m³ Cc = 0.1 eo = 0.6arrow_forwardA square footing is subjected to an inclined load as shown in the figure below. If the size of the footing ,B=2.25 m , determine the gross allowable inclined load , Q, that the footing can carry. Given: = 120 andF.S = 3.5.arrow_forwardA square footing which carries an axial load of 132530 kg has its bottom resting on a ground water table at a depth of 2.5 m from the ground surface. Nc = 35, Nq = 22, Nγ = 19. Take PDRY = 1846 kg/m3 and PSAT = 1965 kg/m3, C = 1605 kg/m2. (Nc = 35, Nq = 22, Nγ = 19). Compute the required width of the footing using a factor of safety of 3.arrow_forward
- #3#.arrow_forward2) A square footing carries an allowable load of 59130kg including its own weight. The bottom of footing is 1.0m below ground surface and water table coincide with bottom of footing. Assume General shear failure. Unit Weight = 1846kg/cu.m c= 1605kg/sqm Nc = 35 Nq=22 Ny=19 1.0m Sat unit wt = 1956kg/cu.marrow_forward0:YA O A comprehensive.. Example (1): A strip footing of width 3 m is founded at a depth of 2 m below the ground surface in a (c - 0) soil having a cohesion c = 30 kN/m? and angle of shearing resistance o = 35°. The water table is at a depth of 5 m below ground level. The moist weight of soil above the water table is 17.25 kN/m. Determine (a) the ultimate bearing capacity of the soil, (b) the net bearing capacity, and (c) the net allowable bearing pressure and the load/m for a factor of safety of 3. Use the general shear failure theory of Terzaghi. Example (2): If the soil in Ex. (1) fails by local shear failure, determine the net safe bearing pressure. All the other data given in Ex. (1) remain the same. Example (3): If the water table in Ex. (1) rises to the ground level, determine the net safe bearing pressure of the footing. All the other data given in Ex. (1) remain the same. Assume the saturated unit weight of the soil ya= 18.5 kN/m'. Example (4): If the water table in Ex.1…arrow_forward
- Determine the elastic settlement using the Schmertmann method of the 10'x 10' footing as shown below. Estimate the elastic modulus using Es = 10(N + 15), where Es is in ksf and N is the corrected SPT value. Loose sand Medium dense sand Loose sand Dense sand Very loose sand DEPTH 5° 10' 15' 20' 25' SPT 10 21 11 15 41 4 Q=250 kips 10' x 10' 0 0.2 0.4 0.6 STRAIN & Layer 1 Layer 2 Layer 3 Layer 4 Laver 5arrow_forward1. A 3m x 3m square footing is constructed at a depth of 2m in a 26m deep clay layer with following soil properties: ] =16.5kN/m³, Normally Consolidated Clay, e̟= 0.65, Cc = 0.25,s=0.5 and Es= 6.0 MN/m2. If there is a 1000kN structural load on the footing, calculate the consolidation settlement of the footing.arrow_forwardA square footing is shown on the right. The footing is subjected to an eccentric load. For the following cases, determine the gross allowable load that the Qult Unit weight of soil = y (or density = F footing could carry. Use Meyerhof's procedure and Fs = 4. Given: p = 1950 kg/m³ ; c' = 0 $ = 40° D,= 1.4 m ; В 3 3 m ;x = 0.5 %3D y = 0arrow_forward
- Question Attachedarrow_forwardA strip footing shown is resting on loose sand has the following data (refer to figure h = 0.95 m Df = 1.9 m B = 1.8 m Unit weight of soil above GWT = 1750 kg/m3 Saturated Unit weight of soil = 1950 kg/m3 c = 12 kPa Angle of internal friction = 30 degrees Calculate the following: Net Allowable Bearing Capacity of the footing using Terzaghi’s assumption, kPa. Use FS = 2.5arrow_forwardCalculate the Safe bearing capacity per unit area of(i) a strip footing 1 m wide (ii) a square footing 3m x 3m (iii) a circular footing of 3m diameter. (iv) a rectangular footing of 1.3x 2.2 m. Unit weight of the soil 1.8 t/m3, cohesion = 2t/m2 And Ф = 200, Nc =17.5, Nq = 7.5 and N γ = 5. Depth of footing is 1.6m below ground surfacearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305635180Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305635180Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305635180
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning