
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
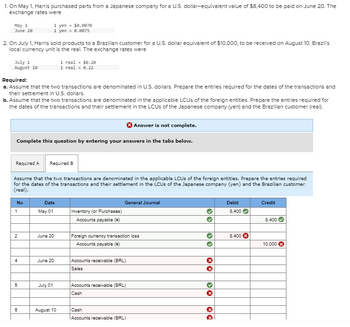
Transcribed Image Text:1. On May 1, Harris purchased parts from a Japanese company for a U.S. dollar-equivalent value of $8,400 to be paid on June 20. The
exchange rates were
May 1
June 20
2. On July 1, Harris sold products to a Brazilian customer for a U.S. dollar equivalent of $10,000, to be received on August 10. Brazil's
local currency unit is the real. The exchange rates were
July 1
August 10
Required:
a. Assume that the two transactions are denominated in U.S. dollars. Prepare the entries required for the dates of the transactions and
their settlement in U.S. dollars.
b. Assume that the two transactions are denominated in the applicable LCUs of the foreign entities. Prepare the entries required for
the dates of the transactions and their settlement in the LCUs of the Japanese company (yen) and the Brazilian customer (real).
Answer is not complete.
Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below.
No
Required A
Required B
Assume that the two transactions are denominated in the applicable LOUs of the foreign entities. Prepare the entries required
for the dates of the transactions and their settlement in the LCUs of the Japanese company (yen) and the Brazilian customer
(real).
1
2
4
5
1 yen $0.0070
1 yen = 0.0075
6
Date
May 01
June 20
1 real = $0.20
1 real = 0.22
June 20
July 01
August 10
Inventory (or Purchases)
Accounts payable ()
General Journal
Foreign currency transaction loss
Accounts payable (+)
Accounts receivable (BRL)
Sales
Accounts receivable (BRL)
Cash
Cash
Accounts receivable (BRL)
33
33
XX
››
XX
Debit
8,400✔
8,400 X
Credit
8,400
10,000 X
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Full conceptarrow_forwardChapter 18, Question 4. Attached is a similar question with answers. Please answer in similar formatarrow_forwardASSUME THAT THE U.S. DOLLAR IS THE FUNCTIONAL CURRENCY. Ruthie Inc. had a debit adjustment of $7900 for the year ended December 31, 2019, from restating its foreign subsidiary's accounts from their local currency units into U.S. dollars. Additionally, Ruthie had a receivable from a foreign customer. It is denominated in the customer's local currency. On December 31, 2018, this receivable for 300,000 local currency units (LCU) was correctly included in Ruthie's balance sheet at $124200. When the receivable was collected on February 15, 2019, the U.S. dollar-equivalent was $122200. In Ruthie's 2019 consolidated statement of income, how much should be reported as foreign exchange gain/(loss) in computing net income? BE SURE TO TYPE A SIMPLE NUMBER WITH NO COMMAS OR DOLLAR SIGNS. FOR EXAMPLE, TYPE 1000 INSTEAD OF $1,000. IF THE NUMBER IS NEGATIVE, TYPE -1000 INSTEAD OF ($1,000) Your Answer:arrow_forward
- 1arrow_forwardSuppose that Retrojo Inc. is a U.S. based MNC that will need to purchase F$1.10 million (Fijian dollars, F$) worth of imports from Fiji in 90 days. Currently, the spot rate for the Fijian dollar is $0.53 per F$. If Retrojo were to exchange U.S. dollars for the required F$1,100,000.00 Fijian dollars, it would need $ (U.S. dollars). If Retrojo waits 90 days to make this exchange (perhaps due to insufficient funds on hand), and the Fijian dollar appreciates to $0.64 during those 90- days, then Retrojo would need $ (U.S. dollars). Thus, if Retrojo believes that the Fijian dollar will appreciate, it can its exposure to such exchange rate risk by locking in the original exchange rate through the use of a forward contract.arrow_forwardOn November 6, 20X7, Zebra Corporation purchased merchandise from an unaffiliated foreign company for 50,000 units of the foreign company's local currency. On that date, the spot rate was $1.259. Zebra paid the bill in full three months later when the spot rate was $1.258. The spot rate was $1.255 on December 31, 20X7. What amount should Zebra report as a foreign currency transaction gain in its income statement for the year ended December 31, 20X7? O $50 O $150 O $0 O $200 (1arrow_forward
- Winston Corp., a U.S. company, had the following foreign currency transactions during 2021: ( 1.) Purchased merchandise from a foreign supplier on July 16, 2021 for the U.S. dollar equivalent of $47,000 and paid the invoice on August 3, 2021 at the U.S. dollar equivalent of $54,000. (2.) On October 15, 2021 borrowed the U.S. dollar equivalent of $315,000 evidenced by a non-interest-bearing note payable in euros on October 15, 2022. The U.S. dollar equivalent of the note amount was $295,000 on December 31, 2021, and $299,000 on October 15, 2022. What amount should be included as a foreign exchange gain or loss from the two transactions for 2022?arrow_forwardHarris Incorporated had the following transactions: On May 1, Harris purchased parts from a Japanese company for a U.S. dollar–equivalent value of $7,000 to be paid on June 20. The exchange rates were May 1 1 yen = $0.0070 June 20 1 yen = 0.0075 On July 1, Harris sold products to a Brazilian customer for a U.S. dollar equivalent of $10,400, to be received on August 10. Brazil’s local currency unit is the real. The exchange rates were July 1 1 real = $0.20 August 10 1 real = 0.22 Required: Assume that the two transactions are denominated in U.S. dollars. Prepare the entries required for the dates of the transactions and their settlement in U.S. dollars. Assume that the two transactions are denominated in the applicable LCUs of the foreign entities. Prepare the entries required for the dates of the transactions and their settlement in the LCUs of the Japanese company (yen) and the Brazilian customer (real).arrow_forwardASSUME THAT THE LOCAL CURRENCY UNIT IS THE FUNCTIONAL CURRENCY. Cade Inc. had a debit adjustment of $6400 for the year ended December 31, 2019, from restating its foreign subsidiary's accounts from their local currency units into U.S. dollars. Additionally, Cade had a receivable from a foreign customer. It is denominated in the customer's local currency. On December 31, 2018, this receivable for 300,000 local currency units (LCU) was correctly included in Cade's balance sheet at $121000. When the receivable was collected on February 15, 2019, the U.S. dollar-equivalent was $123800. In Cade's 2019 consolidated statement of income, how much should be reported as foreign exchange gain/(loss) in computing net income? BE SURE TO TYPE A SIMPLE NUMBER WITH NO COMMAS OR DOLLAR SIGNS. FOR EXAMPLE, TYPE 1000 INSTEAD OF $1,000. IF THE NUMBER IS NEGATIVE, TYPE -1000 INSTEAD OF ($1,000) Your Answer:arrow_forward
- Vikramarrow_forwardTristan Narvaja, S.A. (A). Tristan Narvaja, S.A., is the Uruguayan subsidiary of a U.S. manufacturing company. Its balance sheet for January 1 is shown in the popup window, E. The January 1 exchange rate between the U.S. dollar and the peso Uruguayo ($U) is $U24/$. Determine Tristan Narvaja's contribution to the translation exposure of its parent on January 1, using the current rate method. a. Determine Tristan Narvaja's contribution to the translation exposure of its parent on January 1st, using the current rate method. b. Calculate Tristan Narvaja's contribution to its parent's translation loss if the exchange rate on December 31st is $U24/$. Assume all peso Uruguayo accounts remain as they were at the beginning of the year. a. Using the current rate method, what is Tristan Narvaja's contribution to the translation exposure of its parent on January 1st? $U (Round to the nearest peso Uruguayo.)arrow_forwardLost Pigeon Aviation, a U.S. company, produces and exports industrial machinery overseas. It recently made a sale to a Japanese manufacturing firm for ¥694 million, but the Japanese firm has 60 days before it must make the payment to Lost Pigeon Aviation The spot exchange rate is ¥132.78 per dollar, and the 60-day forward rate is ¥134.72 per dollar. Is the yen selling at a premium or at a discount in the forward market relative to the U.S. dollar? The yen is trading at a discount in the forward market. In the forward market, the yen is trading at a premium.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education