
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
thumb_up100%
1. How much Is ending raw materials inventory?
2. How much is in ending work in process inventory?
3. How much is in ending finished goods inventory?
4. How much is gross profit?

Transcribed Image Text:This is a new manufacturing corporation that issued
$50000 common stock for cash on the first day. All
overhead expenses are paid immediately by cash. To
make it easy, there are no other operating expenses and
no income tax. No Dividend is declared for the year. Post
all journal entries in the General Ledger T-accounts and
using their respective balances prepare an Income
Statment and Balance Sheet for the first month of the
operation. Use a blank paper for posting into General
Ledger and preparation of the financial statements.
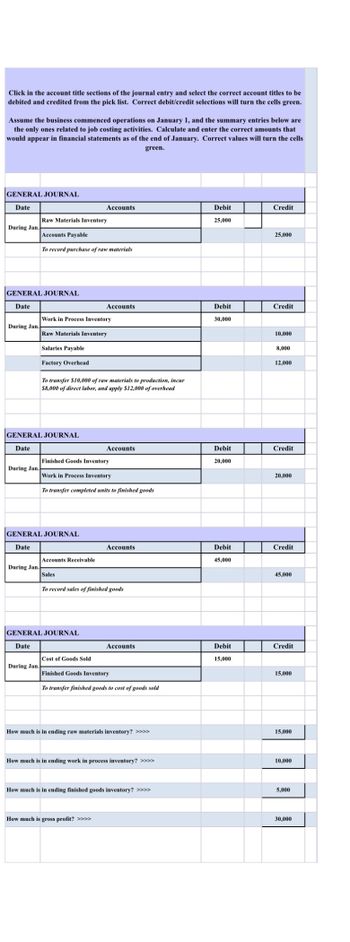
Transcribed Image Text:Click in the account title sections of the journal entry and select the correct account titles to be
debited and credited from the pick list. Correct debit/credit selections will turn the cells green.
Assume the business commenced operations on January 1, and the summary entries below are
the only ones related to job costing activities. Calculate and enter the correct amounts that
would appear in financial statements as of the end of January. Correct values will turn the cells
green.
GENERAL JOURNAL
Date
During Jan.
GENERAL JOURNAL
Date
During Jan.
During Jan.
Raw Materials Inventory
Accounts Payable
To record purchase of raw materials
During Jan.
GENERAL JOURNAL
Date
Salaries Payable
Factory Overhead
During Jan.
Work in Process Inventory
Raw Materials Inventory
GENERAL JOURNAL
Date
To transfer $10,000 of raw materials to production, incur
$8,000 of direct labor, and apply $12,000 of overhead
Accounts Receivable
Accounts
Finished Goods Inventory
Work in Process Inventory
To transfer completed units to finished goods
Sales
GENERAL JOURNAL
Date
Accounts
Cost of Goods Sold
Accounts
To record sales of finished goods
Accounts
How much is gross profit? >>>>
Accounts
Finished Goods Inventory
To transfer finished goods to cost of goods sold
How much is in ending raw materials inventory? >>>>
How much is in ending work in process inventory? >>>>
How much is in ending finished goods inventory? >>>>
Debit
25,000
Debit
30,000
Debit
20,000
Debit
45,000
Debit
15,000
Credit
25,000
Credit
10,000
8,000
12,000
Credit
20,000
Credit
45,000
Credit
15,000
15,000
10,000
5,000
30,000
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Which of the following best defines " stockout costs"? A) They are physical goods used in operations. B) They are costs associated with retrieving inventory items from a workshop C) They are costs associated with interruptions to assembly lines D) They are associated with inventory being unavailable when needed to meet demand. E) None of the above.arrow_forwardin a merchandising business gross profit is equal to the sales revenue minus (a) the sum of cost of goods sold and sales commissions (b) cost of goods sold (c) the sum of cost of goods sold and operating expenses (d) the sum of cost of goods sold, operating expenses and prepaid expensesarrow_forwardGross profit is: The amount left over after cost of goods sold is subtracted from net sales. A.Net sales less operating expenses. B.Sales less sales discount. C.less sales discounts. D.Net sales less selling expensesarrow_forward
- When overhead is overapplied, is the balance of Cost of Goods Sold, before adjustment, too low ortoo high? Why?arrow_forwardWhat is the purpose of the lower of cost or net realizable value rule? What would happen if a company was to report their inventory at replacement cost?arrow_forward3. As product costs expire(expensed), they become part of a. selling expenses. b. inventory. C. cost of goods sold. d. sales revenue.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education