
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
1. Determine the Reaction Order for HCl using calculations described in the background section. Show your work. Note that your answer will probably not be a whole number as it is in the examples, so round to the nearest whole number.
2. Determine the Reaction Order for Na2S2O3 using calculations described in the Background section. Show your work. Note that your answer will probably not be a whole number as it is in the examples.
3. Write the rate law for the reaction between HCl and Na2S2O3.
4. Describe sources of error in this experiment?
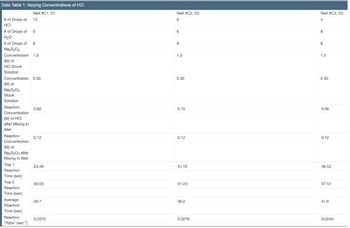
Transcribed Image Text:Data Table 1: Varying Concentrations of HCI
Well #C1, D1
12
of Drops of
HCI
of Drops of 0
H₂O
# of Drops of 8
Na₂S₂O₂
Concentration 1.0
(M) of
HCI Stock
Solution
Concentration 0.30
(M) of
Na₂S₂O3
Stock
Solution
Reaction
Concentration
(M) of HCI
after Mixing in
Well
Reaction
Concentration
(M) of
Na₂S₂O3 after
Mixing in Well
Trial 1
Reaction
Time (sec)
Trial 2
Reaction
Time (sec)
Average
Reaction
Time (sec)
Reaction
"Rate" (sec¹)
0.60
0.12
23.46
30.03
26.7
0.0375
Well #C2, D2
6
6
8
1.0
0.30
0.15
0.12
41.15
31.22
36.2
0.0276
Well #C3, D3
4
8
8
1.0
0.30
0.06
0.12
46.12
37.12
41.6
0.0240
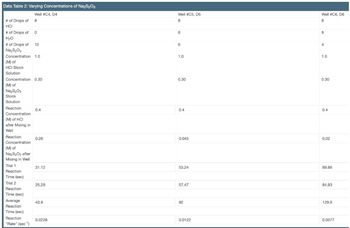
Transcribed Image Text:Data Table 2: Varying Concentrations of Na₂S₂O3
Well #C4, D4
#of Drops of 8
HCI
#of Drops of 0
H₂O
# of Drops of 12
Na₂S₂O3
Concentration 1.0
(M) of
HCI Stock
Solution
Concentration 0.30
(M) of
Na S₂0₂
Stock
Solution
Reaction
Concentration
(M) of HCI
after Mixing in
Well
Reaction
Concentration
(M) of
Na₂S₂O, after
Mixing in Well
Trial 1
Reaction
Time (sec)
Trial 2
Reaction
Time (sec)
Average
Reaction
Time (sec)
Reaction
"Rate" (sec¹)
0.4
0.28
31.12
25.29
43.8
0.0228
Well #C5,D5
8
6
1.0
0.30
0.4
0.045
53.24
57.47
82
0.0122
Well #C6, D6
8
8
4
1.0
0.30
0.4
0.02
89.86
84.93
129.9
0.0077
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Pre-Lab Preparation 1. Read about chemical reaction rates and rate laws. Take notes on how stoichiometry affects rate (for instance, if 2A + B → C, how do the reaction rates for A and B compare?), what a rate law is, and the three most common rate orders. 2. For the reaction below (the one you will be studying during this lab), write an expression for the reaction rate in terms of changing concentration over time for each species in the overall reaction (one is given as an example). S20g (aq) + 31 (aq) = 2S0, (aq) +l3 (aq) -A[S,0,) rate = Atime I- a. What does it mean if a concentration change over time is written as being negative? b. What does it mean if a concentration change over time is written as being positive? 3. What does activation energy refer to? There are two equations which may be used to calculate this, one with an exponent and a linear form of the same equation. Write down both. 4. What does collision frequency refer to?arrow_forward9. Write a generic rate law for each line in the graph below and give the appropriate units of k for the graphs below. Rate Mos-1 (2) (3) [A] 10. Convert the integrated rate law for a 1st-order reaction to the slope-intercept form and draw a general graph making sure to identify the y-intercept, slope, x-intercept (with appropriate labels), and label the y- and x-axes with the appropriate labels.arrow_forwardAb 22arrow_forward
- Please show all work!arrow_forwardDetermine the Reaction Order for HCI using calculations described in the background section. Show your work. Note that your answer will probably not be a whole number as it is in the examples, so round to the nearest whole numberarrow_forwardRate Expressions: Write the rate expression and the rates of all other species using the given rate for the stated reactions. Make sure the reactions are balanced. 3. N₂ + O₂ → N₂0s N₂ + S0₂ → N₂ 205 Rate of depletion of O₂ = 0.79M/s 4. C₂H6+ O₂-3H₂O +2CO₂ Rate of formation of CO₂= 1.32M/s 5. H₂O2)→ H₂O(g) + O2(g) Rate of formation of H₂O = 1.21M/sarrow_forward
- 23 eBook Print References In the SN2 reaction, the "2" stands for Multiple Choice two reactants in the reaction. two steps in the reaction. two intermediates in the reaction. bimolecular kinetics for the reaction.arrow_forwardTIAarrow_forward#26 please. I got 3 A + 4 B and 6 C. I would like to see your steps This is not a graded question as it is a practice question . I am 60 years old and helping my son prepare for the AP exam in a few months. We do questions at the back of the textbook by Zumdahl and Zumdahlarrow_forward
- Answer all the questions in the image.arrow_forwardew K History Bookmarks DZL Rate Laws Expe X Profiles Tab Determination c X 1 Homework 2 ttempt 1 Listen Window my.edu/d21/le/content/408344/viewContent/17004406/View Help Your Answer: Rates Law Expe X D21 4. CLASS SLIDE X 3 What is the rate constant for a reaction based on the following experimental information? Expt Rate (M/s) [A] (mol/L) [B] (mol/L) 1 0.5170 0.700 0.648 2 1.4912 1.189 0.648 1.2205 1.529 D21 Activity Assignr X 0.700 Report your answer to THREE significant figures. A ALEKS-Isabell x Earrow_forward2. At a particular time during the combustion of propanol above, propanol is consumed at a rate of 0.5 M/s. a. At what rate is molecular oxygen consumed? Show your work. b. At what rate is carbon dioxide produced? Show your work.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY