
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Question 2 and 3 please
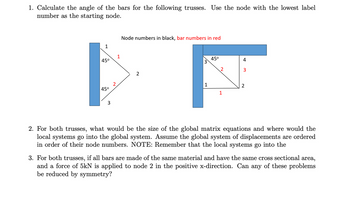
Transcribed Image Text:1. Calculate the angle of the bars for the following trusses. Use the node with the lowest label
number as the starting node.
1
1
45°
45°
3
Node numbers in black, bar numbers in red
45°
4
3
2
1
2
1
2. For both trusses, what would be the size of the global matrix equations and where would the
local systems go into the global system. Assume the global system of displacements are ordered
in order of their node numbers. NOTE: Remember that the local systems go into the
3. For both trusses, if all bars are made of the same material and have the same cross sectional area,
and a force of 5kN is applied to node 2 in the positive x-direction. Can any of these problems
be reduced by symmetry?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- 3arrow_forwardCompute the position and orientation of the tool point P from the given D-H table for the displacement variable e1=900 e2=90° and e3=90⁰. a1= 100 mm, a2= 100mm and a3 = 50mm Note: find the position and orientation using step by step procedure Present the roll, pitch, yaw and displacement in x,y and z axis. use the composite transformation matrix H-¹T₁= [ce; -se,ca; SO Sα₁ se, co,Ca; -C0₁Sα; 0 Sα₁ Cα₁ 0 0 0 aC0₁] aS0₂ d₁ 1 Joint 1 2 3 Figure 3 3-DOF (Industrial manipulator arm) 0 d α 0₁ 0 a1 02 0 a2 03 | 0 a³0 a -90 0arrow_forwardUSE MATLAB (Convolutional Code) The vector representation of a convolutional code is g1=[1 1]and g2=[1 0]. If the received sequence is 11 11 01 10, please use Viterbi Algorithm todecode it. Please show the full trellis diagram, including the updated trellis statemetrics.arrow_forward
- I having a problem with my code in MATLAB. In the following code results for r is just a 1x3 matrix. Although inside the while loop r equals to multiple 1x3 matrices. I need r equal to one matrix that is of size 27032x3. So, I just need the multiple r matrices to merge together to get one big matrix. I need that matrix to retain its value outside the while loop as well. cc=0; % set line counter JD = 2460626.666667; fid = fopen('tle_catalog.txt'); % load the TLE tline2='gg'; while ischar(tline2) cc = cc+1; % counter name = fgets(fid);% for the ones with three lines tline1 = fgets(fid); % collect first line of two line elements tline2 = fgets(fid); % collect second line of two line elements if tline2>0 % stop at the end of the file % initialize the propagation [satrec, startmfe, stopmfe, deltamin] ... = twoline2rv(721, tline1, tline2, 'c', 'd'); time_JD = tline1(21:32); yeardayhour = str2double(regexp(tline1, '(\d{2})(\d{3})(\.\d+)', 'tokens', 'once')); dn =…arrow_forwardA frame moves along its n-axis a distance of 2 units and is then rotated about the o-axis an angle 60° followed by a rotation about the z-axis by 90°. It was then translated about the a-axis by 2 units and finally rotated about the x-axis by 45°. Construct the transformation matrix equation. Compute the total transformation performed by the frame. Compute the joint variables that had to be made if similar location and orientation were to be created using cylindrical and RPY configuration. The initial point is located at P=[5 3 4]^Tarrow_forwardQuestion: What is the radix component for the integer -356? Subject name: Microcomputer engineering Department : mechanical Engineeeringarrow_forward
- Consider the figure as shown below. O-XoYoZo is the reference frame and O-X₁Y₁Z₁ is the frame attached to the tool. Sketch the tool position after each intermediate position of the operation of the tool about the reference frame: roll π/2(rotate about Zo), pitch -T/2(rotate about Yo), yaw π/2(rotate about Xo). Please write the final rotation matrix expression. ZI,Zo XI,Xo Yı, Yoarrow_forwardDon't Use Chat GPT Will Upvote And Give Handwritten Solution Pleasearrow_forwardI'm confused on starting the problem and I'm lost. Please helparrow_forward
- Solve all parts !arrow_forwarda 02 02 R₁ ground d R3 b For the 3Bar Inverted Crank Slider shown, 1. Starting with the position equation R=Au, where A is the rotation matrix about the z axis and u is a point on the position vector, derive the velocity equations in both algebraic and matrix form to solve for w3 and b. What are the vector position and velocity equations? Your matrix equation must be in the form [ BH] 2. From part 1 derive the matrix equation to solve for @3 and b. B-[%]-[ ]] B: 3. With the values R₂ = 2 in, R3 = 10 in, R₁ = 8 in, 0₂ = 40°, 03 = 185° and w2= 10 rad/sec. solve for @3 and b. B -7--0 Do not forget units.arrow_forwardPoints for stress vs strain (in image) Assume the compressive concrete strength (f’c) is 3,000 lb/in2 (psi)Calculate a cubic function (3rd order polynomial – Ax3+Bx2+Cx+Constant)Use this function to create a function that describes the slope of the cubic function (the derivative of thecubic function). This new function allows you to calculate the tangent to any point along the curve. Thetangent is the modulus of elasticity (E). The concrete code provides a formula to calculate E for concrete. That formula is:E = 57,000√??′, where f’c is in units of psi, and E is in units of psi.Use the derivative function you calculated to locate the point on the curve where the slope of the curvematches E using the concrete code formula. Express that stress point on the curve as a percentage ofthe compressive strength of the concrete. Now, calculate the secant modulus for the test case using 1,500 psi (50% f’c) as the arbitrary point onthe curve.Assume fracture occurs at the last point…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY