
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Calculate ΔH for the reaction: C2H4 (g) + H2 (g) → C2H6 (g), from the following data.
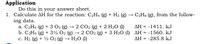
Transcribed Image Text:Application
Do this in your answer sheet.
1. Calculate AH for the reaction: C2H4 (g) + H2 (g)
ing data.
a. C2H4 (g) + 3 02 (g) → 2 CO2 (g) + 2 H20 (1)
b. C2H6 (g) + 3½ 02 (g) → 2 CO2 (g) + 3 H2O (1) AH = -1560. kJ
c. H2 (g) + ½ O2 (g) → H2O (1)
C2H6 (g), from the follow-
AH = -1411. kJ
%3!
%3D
AH = -285.8 kJ
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A) Given the standard enthalpy changes for the following two reactions:(1) 2C(s) + H2(g)C2H2(g)...... ΔH° = 226.7 kJ(2) 2C(s) + 2H2(g)C2H4(g)......ΔH° = 52.3 kJwhat is the standard enthalpy change for the reaction:(3) C2H2(g) + H2(g)C2H4(g)......ΔH° = ?------- kJ B) Given the standard enthalpy changes for the following two reactions:(1) 2Pb(s) + O2(g)2PbO(s)...... ΔH° = -434.6 kJ(2) Pb(s) + Cl2(g)PbCl2(s)......ΔH° = -359.4 kJwhat is the standard enthalpy change for the reaction:(3) 2PbCl2(s) + O2(g)2PbO(s) + 2Cl2(g)......ΔH° = ?------ kJarrow_forwardGiven the standard enthalpy changes for the following two reactions:(1) N2(g) + 2O2(g) -> 2NO2(g)...... ΔH° = 66.4 kJ(2) 2N2O(g) -> 2N2(g) + O2(g)......ΔH° = -164.2 kJwhat is the standard enthalpy change for the reaction:(3) 2N2O(g) + 3O2(g) -> 4NO2(g)......ΔH° = ?_____ kJarrow_forwardUse the table below to determine ΔH for the following reactionN 2H 4(g) + H 2O(g) ↔ NH 2OH(g) + NH 3(g) Bond Energies, kJ/mol Single Bonds H C N O S F Cl Br I H 432 C 411 346 N 386 305 167 O 459 358 201 142 S 363 272 --- --- 286 F 565 485 283 190 284 155 Cl 428 327 313 218 255 249 240 Br 362 285 243 201 217 249 216 190 I 295 213 --- 201 --- 278 208 175 149 Multiple Bonds C=C 602 C=N 615 C=O 799 C≡C 835 C≡N 887 C≡O 1072 N=N 418 N=O 607 S=O (in SO2) 532 N≡N 942 O2 494 S=O (in SO3) 469arrow_forward
- Using the table of thermodynamic data provided, for the reaction below: CS₂(1) + 302(g) → CO2(g) + 2SO2(g) Compound CO₂(g) CS₂(1) O₂(g) SO₂(g) SO₂(g) AHºf (kJ/mol) -393.5 89.0 0 -296.8 -395.7 S°(J/K mol) 213.8 151.3 205.15 248.2 256.8 Determine/calculate and report the following values in the labelled boxes below: a) The standard enthalpy change (AH°, in kJ/mol) of the reaction. b) The standard entropy change (AS°, in J/K mol) of the reaction. c) The standard free energy change (AG°, in kJ/mol) of the reaction. d) The free energy change (AG, in kJ/mol) of the reaction at 7.50 x 10² K.arrow_forwardHow much energy is required to break the bonds in the molecule of NO, BCl3, and NO2? and How do I find the ΔH of the molecule from the elements in their standard states?arrow_forward(b) An aqueous solution of acetic acid can be prepared by the reaction of ethanol with oxygen : CH3CH2OH (1) + O2 (g) –→ CH3COOH (1) + H2O (1) Write thermochemical equations for enthalpy of formation of the given compounds and calculate AH for the reaction, given the following data. Enthalpy of formation, AHf (kJmol") -277.8 Compound CH;CH2OH (1) CH3COOH (I) H2O (1) -485.0 -286.0arrow_forward
- The first step in the production of nitric acid from ammonia involves the oxidation of NH3. 4 NH3(g) + 5 O₂ (g) → 4 NO(g) + 6 H₂O(g) 2 a Use standard enthalpies of formation from the table below to calculate the standard enthalpy change for this reaction. Species AfH (kJ/mol) NH3(g) -45.90 NO(g) +90.29 H₂O(g) -241.83 Standard enthalpy change Submit = kJ/mol-rxnarrow_forward28. Write the equation that corresponds to the standard enthalpy of formation for each of the following compounds: a) NaI(s), b) HC1O,(g), and c) CH;OCH;(g)arrow_forward2. Please calculate the standard enthalpy of reaction (AHrxn, in kJ/mol) for the preparation of nitrous acid, HNO2, using the thermodynamic data given below. Preparation of nitrous acid: HCl(g) + NaNO2(s) → HNO2(1) + NaCl(s) 2NaCl(s) + H₂O(l) → 2HCl(g) + Na₂O(s) NO(g) + NO₂(g) + Na2O(s) → 2NaNO2 (s) NO(g) + NO₂(g) → N₂O(g) + O₂(g) 2HNO2(1)→ N₂O(g) + O2(g) + H₂O(g) H₂O(1)→ H₂O(g) ΔΗ = 507.31 kJ/mol AH = -427.14 kJ/mol AH = - 42.68 kJ/mol 34.35 kJ/mol ΔΗ ΔΗ = 44.012 kJ/mol =arrow_forward
- The industrial synthesis of chloroform by the reaction of methane with Cl2 is carried out according to the following reaction equation: CH4 (g) + Cl2 (g) → CHCl3 (l) + HCl (g) Using the thermodynamic data provided, calculate DHo (in Kj/mol) for this reaction.arrow_forwardA.) Given the standard enthalpy changes for the following two reactions: (1) 2Ni(s) + O2(g)-2NIO(s) AH° = -479.4 kJ (2) Ni(s) - Cl2(g)–→NIC2(s) AH° = -305.3 kJ what is the standard enthalpy change for the reaction: (3) 2NICI,(s) + O2(g)2NIO(s) + 2C2(g) AH° = ? kJ B.) Given the standard enthalpy changes for the following two reactions: (1) 4C(s) - SH2(g) C,H10(e) AH° = -125.ó kJ (2) C,H(g)2C(s) + 2H2(g) AH° = -52.3 kJ what is the standard enthalpy change for the reaction: (3) 2C,H4(g) + H2(g) ) C,H10(g) AH° = ? kJarrow_forwardConsider the following chemical reaction: C3H8(g) + H2(g) to give C2H6(g) + CH4(g) ΔH° = ? Calculate the enthalpy change for the reaction above using Hess's law Thermochemical data: H2(g) + 1\2O2(g) to give H2O(l) ΔH° =-285.8 kJ ΔH° combustion for CH4(g) ΔH° =-890.0 kJ/mol CO2 giving C(s, graphite) + O2(g) ΔH°= +393.5 kJ ΔH° combustion for C2H6(g) ΔH° =-1560.0 kJ/mol ΔH°f for C3H8(g) ΔH° =-103.8 kJ/molarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY