
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
thumb_up100%
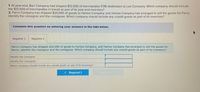
Transcribed Image Text:1. At year-end, Barr Company had shipped $12,500 of merchandise FOB destination to Lee Company. Which company should include
the $12,500 of merchandise in transit as part of its year-end inventory?
2. Parris Company has shipped $20,000 of goods to Harlow Company, and Harlow Company has arranged to sell the goods for Parris.
Identify the consignor and the consignee. Which company should include any unsold goods as part of its inventory?
Complete this questlon by entering your answers in the tabs below.
Required 1
Required 2
Parris Company has shipped $20,000 of goods to Harlow Company, and Harlow Company has arranged to sell the goods for
Parris. Identify the consignor and the consignee. Which company should include any unsold goods as part of its inventory?
Identify the consignor.
Identify the consignee.
Which company should include any unsold goods as part of its inventory?
< Required 1
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
Since you have asked multiple questions, we will solve the first question for you. If you want any specific question to be solved then please specify the question number or post only that question.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Neverstop Corporation sells item A as part of its product line. Information about the beginning inventory, purchases, and sales of item A are given in the following table for the first six months of the current year. The company uses a perpetual inventory system: Date January 1 (beginning inventory) January 24 February 8 March 16 June 11 Purchases Sales Number of Units Unit Cost 560 Number of Units Sales Price $3.70 360 $5.20 660 $3.80 360 $5.20 660 $3.80 Required: 1. Compute the cost of ending inventory by using the weighted-average costing method. (Do not round intermediate calculations and round the final answer to 2 decimal places.) Answer is complete and correct. Ending inventory $ 4,396.40 2. Compute the gross profit for the first six months of the current year by using the FIFO costing method. (Do not round intermediate calculations and round the final answer to 2 decimal places.) Answer is complete and correct. Gross profit $ 1,064.00arrow_forwardCan you please explain how to get the Cost of Goods Solds category using LIFO?arrow_forwardssarrow_forward
- he records at the end of January of the current year for Young Company showed the following for a particular kind of merchandise: Beginning Inventory at FIFO: 19 Units @ $16 = $304 Beginning Inventory at LIFO: 19 Units @ $12 = $228 January Transactions Units Unit Cost Total Cost Purchase, January 9 25 $ 13 $ 325 Purchase, January 20 50 19 950 Sale, January 21 (at $38 per unit) 40 Sale, January 27 (at $39 per unit) 25 Required: Compute the inventory turnover ratio for the month of January under the FIFO and LIFO inventory costing methods. Which costing method is more accurate indicator of the efficiency of inventory management?arrow_forwardRequired information [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] Altira Corporation provides the following information related to its merchandise inventory during the month of August 2021: Aug.1 Inventory on hand—3,700 units; cost $7.80 each. 8 Purchased 18,500 units for $7.20 each. 14 Sold 14,800 units for $13.70 each. 18 Purchased 11,100 units for $6.40 each. 25 Sold 13,800 units for $12.70 each. 28 Purchased 5,700 units for $5.80 each. 31 Inventory on hand—10,400 units. Required:1. Using calculations based on a perpetual inventory system, determine the inventory balance Altira would report in its August 31, 2021, balance sheet and the cost of goods sold it would report in its August 2021 income statement using the FIFO method.arrow_forwardPlease help with Question Barrow_forward
- The units of Product YY2 available for sale during the year were as follows: Dates Transactions Units Unit cost 1-Jan Beginning inventory 10 30 1-Apr Purchase 30 32 16-Jun Purchase 40 35 28-Nov Purchase 20 36 There were 25 units of YY2 in the ending inventory of the year. Instructions: Compute the cost of the ending inventory and the cost of goods sold for the year under the following method (just the number, no $ sign). 1. FIFO Cost of ending inventory Cost of goods sold 2. LIFO Cost of ending inventory Cost of goods sold 3. Weighted average Cost of ending inventory Cost of goods soldarrow_forwardCo.'s purchases and sales of a particular product during the year are shown below: Jan. 1 Beginning Inventory Jan. 18 Purchase 1,500 units @ $ 10 1,250 units @ $ 12 1,500 units @ $ 20 1,750 units @ $ 14 1,750 units @ $ 25 500 units @ $ 15 Jan 20 Sold Jan. 25 Purchase Jan. 27 Sold Jan. 29 Purchase Assuming that company uses perpetual inventory system, determine the cost of goods sold and compute the ending inventory as of Jan. 31 and make the journal entry for Jan. 27 transaction inventory subsidiary ledger for LIF0 cost flow assumption. by using DATE IN OUT BALANCE Quantity Price Total Quantity Price Total Quantity Price Total Jan 1 Jan 18 Jan 20 Jan 25 Jan 27 Jan 29arrow_forwardPatterson Company has the following items at year-end. Identify which items should be included in Patterson's year-end inventory count. 1. Goods held on consignment by Sell For You Company. 2. Goods held by Patterson on consignment that will be sold for another company. 3. Goods in transit sent to a client F.O.B. shipping point. 4. Goods in transit sent to a client F.O.B. destination. 01 & 4 01, 2, 3, & 4 01, 2, & 4 01 & 3arrow_forward
- The following units of a particular item were available for sale during the calendar year: Jan. 1 Inventory 4,000 units at $40 Apr. 19 Sale 2,500 units June 30 Purchase 4,500 units at $44 Sept. 2 Sale 5,000 units Nov. 15 Purchase 2,000 units at $46 The firm uses the weighted average cost method with a perpetual inventory system. Deteremine the cost of goods sold for each sale and the inventory balance after each sale. Present the data in the form illustrated in Exhibit 5.arrow_forwardi need requirement 1- a onlyarrow_forwardCHERRY Company has 10,000 units of merchandise with unit cost of ₱50 at the beginning of the year. Purchases in chronological order during the year are as follows: 2,000 units at ₱51; 1,000 units at ₱52; 500 units at ₱53. The entity sold 13,100 units during the year. What is the ending inventory cost at year-end using FIFO? A. ₱ 20,000 B. ₱ 21,200 C. ₱ 655, 000 D. ₱ 680, 000arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education