
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question

Transcribed Image Text:1. A rigid tank whose volume is 10 liters is initially evacuated. A pinhole develops in the wall, and air
from the surroundings at 1 bar, 25C enters the pressure in the tank becomes 1 bar. No significant heat
transfer beween the contents of the tank and the surroundings occur. Assuming the ideal gas model
with y 1.4 for the air, determine:
(a) final temperature in the tank
(b) amount of air that leaks into the tank
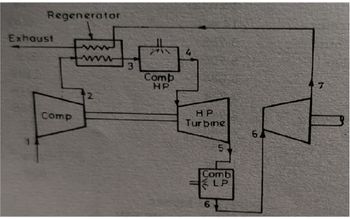
Transcribed Image Text:Regenerator
Exhaust
Comp.
www
3
7711
Comb
HP
HP
Turbine
51
Comb
LP
200
6
7
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 9 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- pls answer completely thanksarrow_forwardThe figure shows data for a portion of the ducting in a ventilation system operating at steady state. The ducts are well insulated and the pressure is very nearly 1 atm throughout. The volumetric flow rate entering at state 2 is AV2 = 4000 ft3/min. Assume the ideal gas model for air with cp = 0.24 Btu/lb·oR and ignore kinetic and potential energy effects. Determine the temperature of the air at the exit, in oF, and the rate of entropy production within the ducts, in Btu/min·oR.arrow_forward4. Choose the correct statement/s with respect to entropy change during a process a. Entropy increases with increase in pressure at constant temperatureb. Entropy increases with increase in temperature at constant pressurec. Entropy can be kept constant by systematically increase both pressure and temperatured. Entropy can not be changedarrow_forward
- 4. A closed, rigid tank is filled with a gas that can be modeled as an ideal gas, initially at 50 °C with a pressure of 3 bar. The gas is heated, and the pressure at the final state is 4 bar. Determine the final temperature, in C. The local atmospheric pressure is 1 bar.arrow_forwardPlease Asaparrow_forwardA rigid tank whose volume is 4 mở, initially containing air at 1 bar, 295 K, is connected by a valve to a large vessel holding air at 6 bar, 295 K. The valve is opened only as long as required to fill the tank with air to a pressure of 6 bar and a temperature of 350 K. Assuming the ideal gas model for the air, determine the heat transfer between the tank contents and the surroundings, in kJ. Qev i 339.86 kJarrow_forward
- Calculate the energy requirement to raise the temperature of 1 kg of water from 60 ° C of water to 100 ° C using the following approach; a. Use of mean specific heat = .... kJ. b. Enthalpy change in water - vapor saturation table = .... kJ.arrow_forwardCalculate the compressor work in kJ required to compress 1 kg of an ideal gas from an initial volume and pressure of 0.65m3 and 101.3kpa to a final pressure of 517kpa. Compression is with n=1.35. A. 133.6 B. 105.8 C. 148.3 D. 142.7arrow_forwardسككينلممسسarrow_forward
- 3.arrow_forwardFor all problems, draw p-v- and a T-s-diagrams indicating states and processes relative tosaturation lines.arrow_forwardAmmonia vapor (working as a refrigerant) enters a valve at 10 bar, 40oC, and leaves at 6 bar.Considering this refrigerant undergoes a throttling process (with insignificant change in temperaturebetween the inlet and the exit), determine its temperature, in oC, when leaving the valve.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY