
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
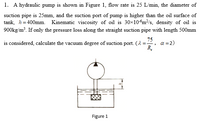
Transcribed Image Text:1. A hydraulic pump is shown in Figure 1, flow rate is 25 L/min, the diameter of
suction pipe is 25mm, and the suction port of pump is higher than the oil surface of
tank, h= 400mm. Kinematic viscosity of oil is 30x10-6m²/s, density of oil is
900kg/m³. If only the pressure loss along the straight suction pipe with length 500mm
75
is considered, calculate the vacuum degree of suction port. (2 =
R,
a =2)
Figure 1
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A commercial venturi meter is placed in a vertical pipe as shown below. Pressure gauges are located at section 1 and section 2 and the pipe and throat diameters are as indicated. Assume that Cd-0.97 and calculate the downward discharge of water corresponding to pressures p1=65 kPa and p2=40 kPa.. Also, calculate the velocity at section 2. 20 cm 1 0.4 m 2 10 cmarrow_forwardComplete solution and correct units pls. Thanksarrow_forwardA hydraulic pump is shown in the following Figure, flow rate is 25 L/min, the diameter of suction pipe is 30mm, and the suction port of pump is higher than the oil surface of tank, h=300mm. Kinematic viscosity of oil is 30x10-“m²/s, density of oil is 900kg/m³. If only the pressure loss along the straight suction pipe with length 400mm is considered 75 (1 = a = 2, g=9.8) R. (1) Calculate the flow velocity in the suction pipe; (2) Judge the flow state in suction pipe; (3) Calculate the pressure loss along the straight suction pipe; (4) Calculate the vacuum degree of suction port.arrow_forward
- 5. The below figure shows a pipe with a circular cross section of diameter D= 10 cm. Water enters the left end with a velocity 3 cm/s. The dynamic viscosity of water is 8.90 × 10-4 Pa·s, Find the type of flow. a. No flow b. Laminar flow с. Transitional flow d. Turbulent flowarrow_forward1. A piston-cylinder is producing a viscous oil flow, which has the flow rate of Q, radius R=1.5 mm, and stroke L-5 mm. The fluid density is p = 800 kg/m³ and the viscosity is μ = 0.5 Pa-s. The pressure to drive the flow is p=6.25 Pa. a. How many non-dimensional groupings can be obtained? Derive them. b. If the flow transitions at Re = PV(2R) =2300. Is the generated flow laminar or turbulent given Q=20 mL/s? LL c. Assume the pressure gradient is uniform on the cross-section and can be calculated using OP=-. The velocity profile in the cylinder is u(r) = ax - [1-(²]. Sketch the velocity profile. Calculate the shear stress at the R² ap 2UÔI cylinder wall and label the direction. d. Calculate the flow rate Q with the velocity profile in (c).. e. If the shear stress is uniform over the cross-section, i.e. T = C, what's the pressure gradient distribution and sketch it? L L. Rarrow_forwardi need the answer quicklyarrow_forward
- at point a in pipeline carrying water, the diameter is 1m, the pressure is 98kPa and the velocity is 1m/s. at point B, 2m higher than A, the diameter is 0.5m and the pressure is 20kPa. Determine the direction of flow. need answer pleasearrow_forwardA fan has a suction static pressure of 40mm of water vacuum with air velocity of 5m/s. The discharge has 160mm of water gage and discharge velocity of 9m/s. What is the total head of the fan if air density is 1.2kg/m3, mm of water gauge. Answer: 203.43arrow_forwardQ(in) is a constant inflow which maintains the water level in the tank. Find the horizontal force needed to hold the tank stationary. If you could make any notes on steps in the method to make it clearer that would be great too. Thanks in advance!arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY