
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
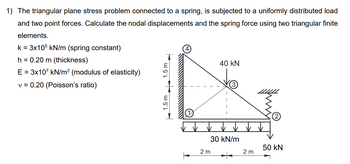
Transcribed Image Text:1) The triangular plane stress problem connected to a spring, is subjected to a uniformly distributed load
and two point forces. Calculate the nodal displacements and the spring force using two triangular finite
elements.
k = 3x105 kN/m (spring constant)
h = 0.20 m (thickness)
E = 3x107 kN/m² (modulus of elasticity)
v = 0.20 (Poisson's ratio)
1.5 m
40 kN
30 kN/m
50 kN
2 m
2 m
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 8 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- A close-coiled helical spring is made of a wire of diameter 20 mm. The mean radius of the coils is 100 mm. Find the number of turns required and the maximum axial load permissible if the shear stress is not to exceed 100 MPa and the maximum elongation is limited to 40 mm. G = 83 GPa.arrow_forwardParvinbhaiarrow_forwardSolid Mechanics In the figure, solid copper rod with expansion coefficient αB = 165.10-7 1 / 0C It is 20 mm in diameter. Inner diameter is 2mm larger than this bar and expansion into a steel pipe of 30 mm outer diameter with coefficient αÇ = 125.10-7 1 / 0C so that they move together. It is combined with a rigid plate. System with temperature difference Δt = 80 0C Find the stresses that will occur in steel and copper when heated. (Eç= 200 GPa, Eb= 100 GPa)arrow_forward
- I need answer within 20 minutes please please with my best wishesarrow_forwardA cylindrical bar made of brittle material has been subjected to pure torsion by a torque M and tension from the force F (Figure Q6.c). The torque gives rise to the shear stresses T = T = 32 MPa and the force F gives rise to the tensile stress ху yx 0, = 65 MPa. The stress along the y-axis is zero (o, = 0). Determine whether there will be a failure due to the maximum tensile stress if the tensile strength of the material is 90 MPa. F X Figure Q6.carrow_forwardTwo concentric plain helical springs of the same length are wound out of the same wire circular in cross section and supports a compressive load P. The inner spring consists of 20 turns of mean dimeter 160 mm and the outer spring has 18 turns of mean diameter 200 mm. Calculate the maximum stress induced in the spring if the diameter of wire is equal to 10 mm and Pis equal to 1000 N. (Take K,-1)arrow_forward
- The bar shown in the figure is made of cold-drawn steel, having an yield strength of 280 MPa. Loads applied are F = 1 kN, P = 5 kN, and torque T = 20 kN. For each element shown in the figure (element A and element B, separately, • Determine the principal stresses at A and B (eigenvalues) • Using DET, determine whether the bar will yield. What is the factor of safety for the loading situation shown, based on DET? 15-mm D. -100 mmarrow_forward2. A composite spring has two closed coiled springs connected in series, each spring has 12 coils at a mean diameter of 25mm. Find the wire diameter for one if the other is of 2.5mm diameter and the stiffness of the composite spring is 700N/m. Estimate the greatest load that can be carried by the composite spring, and the corresponding extension, for a maximum shear stress of 180MPa. Take G=80GPa.arrow_forward2-A wheel of diameter d and width w carrying a load F rolls on a flat rail. Estimate the maximum contact pressure for these materials. Por vedit -3D d 5 in 150 mm 3 in W 2 in 40 mm 1.25 in F 600 lbf 2 kN 250 lbf Wheel Material Steel Steel Cast iron Rail Material Steel Cast iron Cast iron.arrow_forward
- Consider the loaded shaft illustrated in Figure Q4 (i). The shaft is simply supported at A and D. The shoulder fillet radius is 0.3 cm at B and C. If the shaft is subjected to a force of F-800 N, determine the following: (a) The reaction forces at the two ends of the shaft A and D. (b) The bending moments at shoulder fillets B andC. (c) The nominal stresses at shoulder fillets B and C. (d) The stress concentration factor at shoulder fillet B. (e) The maximum stress in the shaft taking into account stress concentrations. 800 N T-0.3 can A d, - 3 cm d, = 5 cm d, - 3 cm 5 cm 8 cm 8 cm 12 cm Figure Q4 (i) The reference parameters are shown in Figure Q4 (ii) in the page that follows. For 0.002 srlds 0.3 and 1.01 s Dlds 6.0, the stress concentration factor for bar bending is given as: kn -4.4 = 0.632 + 0.377 -0.14 – 0.363(P/a)" + 0.503(P/a) 1- 2.39(P/a) + 3.368(2la)* -0.5 The nominal stress is: 32M %3D nd3arrow_forwardFor the rod in the figure, an allowable stress of 10 ksi, calculate the maximum torque T which can be applied. d= 0.5 in, D= 0.835 in, r= 0.045 in .arrow_forwardConsider a one-element triangular mesh shown in Figure 2. The edge AC is fixed. The edge BC is subject to lin- early varying traction normal to the edge as shown in Figure 2. Assume plane-stress conditions with thickness 1 = 1 cm and Young's modulus E = 70 GPa and Poisson's ratio v = 0.3. 150 kN/m 50 kN/m C (0,0.3) B (0.4,0.3) a) Specify the boundary condi- tions. b) Construct the stiffness matrix. A (0,0) c) Calculate the global force ma- Figure 2: Triangular element. All coordinates are in meters. trix. d) Solve for the unknown displace- ments and compute the stress at (0.1, 0.2).arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY