
Calculus: Early Transcendentals
8th Edition
ISBN: 9781285741550
Author: James Stewart
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
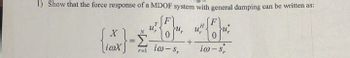
Transcribed Image Text:1) Show that the force response of a MDOF system with general damping can be written as:
X
liax)
-Σ
=
ral
iw-s,
+
{0}
iw-s,
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Show that t, e^t, and sin(t) are linearly independent.arrow_forwardCalculate az/ax, where xez + zeY = x + y.arrow_forwardConsider the Squirrel-Coyote system given by S' = 2S-4SC C' = SC-C (1) Sketch the nullclines of the system and label them (as S- or C-nullclines). Add arrows to each nullcline and each distinct region of the phase plane to indicate the direction of the vector field there. (No need to draw the whole vector field, just a single arrow to show direction in each significant place.)arrow_forward
- If A = yz(^2) i - 3xz(^2) j + 2xyz k , B = 3x i + 4z j - xy k and ∅= xyz , find (a) Ax (∇∅), (b) (Ax ∇) ∅, (c) (∇x A) x B, (d) B. ∇x A.arrow_forwardMatch each of the functions (a)-(c) with the corresponding gradient vector field from those in (I)-(VI). Enter your answer as upper case roman numerals: I, II, III, etc. (a) f(x, y) = x cos(y) (b) f(x, y) = (x - 2)²(y-2)/5 (c) f(x, y) = sin(x) · cos(y) (click on an image to enlarge it) IV II V II VIarrow_forwardLet q = - 2xy - y² + 2xz+2yz + z² be a quadratic form on R³ viewed as a polynomial in 3 variables. Find a linear change of variables tou, v, w that puts q into the canonical form in `Sylvester's law of inertia'!. What are the values of the associated indices s, t? Select one: O We let u = √3(x − y + 2), v = x+y, w = (x - y)/2 to find that q = u²+². Hence s = 2, t = 0 in Sylvester's law of intertia. O We let u = x - 2y, v = z+y, w = √3y to find that q=u²v² w². Hence s = 1,t = 2 in Sylvester's law of intertia. O we let u = x, v= √2(x+y), w = x+y+z to find that q = u²v² + w²2. Hence s = 2, t = 1 in Sylvester's law of intertia. O None of the others apply O The quadratic form does not obey the condition to be diagonalisable over R. This is because the minimal polynomial of the corresponding matrix is not a product of distinct linear factors. Hence Sylvester's law of inertia does not apply. By convention, we set s = t = ∞ when this happens.arrow_forward
- 3. (12) Let V = R². Define vector addition and scalar multiplication as follows: (u1, uz)O(v1, v2) = (u1V1, U2V2) and c(u1,u2) = (u,C, u2^), c > 0 (a) Does V have an additive identity? If so, what would it be? (b) Does the distributive axiom c(uOv) = cu@cv hold? (Show why or why not). 4arrow_forwardSection 17.7) Verify Stokes' Theorem for F(x, y, z) = if C' is the intersection of z = 4 + y and x² + y² = 4 counterclockwise when viewed from above.arrow_forward1. (Section 17.1) Match the vector fields with their sketches below by placing the letter of the function in the corresponding blank: (I) F(x, y) = (II) F(x, y) = (III) F(x, y) = (IV) F(x, y) = Vector Field: (B) Vector Field: (A) (C) Vector Field (D) 0 Vector Field:arrow_forward
- Draw approx. solution for the directional field for the first order with the initial condition y(0) = -1.8arrow_forwardShow whether the following functions are wave functions or not. 1. У(х, t) еxp(ikx) = A- exp (i(ot-Ф)) кЗх3-0313-3kоxt(kx-ot)-iф)) 2 У(х, t) 3. y(x, t) Aexp(i(k³x³-w³t³-3kwxt(kx-wt)-ip)) Аехр (i(-kx? + оt))arrow_forwardLet a=<−5,0,−3> and b=<4,0,2> Show that there are scalars s and t so that sa+tb=<27,0,15>.s = ? t = ?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning

Calculus: Early Transcendentals
Calculus
ISBN:9781285741550
Author:James Stewart
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)
Calculus
ISBN:9780134438986
Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. Weir
Publisher:PEARSON

Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)
Calculus
ISBN:9780134763644
Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric Schulz
Publisher:PEARSON

Calculus: Early Transcendentals
Calculus
ISBN:9781319050740
Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert Franzosa
Publisher:W. H. Freeman


Calculus: Early Transcendental Functions
Calculus
ISBN:9781337552516
Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. Edwards
Publisher:Cengage Learning