
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics
8th Edition
ISBN: 9781259696527
Author: J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
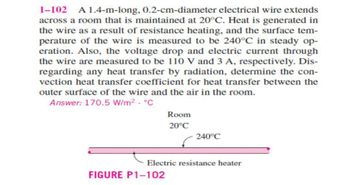
Transcribed Image Text:1-102 A 1.4-m-long, 0.2-cm-diameter electrical wire extends
across a room that is maintained at 20°C. Heat is generated in
the wire as a result of resistance heating, and the surface tem-
perature of the wire is measured to be 240°C in steady op-
eration. Also, the voltage drop and electric current through
the wire are measured to be 110 V and 3 A, respectively. Dis-
regarding any heat transfer by radiation, determine the con-
vection heat transfer coefficient for heat transfer between the
outer surface of the wire and the air in the room.
Answer: 170.5 W/m². °C
Room
20°C
FIGURE P1-102
240°C
Electric resistance heater
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- A rubber insulated copper wire 2 mm diameter is carrying electric current and exposed to a uniform temperature of air at 40°C. What will be the maximum steady current in amperes that can be allowed if the rubber insulation is not to get heated above 45°C? Insulation thickness=1 mm Thermal conductivity of rubber= 0.15 W/m-K Air film coefficient= 10 W/m2-K Electrical resistivity of copper=10-7 ohm-m A 10.45 A В 2.1 A C) 14.5 A D 4.25 A E 9.65 A F None of thesearrow_forwardfor chemical engineersarrow_forwardTwo identical 7.5-cm cubes of copper at 425 and 90°C are brought into contact. Assuming that the blocks exchange heat only with each other and that there is no resistance to heat flow as a result of the contact of the blocks, plot the temperature of each block as a function of time, using the lumped-capacity method of analysis. That is, assume the resistance to heat transfer is the conduction resistance of the two blocks. Assume that all surfaces are insulated except those in contact.arrow_forward
- The exhaust duct from a heater has an inside diameter of 114.3 mm with ceramic walls 6.4 mm thick. The average k=1.52 W/m· K. Outside this wall, an insulation or rock wool 102 mm thick is installed. The thermal conductivity of the rock wool is k= 0.046+ 1.56 x 104 T°C (W/m · K). The inside surface * = temperature of the ceramic is T1 = 588.7 K, and the outside surface temperature of the insulation is 311 K. Calculate the heat loss for 1.5 m of duct and the interface temperature T2 between the ceramic and the insulation. [Hint: The correct value of km for the insulation is that evaluated at the mean temperature of (T2 + T3)/2. Hence, for the first trial assume a mean temperature of, say, 448 K. Then calculate the heat loss and T2 Using this new T2, calculate a new mean temperature and proceed as before.]arrow_forward(a) What is the heat loss per unit length of the pipe?(b) The pipe material is switched to PTFE (k = 0.38 W/(m⋅K)). To maintain the same heat loss as theprevious question, if all other parameters are to remain the same as before, what is the required thicknessof the pipe wall in centimeters?arrow_forwardExample • The cylinder is made from aluminum with diameter and thickness of 5 cm and 1 cm respectively. The wall temperature in the inside of cylinder is 50°C, while the temperature of the air is 30°C. the coefficient of convection in the air is 10 W/m2-C. Calculate the heat loss from the cylinder per unit length! • Calculate the thickness of the insulation so heat loss from cylinder will decrease 50% of initial condition. Thermal conductivity of the isolator (k) : 0.5 W/m°C state.pptx 7 MB VIEW Tampilkan semuaarrow_forward
- À wall of area 30 m² having a density of 1500 kg/m', thermal conductivity 30 W/m.K, and specific heat capacity 4 kJ/kg.K. The temperature distribution across a wall 0.5 m thick at a certain instant of time is given as T(x) = 30-5 x-7x The wall is generating a uniform heat (q.) of 1000 W. (1) Find the rate of heat transfer entering and leaving the wall (in W). (2) Find rate of energy stored in Watt. (3) Find (dFT/dx²) (4) Derive the change in temperature with respect to time equation (time rate of temperature change)- remember to substitute the value of (d T/dx²) from (part 3) and values of all other properties into final equation. %3Darrow_forwardQ3) A fused-quartz sphere has a thermal diffusivity of 9.5 x 107 m²/s, a diameter of 2.5 cm, and a thermal conductivity of 1.52 W/m. °C. The sphere is initially at a uniform temperature of 25 °C and is suddenly subjected to a convection environment at 250 °C. The convection heat-transfer coefficient is 110 W/m². °C. Calculate the temperatures at the center and at a radius of 5 mm after a time of 8 min.arrow_forward.240mm steam main pipe, 210m long is covered with 50mm of high temperature insulation (k-0.092 W/m °C) and 40mm of low temperature insulation (k-0.062 W/m °C). The inner and the outer surface temperature as measured are 390 °C and 40 °C respectively. Calculate: 1- The total heat loss per hour. 2- The temperature between two layers of insulation.arrow_forward
- A copper electric wire of radius R, = 1 mm is isolated by a layer of PVC so that the outer radius of the wire Rg = 2 mm, as shown in Figure below. The wire exchanges heat with the air at 20°C according to a heat transfer coefficient h=20 W/m2°c: Given that : k=copper electrical conductivity=4.0 × 1070hm-'m¯! kpvc= PVC thermal conductivity = 0.3- m°C kco = copper thermal conductivity = 100 m°C %3D (amp/m)² And that the electrical heating source is given by : S, amp²s /kgm³ If the temperature (T,) on the outer surface (r = RG) is 25°C, what is the electrical current C (amp) that passes through this wire? Dont forget to state your hypothesis clearly. Hi, Could you please tell me what the book's name is? Thank you!arrow_forwardIn a movie theater in winter, 500 people are watching a movie. The heat losses through the walls, windows, and the roof are estimated to be 150,000 Btu/h. Determine if the theater needs to be heated or cooled.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
 Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning
Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The
Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The

Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781259696527
Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY

Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9780133887518
Author:H. Scott Fogler
Publisher:Prentice Hall


Industrial Plastics: Theory and Applications
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781285061238
Author:Lokensgard, Erik
Publisher:Delmar Cengage Learning

Unit Operations of Chemical Engineering
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9780072848236
Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter Harriott
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The