
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
-
01. Referring to Fig 2d and the attached table, determine whether average pre-tax income of the top 10%, top 5%, top 1% of households by income has increased or decreased in the recession years of 1980-81, 1990-91, and 2001 (as compared to immediately prior year).Increaseddecreased
QUESTION 2
-
02. Referring to Fig 2d and the attached table, determine whether average pre-tax income of the top 10%, top 5%, top 1% of households by income has increased or decreased following the major tax cut years of 1982, 1987, and 2002-03.Increaseddecreased
QUESTION 3
-
03. Referring to Fig 2d and the attached table, determine whether average federal individual income tax payments of the top 10%, top 5%, top 1% of households by income, has increased or decreased in the recession years of 1980-81, 1990-91, and 2001 (as compared to immediately prior year).Increaseddecreased
QUESTION 4
-
04. Referring to Fig 2d and the attached table, determine whether average federal individual income tax payments of the top 10%, top 5%, top 1% of households by income, has increased or decreased following the major tax cut years of 1982, 1987, and 2002-03.Increaseddecreased
QUESTION 5
-
05. Referring to Fig 2d, the attached table, and you answers the questions 1 through 4, is it reasonable to infer that pre-tax income is a more important determinant of tax revenue than tax rates (assuming that tax cuts are expected to decrease tax revenue)?YESNo
QUESTION 6
-
06. Referring to Fig 4b and the attached table, determine whether the shares of federal individual income taxes paid by the top 10%, top 5%, top 1% of households by income, has increased or decreased in the recession years of 1980-81, 1990-91, and 2001 (as compared to immediately prior year).Increaseddecreased
QUESTION 7
-
07. Referring to Fig 4b and the attached table, determine whether the shares of federal individual income taxes paid by the top 10%, top 5%, top 1% of households by income, has increased or decreased following the major tax cut years of 1982, 1987, and 2002-03.Increaseddecreased
QUESTION 8
-
08. Referring to Fig 4b and the attached table, what is remarkable about the shares of federal individual income taxes paid by the bottom 40% of households by income, since 2002?a) The share of federal individual income taxes paid by the bottom 40% have not changed much.b) The share of federal individual income taxes paid by the bottom 40% have been increasing.c) The share of federal individual income taxes paid by the bottom 40% have been decreasing.d) The share of federal individual income taxes paid by the bottom 40% have turned negative.
QUESTION 9
-
09. Referring to Fig 4b, the attached table, and your answers to questions 7 and 8 above, is it reasonable to infer that income tax rate cuts tend to increase the share of taxes paid by top income taxpayers?YESNO
QUESTION 10
-
10. In 1979, the share of federal individual income taxes paid by the bottom 80% of taxpayers by income is ______%.
QUESTION 11
-
11. In 2007, the share of federal individual income taxes paid by the bottom 80% of taxpayers by income is ______%.
QUESTION 12
-
12. Referring to Fig 4b, the attached table, and your answers to questions 7, 8, 10, and 11 above, and assuming the "share" of taxes paid is the measure of "fair share," is it reasonable to infer that the rich DO pay their fair share of federal individual income taxes, especially as compared to the bottom 80% of taxpayers by income?YESNO
QUESTION 13
-
(1a) The Net federal government saving (budget deficit) for the 4th quarter of 2019 is:$______ billions.
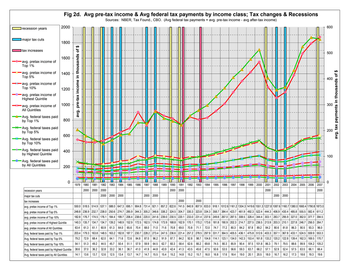
Transcribed Image Text:recession years
Imajor tax cuts
Itax increases
avg. pretax income of
Top 1%
avg. pretax income of
Top 5%
avg. pretax income of
Top 10%
avg. pretax income of
Highest Quintile
avg. pretax income of
All Quintiles
Avg. federal taxes paid
by Top 1%
Avg. federal taxes paid
by Top 5%
--Avg. federal taxes paid
by Top 10%
➡+Avg. federal taxes paid
by Highest Quintile
Avg. federal taxes paid
by All Quintiles
Fig 2d. Avg pre-tax income & Avg federal tax payments by income class; Tax changes & Recessions
Sources: NBER, Tax Found., CBO. (Avg federal tax payments = avg. pre-tax income - avg after-tax income)
2000
1800
1600
1400
1200
1000
800
600
400
200
0
recession years
major tax cuts
tax increases
avg. pretax income of Top 1%
avg. pretax income of Top 5%
avg. pretax income of Top 10%
avg. pretax income of Highest Quintile
avg. pretax income of All Quintiles
Avg. federal taxes paid by Top 1%
Avg. federal taxes paid by Top 5%
Avg. federal taxes paid by Top 10%
Avg. federal taxes paid by Highest Quintile
Avg. federal taxes paid by All Quintiles
avg. pre-tax income in thousands of $
(XXX 7 X - X PX K
2000 2000
E
||
1979 1980 1981 1982 1983 1984 1985 1986 1987 1988 1989 1990 1991 1992 1993 1994 1995 1996 1997 1998 1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007
2000 2000 2000
2000 2000
2000
2000
2000 2000 2000
2000 2000
T
2000
2000
550.0 518.5 514.9 537.1 588.0 647.3 695.1 904.8 731.4 921.1 857.2 822.6 741.5 840.9 807.9 833.0 918.1 1012.6 1161.2 1304.3 1419.6 1551.3 1227.8 1087.6 1160.7 1380.0 1660.4 1790.8 1873.0
248.8 236.9 232.7 238.0 250.6 274.7 285.9 344.3 305.2 346.6 338.2 324.5 304.7 330.3 323.8 334.3 358.7 384.4 423.7 461.9 492.3 522.4 444.3 406.9 430.4 485.8 555.5 582.4 611.2
182.8 176.7 174.5 176.1 184.4 199.7 206.4 238.6 220.0 241.6 239.0 230.5 220.1 233.0 231.4 237.6 249.8 267.0 287.5 308.5 328.4 344.4 303.1 283.7 295.9 327.0 362.0 377.7 394.5
140.3 135.7 134.7 134.7 139.2 148.9 152.9 172.5 162.5 174.8 173.9 168.8 162.9 170.1 170.2 173.6 181.8 190.9 202.3 214.7 227.5 236.5 213.9 203.3 210.1 227.8 246.7 256.0 264.7
63.4 61.3 61.1 60.9 61.3 64.0 65.6 70.4 68.0 71.0 71.6 70.8 69.0 70.8 71.1 72.0 74.7 77.2 80.3 84.2 87.8 89.2 84.2 80.6 81.8 86.3 90.5 93.3 96.0
203.4 179.3 163.8 148.5 163.2 182.8 187.7 230.7 228.2 273.4 247.5 236.6 221.4 257.2 278.5 297.9 331.7 364.5 405.5 436.1 475.8 512.6 403.3 357.1 367.8 433.1 524.5 559.9 553.3
79.2 72.9 68.4 62.0 64.1 71.6 72.6 84.8 87.0 96.2 91.9 87.7 84.2 92.8 98.7 104.8 114.1 123.1 134.0 142.3 153.4 161.8 133.2 120.2 122.8 139.4 162.3 169.5 170.7
54.1 51.3 49.2 44.5 45.7 50.4 51.1 57.9 59.9 64.5 62.7 60.3 58.4 62.6 66.2 69.8 74.5 80.3 85.9 90.4 97.5 101.8 86.3 79.1 79.5 88.6 99.9 104.2 105.2
38.6 37.0 36.2 32.8 33.2 36.1 36.7 41.0 41.9 44.8 43.9 42.4 41.3 43.5 45.6 47.5 50.6 53.5 56.6 59.3 63.7 66.2 57.1 52.9 52.4 57.5 63.5 66.1 66.4
14.1 13.6 13.7 12.6 12.5 13.4 13.7 14.7 14.7 15.5 15.4 15.2 14.8 15.2 15.7 16.0 16.8 17.6 18.4 19.0 20.1 20.5 18.0 16.7 16.2 17.3 18.6 19.3 19.6
600
500
400
300
200
100
0
avg. tax payments in thousands of $
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Question 1 Which of the following accurately describes the phenomenon of crowding out? O government borrowing pushes up interest rates, driving out private investment and consumption O government spending drive up the budget deficit O government spending causes more goods to be allocated to the public sector and fewer are available for the private sector O Increasing the proportion of public sector spending in the composition of GDP renders production less competitive and therefore less efficient.arrow_forward4. 1) Consider the following categories of taxes: I. wealth tax II. consumption tax III. Direct tax IV. Indirect tax Using the above categories only, an estate tax can be considered to be: a. III. only b. IV. only c. Both I. and III. d. Both I. and IV. e. Both II. and IV. 2) Which of the following is true of all social insurance programs? a. They are paid for by funds contributed only by employers. b. They are paid for by funds contributed only by employees. c. The initiation of payments depends on the occurrence of some kind of event in a person's life. d. Whether a person receives payments is contingent on the wealth and/or income of the covered person.arrow_forward24. Impact on Taxes. Lawrence has a marginal tax rate of 24%. He suddenly realizes that he neglected to include a $5,000 tax deduction. How will this oversight affect his taxes? =Lawrence paid $1200 excess tax because Lawrence neglected $ 5000 tax deduction 25. Impact on Taxes. From question 24, if Lawrence had forgotten a $5000 tax credit (instead of a $5000 tax deduction), how would his taxes be affected?arrow_forward
- Question: Solve for the equilibrium level of output in the following two scenarios: there isan income tax t=0.1, The income tax would result in the total amount of tax to be the lump sum tax and the income tax rate on income when t=0.1t=0.1 Y=−5+0.5(Y−250−0.1Y)+200+300+50' =−5+0.5(0.9Y−250)+550 =−5+0.45Y−125+550 =0.45Y−420 0.55Y=420Y=4200.55=763.636≅763.64 Please explain this solution. Where does the 0.45Y come from?arrow_forwarda tax decrease will decrease consumption a tax increase will increase consumption consumption and after-tax income are unrelated consumption varies inversely with after-tax incomes consumption varies directly with after-tax incomesarrow_forwardIf low-income families pay 10% of their income in taxes while high-income families pay 20% of their income in taxes, the tax system is which of the following? Group of answer choices Unfair Regressive Excessive Proportional Progressivearrow_forward
- The table below shows hypothectical figures of revenue and spending for the Canadian government. For simplicity, assume that all of the spending grants to other levels of government were spent in Canada on goods and services. REVENUES Personal income taxes Corporate income taxes Other income taxes. GST and excise taxes EI premiums Federal Government's Budget Plan for Fiscal Year ($billion) OUTLAYS $95 36 5 47 13 17 Transfers to persons Spending grants to other levels of government Public debt charges Direct program spending Total Outlays Projected Budget Plan Surplus Other revenues Total Revenues 213 a. The projected NTR in this budget plan is $ b. The value of NTR less government spending on goods and services (G) is $ billion. billion. $42 36 31 100 209 4arrow_forwardRefer to the tax table below. If your taxable income is $8,000, your average and marginal tax rates are Taxable Income Total Tax $ 2,000 $ 200 4,000 600 6,000 1,200 8,000 2,000 10,500 3,000 25% average rate and 25% marginal rate on additional income. 25% average rate and 40% marginal rate on additional income. 20% average rate and 30% marginal rate on additional income. 25% average rate with a marginal rate that can not be determined.arrow_forward10. Compare and contrast the different forms of fiscal policy. Expansionary Fiscal Policy Contractionary Fiscal Policy Government Spending Taxes Aggregate Demand National Debt Economic Growth Inflation Employmentarrow_forward
- Compare the tax breaks for two different income groups in the Bush 2006 tax billarrow_forwardDescribe the potential consequences of maintaining high public debt.arrow_forwardTax Bracket : 0-$20,000 = 10% $20,001-$60,000 = 15% $60,001-$100,000 = 35% _______________________________ Jessica makes $25,000. How much tax does she pay? A. $3,000 B. $3,750 C. $2,750 D. $1,200arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education