
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
A vaulter holds a 29.4-N pole in equilibrium by exerting an upward force with U→ her leading hand and a downward force D→ with her trailing hand as shown in Figure P12.12. Point C is the center of gravity of the pole. What are the magnitudes of (a) U→ and (b) D→ ?
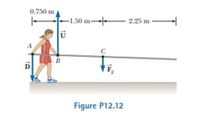
Transcribed Image Text:0.750 m
-1.50 m
2.25 m
C
Figure P12.12
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- $ 4 101 R F V A uniform, aluminum beam 9.00 m long, weighting 300 N, rests symmetrically on two supports 5.00 m apart. A boy weighing 600 N starts at point A and walks toward the right. (Figure 1) Figure < 1 of 1 % f5 5 T G B f6 Y H OD & N 7 B f8 * 4+ 00 8 M fg K ly 9 Part A How far beyond point B can the boy walk before the beam tips? VE ΑΣΦ ? 1 = Submit f10 | Request Answer Part B How far from the right end of the beam should support B be placed so that the boy can walk just to the end of the beam without causing it to tip? IVE ΑΣΦ ? 8:44 P 5/29/202 BA P 8 O 1 = Submit 99+ L alt Request Answer Pearson f11 hulu f12 ctrl [ + (6 = الالالال ins prt sc m ] pause m delete backspace ^ V home Review | Constants enter num lock T shift end 7 home ↑ A endarrow_forwardWhen you bend over, a series of large muscles, the erector spinae, pull on your spine to hold you up. Figure shows a simplified model of the spine as a rod of length L that pivots at its lower end. In this model, the center of gravity of the 320 N weight of the upper torso is at the center of the spine. The 160 N weight of the head and arms acts at the top of the spine. The erector spinae muscles are modeled as a single muscle that acts at an 12° angle to the spine. Suppose the person shown bends over to an angle of 30° from the horizontal. a. What is the tension in the erector muscle? Hint: Align your x-axis with the axis of the spine.b. A force from the pelvic girdle acts on the base of the spine. What is the component of this force in the direction of the spine? (This large force is the cause of many back injuries).arrow_forwardTwo people carry a heavy electric motor by placing it on a light board 2.10 mm long. One person lifts at one end with a force of 450 NN, and the other lifts the opposite end with a force of 570 NN. What is the weight of the motor? Express your answer in newtons. Where along the board is its center of gravity located? Express your answer in meters. Suppose the board is not light but weighs 190 NN, with its center of gravity at its center, and the two people each exert the same forces as before. What is the weight of the motor in this case? Express your answer in newtons. Where is its center of gravity located? Express your answer in meters.arrow_forward
- a. A 1200-N uniform boom of length 2.00 m is supported by a cable, as shown in the figure. The boom is pivoted at the bottom, and a 2000-N weight hands from its top. Find the tension in the cable and the components of the reaction force exerted on the boom by the floor. For the next two parts you can assume that the 2000-N weight is concentrated at the top end of the boom. b. Determine the total moment of inertia of the boom/weight system around the pivot point. c. The cable now breaks, and the boom pivots until the right end hits the floor. Determine the velocity of the right end at the instant before it hits the floor.arrow_forwardReview Conceptual Example 7 before starting this problem. A uniform plank of length 5.0 m and weight 225 N rests horizontally on two supports, with 1.1 m of the plank hanging over the right support (see the drawing). To what distance x can a person who weighs 462 N walk on the overhanging part of the plank before it just begins to tip? 41.1 maarrow_forwardA solid sphere, made of acrylic plastic with a density of 1.1 g/cm3,1.1 g/cm3, has a radius of 5.0 cm.5.0 cm. A very small "eyelet" is screwed into the surface of the sphere and a horizontal support rod is passed through the eyelet, allowing the sphere to pivot around this fixed axis, as shown in the figure. If the sphere is displaced slightly from equilibrium on the surface of Earth, determine the period ?T of its harmonic motion when it is released.arrow_forward
- Review Conceptual Example 7 before starting this problem. A uniform plank of length 5.0 m and weight 225 N rests horizontally on two supports, with 1.1 m of the plank hanging over the right support (see the drawing). To what distance x can a person who weighs 375 N walk on the overhanging part of the plank before it just begins to tip? X = i 41.1 m²arrow_forwardQuestion 4: A box (M = 140 kg) is sitting on a 6.0 m light uniform board (with negligible mass). The board is supported by two pivots one at each end. The box is sitting x = 1.6 m from the left side of the board as shown. What is the magnitude of the normal force produced by the pivot at the right end (ng) measured in Newtons? M 6.0 m- /В DBarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON