
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
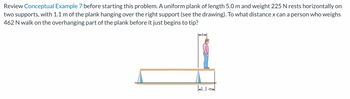
Transcribed Image Text:Review Conceptual Example 7 before starting this problem. A uniform plank of length 5.0 m and weight 225 N rests horizontally on
two supports, with 1.1 m of the plank hanging over the right support (see the drawing). To what distance x can a person who weighs
462 N walk on the overhanging part of the plank before it just begins to tip?
41.1 ma
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A beam resting on two pivots has a length of L = 6.00 m and mass M = 77.0 kg. The pivot under the left end exerts a normal force n1 on the beam, and the second pivot placed a distance ℓ = 4.00 m from the left end exerts a normal force n2. A woman of mass m = 61.5 kg steps onto the left end of the beam and begins walking to the right as in the figure below. The goal is to find the woman's position when the beam begins to tip. (a) Use the force equation of equilibrium to find the value of n2 when the beam is about to tip. (b) Using the result of part (c) and the torque equilibrium equation, with torques computed around the second pivot point, find the woman's position when the beam is about to tip.x = (c) Check the answer to part (e) by computing torques around the first pivot point.x = (d)Except for possible slight differences due to rounding, is the answer the same for F and E?arrow_forwardA uniform ladder stands on a rough floor and rests against a frictionless wall as shown in the figure. Since the floor is rough, it exerts both a normal force N1 and a frictional force f1 on the ladder. However, since the wall is frictionless, it exerts only a normal force N2 on the ladder. The ladder has a length of L = 4.4 m, a weight of WL = 53.5 N, and rests against the wall a distance d = 3.75 m above the floor. If a person with a mass of m = 90kg is standing on the ladder, determine the following. (a) the forces exerted on the ladder when the person is halfway up the ladder (Enter the magnitude only.) N1 = ? N N2 = ? N f1 = ? N (b) the forces exerted on the ladder when the person is three-fourths of the way up the ladder (Enter the magnitude only.) N1 = ? N N2 = ? N f1 = ? Narrow_forwardA uniform 10.0 m ladder of weight WL=375 N leans against a frictionless wall. There is a force of static friction between the floor and the bottom of the ladder. A person weighing Wp stands 7.4 m between the bottom of the ladder. Draw a free body diagram for the ladder. Draw a torque diagram for the ladder. Determine the force that the wall exerts on the top of the ladder. Determine the force of static friction exerted on the ladder by the floor.arrow_forward
- A beam resting on two pivots has a length of L = 6.00 m and mass M = 87.0 kg. The pivot under the left end exerts a normal force n₁ on the beam, and the second pivot placed a distance = 4.00 m from the left end exerts a normal force n₂. A woman of mass m = 52.0 kg steps onto the left end of the beam and begins walking to the right as in the figure below. The goal is to find the woman's position when the beam begins to tip. -L- m M (a) Sketch a free-body diagram, labeling the gravitational and normal forces acting on the beam and placing the woman x meters to the right of the first pivot, which is the origin. (Submit a file with a maximum size of 1 MB.) Choose File No file chosen (b) Where is the woman when the normal force n₁ is the greatest? x = L m (c) What is n, when the beam is about to tip? N (d) Use the force equation of equilibrium to find the value of n₂ when the beam is about to tip. N (e) Using the result of part (c) and the torque equilibrium equation, with torques computed…arrow_forwardA hiker, who weighs 659 N, is strolling through the woods and crosses a small horizontal bridge. The bridge is uniform, weighs 4280 N, and rests on two concrete supports, one on each end. He stops 1/5 of the way along the bridge. What is the magnitude of the force that a concrete support exerts on the bridge (a) at the near end and (b) at the far end?arrow_forwardThe figure shows a 4.20-kg, 1.80-m-long rod hinged to a vertical wall and supported by a thin wire. The wire and rod each make angles of 45° with the vertical. When a 10.0-kg block is suspended from the midpoint of the rod, the tension T in the supporting wire is 49.3 N. The wire will break when the tension exceeds 75.0 N. 45° 45° T 10kg Tipler & Mosca, Physics for Scientists and Engineers, 6e © 2008 W.H. Freeman and Company What is the maximum distance dmax from the hinge from which the block can be suspended? dmax = marrow_forward
- Don't Use Chat GPT Will Upvote And Give Handwritten Solution Pleasearrow_forwardA beam resting on two pivots has a length of L = 6.00 m and mass M = 77.0 kg. The pivot under the left end exerts a normal force n₁ on the beam, and the second pivot placed a distance = 4.00 m from the left end exerts a normal force n₂. A woman of mass m = 61.0 kg steps onto the left end of the beam and begins walking to the right as in the figure below. The goal is to find the woman's position when the beam begins to tip. m L M (a) Sketch a free-body diagram, labeling the gravitational and normal forces acting on the beam and placing the woman x meters to the right of the first pivot, which is the origin. (Submit a file with a maximum size of 1 MB.) Choose File No file chosen This answer has not been graded yet. (b) Where is the woman when the normal force ₁ is the greatest? X = m (c) What is n₁ when the beam is about to tip? N (d) Use the force equation of equilibrium to find the value of n₂ when the beam is about to tip. N (e) Using the result of part (c) and the torque equilibrium…arrow_forward+ A uniform ladder stands on a rough floor and rests against a frictionless wall as shown in the figure. Since the floor is rough, it exerts both a normal force N, and a frictional forcef, on the ladder. However, since the wall is frictionless, it exerts only a normal force N₂ on the ladder. The ladder has a length of L = 4.2 m, a weight of W, = 66.5 N, and rests against the wall a distance d = 3.75 m above the floor. If a person with a mass of m= 90 kg is standing on the ladder, determine the following. (a) the forces exerted on the ladder when the person is halfway up the ladder (Enter the magnitude only.) N₂ N₂- 4- (b) the forces exerted on the ladder when the person is three-fourths of the way up the ladder (Enter the magnitude only.) N₂ N₂ Additional Materialsarrow_forward
- You're carrying a 3.4-m-long, 24 kg pole to a construction site when you decide to stop for a rest. You place one end of the pole on a fence post and hold the other end of the pole 35 cm from its tip. How much force must you exert to keep the pole motionless in a horizontal position?arrow_forwardA 2.99 m long ladder that has a mass of 5.84 kg leans against a frictionless wall. The coefficient of static friction between the ladder and the floor is 0.589. What is the maximum angle that the ladder can make with the floor without slipping if a 87.6 kg person stands half-way up the ladder? θ = °arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON