
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
An advanced spatial disorientation trainer is programmed to only rotate and translate in the horizontal plane. The pilot’s location is defined by the relationships r= 8(1 – e-t) and where r, 0, and t are expressed in feet, radians, and seconds, respectively. Determine the radial and transverse components of the force exerted on the 175-lb pilot at t= 3 s.
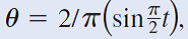
Transcribed Image Text:0 = 2/T(sint).
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 6 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Body U with mass 5m is stacked on the top body W with mass m, and released. The bodies are in contact along the frictionless interface at 45° to the vertical. The body U is in contact with the frictionless vertical wall. Body W lies on the floor with coefficient of friction u. Relevant dimensions are shown in the figure. Express the results in terms of given quantities: m, g, h and µ (except when µ is given numerically). You need not evaluate sin 45° = cos 45° = 2/2. h U: 5m C 45 D W: m 3harrow_forwardEXERCISE 2.53 Collar C is pushed along the guide bar defined by y= 2(1-0.25x²), where x and y have units of meters. The angular speed of arm AB that actuates the motion is the constant value = 20 rad/s, so = ct. Determine the forces exerted on the collar by arm AB and the guide bar at x = 1 m. The mass of the collar is 2 kg, and gravitational effects are ignorable. (Hint: use Cartesian and polar coordinates to solve the problem.)arrow_forwardQ24. The buoyancy force on the 580-kg balloon is F = 6 kN, and the air force acting {C₁.ti-C₂. √t j N, when t is time in on the balloon is Fair seconds, constants C₁ = 24 and C₂ = 240. If the balloon starts from rest, determine its speed after 28 seconds. Neglect the size of the balloon but don't neglect its weight. Please pay attention: the numbers may change since they are randomized. Your answer must include 2 places after the decimal point, and proper SI unit. Take g = 9.81 m/s². Fa air Your Answer: Answer = F = 6 kN unitsarrow_forward
- 1. (bold type indicates a vector) An object of mass m = 10 kg may rotate in a vertical plane about the fixed point P under the action of gravity. The distance d from the point P to the center of mass C is d = 0.5 m. The moment of inertia Ie about the center of mass C is unknown. The object starts at rest in the position shown and is then released. At the instant of release the acceleration of the center of mass is measured to be a, = (-5 m/sec²)j (i.e., downward). Use the given information to determine the moment of inertià I, about the center of mass. Use g = 10 m/sec?. gravity w go P (f ixed)arrow_forwardDon't use chatgpt. I need handwritten solution with free body diagram.arrow_forward|v| = A motor is lifting a crate with mass m = 17kg. The motor provides a force that can be described by the function F = 142√t N. If starting from rest, determine the magnitude of velocity of the crate at time t = 3.2s. m m S F O UBC Engineeringarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY