
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
thumb_up100%
You fire a bullet into a 2 kg wooden block that is hanging at the bottom of a pendulum. When the bullet strikes the block, the pendulum swings upward. The bullet has a mass of 0.02 kg and strikes the block with a speed of 300 m/s.
a. What is the speed of the block and bullet when they first start moving together?
b. What is the maximum height reached by the pendulum?
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
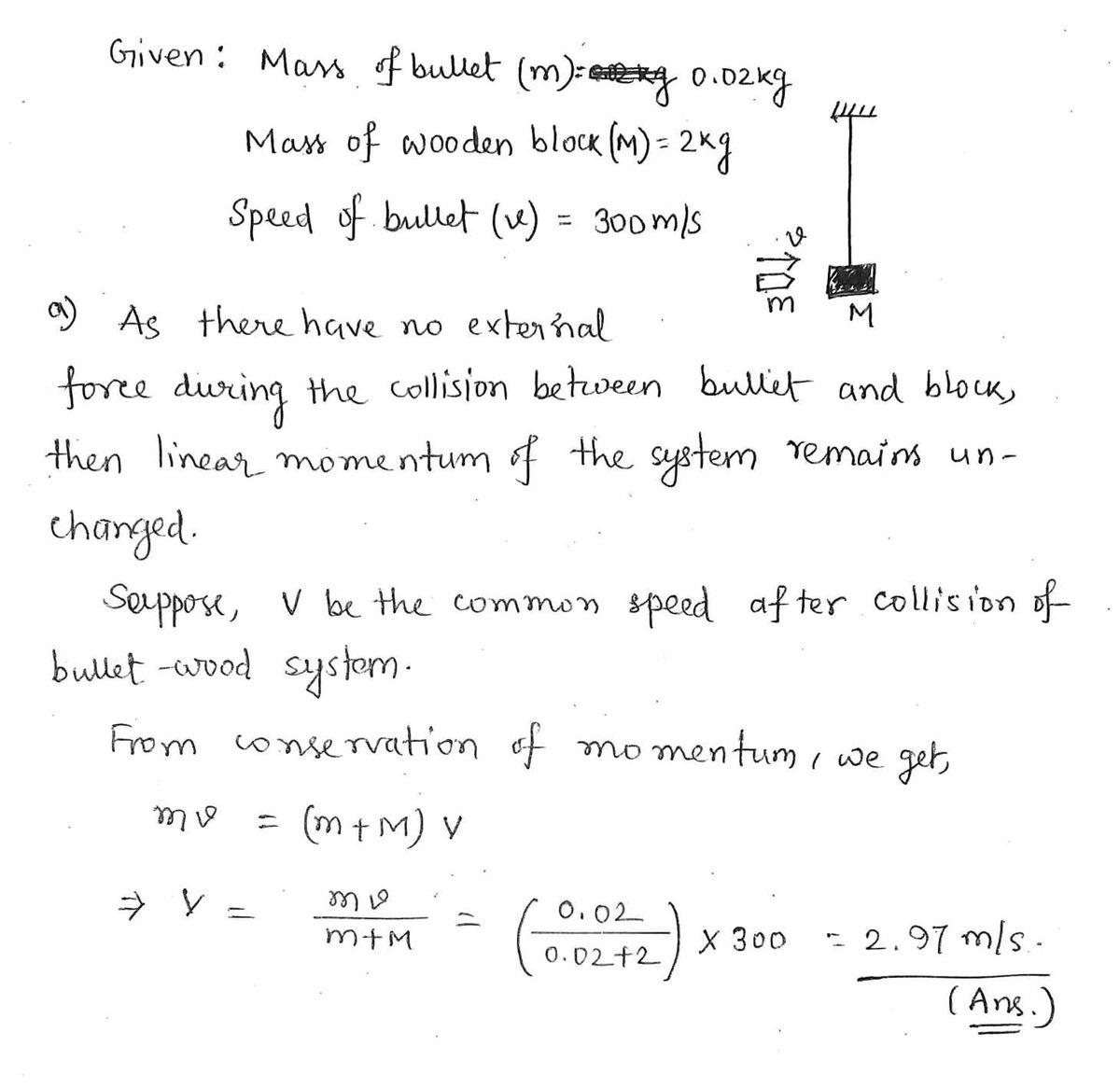
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- a. A 10.0 kg object has an initial velocity of (5.0i + 3.0j) m/s. What is its kinetic energy at this time? KE = ½ mv² where v² = V.Varrow_forwardRonaldo is playing outside and shoots a ball of mass 2 kg horizontally with a speed of 8.0 m/s toward a green cart. The mass of the green cart is 15 kg and it rolls at a speed of 1.0 m/s along a horizontal path with no friction. The ball gets stuck in the card. What is the velocity of the cart after the ball strikes it? What are the initial and final kinetic energies of the system? Is the energy conserved in this collision process? What type of collision process is it?arrow_forward1. Which of the following is NOT an example of potential energy? a. A running woman b. An incredibly compressed spring G. A tightly stretched rubber band d. An apple dangling off a branch 2. A ball drops from a height h. What more do we need to calculate initial potential energy? a. Elasticity of the Ball b. Mass c. Final Velocity d. Horizontal Displacementarrow_forward
- A 2.0-kg pistol fires a 0.90-g bullet with a muzzle speed of 1000 m/s. The bullet then strikes a 10-kg wooden block resting on a horizontal frictionless surface. The block and the embedded bullet then slide across the surface a. What is the kinetic energy of the bullet as it travels toward the block? b. What is the speed of the "bullet + block" system immediately after the bullet is embedded in the block?arrow_forwardi just need help with C and D A big ship with a mass of 5.95 x 10 7 kg has a speed of 11.0 m/s at some instant. A. What is the ship’s kinetic energy? B. How much work is required to stop it? C. How is work related to the mechanical energy? D. What is the magnitude of the constant force required to stop it as it undergoes a displacement of 2.75 km?arrow_forwardAn object is initially held at rest from a height of 4 m. The object is then released. A. Use conservation of energy to find the velocity right before it hits the ground B. Use the position equation to find the time it takes to reach the ground.arrow_forward
- 5. A 60 kg circus performer is swinging from a trapeze bar.A: She is 10 m off the ground with a speed v1. The spring-board platform below her is atits equilibrium length.B: She lets go of the trapeze bar and lands on th spring-board platform, which compresseswhen she lands on it. When she is stationary, she is 2 m off the ground and the springis maximally compressed.C: The spring-board extends and launches her back into the air. As soon as the spring istotally relaxed again, the performer is 3 m off the ground and has a speed v2.D: The performer lands on a platform 10 m above the floor, and she stands stationary. a. Her initial speed v1 = 10 m/s. What is her total energy at point A? b. Between points A and B, assume none of her energy is lost to heat or friction. Whenshe is stationary on the compressed platform at B, how much energy is stored in thespring-board platform? c. When the spring-board platform is fully released at point C, what must her speed v2 be?arrow_forwardA diver of mass 68 kg stands on a diving board 5.0 m above a pool. At the moment of the jump, the diving board transfers its 3400 J of energy to the diver, who leaves the board at an angle of 35°. a. What is the (total) speed of the diver just as they leave the diving board? b. What is the maximum height (relative to the surface of the water) of the diver? c. How long does it take for the diver to reach the surface of the water?arrow_forwardConsider the table. Vehicle 1 Vehicle 2 Vehicle 3 Vehicle 4 Mass (kg) 1000 2000 1000 2000 Velocity (m/s) 20 20 40 40 Kinetic energy (kJ) 200 400 800 1600 The table shows data collected for some vehicles on the road. What conclusion can be drawn about the relationship between mass, velocity, and kinetic energy? Answer Choices: a. If only the mass of the vehicle doubles, the kinetic energy increases by a factor of four. b. If both the mass and the velocity of the vehicle double, the kinetic energy will increase by a factor of eight. c. If only the velocity of the vehicle doubles, the kinetic energy will double. d. If both the mass and the velocity of the vehicle double, the kinetic energy will increase by a factor of four.arrow_forward
- I need help with #1arrow_forward1. A block of mass m is pushed against (but not attached to) a spring with stiffness k so that the spring is compressed a distance Ar. When released, the block slides across the frictionless surface of a shelf a height h above the floor, the then falls to the floor. a. What is the speed of the block at the moment it leaves the shelf? V2 = b. What is the speed of the block at the moment just before it hits the ground? Vr =arrow_forwardI need help with these questions and I need an explanation Is the answer for 8: A. -20 m/s/s B. 3.33 m/s/s C. -6.7 m/s/s D. 20 m/s/s Is the answer for 6: A. 8 m/s B. 40 m/s C. 20 m/sarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON