
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations and Connections
1st Edition
ISBN: 9781133939146
Author: Katz, Debora M.
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
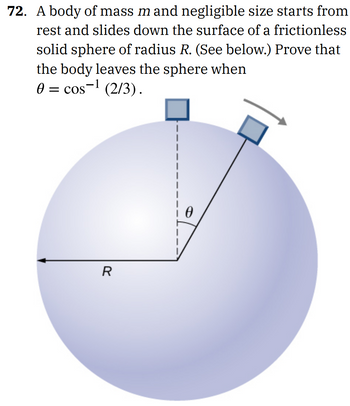
Transcribed Image Text:**Problem 72: Sliding Body on a Sphere**
A body of mass \( m \) and negligible size starts from rest and slides down the surface of a frictionless solid sphere of radius \( R \). Prove that the body leaves the sphere when \( \theta = \cos^{-1}(2/3) \).
**Diagram Explanation:**
- The diagram shows a sphere with radius \( R \).
- A small block is positioned at the top of the sphere and then depicted sliding down its surface.
- The angle \( \theta \) is measured from the vertical centerline to the position of the block along the sphere's surface.
- The point at which the block leaves the sphere is indicated by an arrow moving tangentially away from the sphere.
This scenario is analyzed to find the angle \( \theta \) at which the normal force between the block and the sphere becomes zero. At this angle, the body loses contact and leaves the sphere’s surface.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Consider the Earth and the Moon as a two-particle system. a. Find an expression for the gravitational field g of this two-particle system as a function of the distance r from the center of the Earth. (Do not worry about points inside either the Earth or the Moon.) b. Plot the scalar component of g as a function of distance from the center of the Earth.arrow_forwardTo give a pet hamster exercise, some people put the hamster in a ventilated ball andallow it roam around the house(Fig. P13.66). When a hamsteris in such a ball, it can cross atypical room in a few minutes.Estimate the total kinetic energyin the ball-hamster system. FIGURE P13.66 Problems 66 and 67arrow_forwardCrall and Whipple design a loop-the-loop track for a small toy car. The car starts at height yi above the bottom of the loop, goes through the loop of radius R, and then travels along a flat, horizontal track before coming to rest. Rolling friction between the horizontal track and the car is significant, but it is negligible along the rest of the track. Assume Crall and Whipple release the car from the minimum height yi (found in Problem 56). If the coefficient of rolling friction between the car and the horizontal track is 0.30 and the radius of the loop is 0.45 m, how far does the car travel along the horizontal track from the base of the loop before coming to rest? FIGURE P9.56 Problems 56 and 57.arrow_forward
- Three billiard balls, the two-ball, the four-ball, and the eight-ball, are arranged on a pool table as shown in Figure P7.26. Given the coordinate system shown and that the mass of each ball is 0.150 kg, determine the gravitational force on the eight-ball due to the other two balls.arrow_forwardSaturns ring system forms a relatively thin, circular disk in the equatorial plane of the planet. The inner radius of the ring system is approximately 92,000 km from the center of the planet, and the outer edge is about 137,000 km from the center of the planet. The mass of Saturn itself is 5.68 1026 kg. a. What is the period of a particle in the outer edge compared with the period of a particle in the inner edge? b. How long does it take a particle in the inner edge to move once around Saturn? c. While this inner-edge particle is completing one orbit abound Saturn, how far around Saturn does a particle on the outer edge move?arrow_forwardA system consists of three particles, each of mass 5.00 g, located at the corners of an equilateral triangle with sides of 30.0 cm. (a) Calculate the gravitational potential energy of the system. (b) Assume the particles are released simultaneously. Describe the subsequent motion of each. Will any collisions take place? Explain.arrow_forward
- Chanur Part 11 of 11 - Analyze Now Chandra and Darcel decide to try a problem. Suppose that the height of the incline is h = 15.3 m. Find the speed at the bottom for each of the following objects. X Your response is within 10% of the correct value. This may be due to roundoff error, or you could have a digit accuracy to minimize roundoff error. m/s m/s m/s m/s solid sphere spherical shell hoop cylinder In a race, which object would win? O solid sphere O spherical shell O hoop O cylinder O tie Submit Skip (you cannot come back) H t of MR², it is poss Search HHarrow_forwardP1 A pendulum of length L with a bob of mass m is released from the vertical position without initial speed. Under the suspension point, a nail is fixed at a distance of L – x. The thread of the pendulum gets stuck in the nail during its motion so that the bob starts to move on a circular path of radius x after it has reached its lowest position. L m a) At most how large should x be if the bob executes a complete circle? b) If x = L/3, calculate the tension in the thread when the bob reaches its highest po- sition during the motion after the thread gets stuck in the nail.arrow_forwardExample questions Sad ball Наpрy ball 1. Students are given two spherical balls made of different materials, but of identical mass and diameter to experiment with. Each ball is dropped from an initial height, ho. The "sad ball" comes to rest without visibly bouncing when it strikes the tabletop. The "happy ball" bounces up to a final height h, where h < ho- A fellow student wants to use one of the balls in a carnival game where cups are knocked over by a thrown ball. Which ball should they use, happy or sad? In a clear, coherent, paragraph-length response that may also contain figures and/or equations, explain what physics principles explain why the happy ball bounces higher off of the tabletop and explain which ball makes the better choice as a projectile in the carnival game. A Answer the Question Basic Physics Cite Information Draw it all togetherarrow_forward
- 60 Look at the diagram. a i Calculate the minimum speed v the ball must have in order to make it to position B. ii What speed will the mass have at B? b Given that v= 12.0 ms¹, calculate the speed at A and B. 4.0 m A 2.0 m Barrow_forwardPlease answer Question 8 parts b-darrow_forwardA planet is observed to be in an elliptical orbit around the sun as shown below. Which of the following quantities, if remain constant over the time it takes to complete one orbit? any, planet Sun (a) force exerted by the sun on the planet F (b) momentum p (c) angular momentum L (d) orbital speed v (e) kinetic energy K (f) potential energy U (g) total energy E Explain each of your choices and state any assumptions you made.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781285737027
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning