
Use your knowledge of the velocities and changes in velocities to construct momentum vectors and change in momentum vectors for the blocks. Also draw a final momentum vector for each block corresponding to the same small time interval as in part C. Show the correct relative magnitudes.
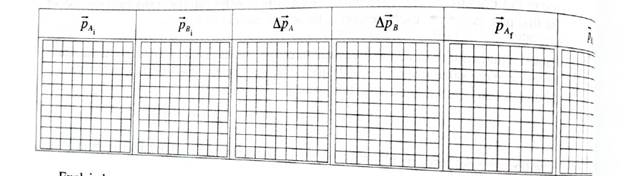
Explain how you determined these vectors.
How would
Learn your wayIncludes step-by-step video

Chapter 3 Solutions
Tutorials in Introductory Physics
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
University Physics Volume 1
University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern Physics
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
- Part A The two spheres A and B each have a mass of 400 g. The spheres are fixed to the horizontal rods as shown in (Figure 1) and their initial velocity is 2 m/s. The mass of the supporting frame is negligible and it is free to rotate. Neglect the size of the spheres. If a couple moment of M = 0.9 N m is applied to the frame, determine the speed of the spheres in 3 s. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. Figure M -0.3 m -0.3 m- B 1 of 1 HÅ ? v= Value Units Submit Request Answer < Return to Assignment Provide Feedbackarrow_forwardPart C Also, find the vertical reactions at the rollers B. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate NB = 4 Value Units ?arrow_forward1. What are the equations for linear momentump and kinetic energy K? Please define the variables. 2. Please define concisely and in your own words the concept of conservation. Describe conservation of momentum and kinetic energy. 3. Briefly describe the difference between elastic and inelastic collisions and give an example of each. Describe these collisions in terms of the kinetic energy and momentum. 4. A moving object collides with and sticks to a stationary object. Do the combined objects move slower, faster or at the same speed as the original moving object? 5. What is the expected value of the ratio of the final and initial momenta, pf/p; ?arrow_forward
- The block's displacement (or change in position) in reference frame R during the period AL * is either upward, downward, or equal to zero? Explain. (Use the velocity arrow from section c.i. to guide your response.) Does the block have an upward, downward, or no net force? Explain. Use the acceleration arrow from section c.i. to help you answer this question: Is the net force doing more work on the block than it is taking off? Explain. Based on your responses to the preceding two questions, how would you answer this question? Test to see whether you've answered section c.iii correctly in terms of net force work done on the block.arrow_forwardProblems 1. A particle of mass m has an initial momentum vector p, = mv, as shown. After being given a sharp blow, the particle has a final momentum vector p, = mv,. Draw on the figure a vector representing the impulse J that must have been delivered to the particle by the sharp blow. Explain your reasoning. 2° mv 1 mv2arrow_forwarda.) If an object is already moving and you applied another force parallel to it and with the same direction, does this mean that another counter force will be generated? Explain. b.) Considering question (a), what if you applied a force lower than the force of momentum (and gravity, etc.) on the object, will it generate a counter force? Explain. c.) On our activity, pushing the object at rest generates a counter force. How is this?arrow_forward
- Two objects have a perfectly elastic collision, as exactly illustrated in the diagram below. The first object (red ball) comes in at some initial speed and strikes the second one (blue ball), which was initially stationary in our reference frame. What is the speed of the blue ball after the collision? Write your answer as a fraction of v1. In other words, if you get v2 = 0.20v1, just enter 0.20. All we know is the proportionality of the masses and the relative speed of the first ball before and after the collision.arrow_forwardConsider the discrete-time system given below and answer the following questions. y[n] = 0.6x[n] + 0.35x[n-3] + 0.05x[n-5] a. Is this an IIR or FIR system, explain b. What is the order of the system c. Find the impulse response h[n] of the given systemarrow_forwardReview I Constants Three objects A, B, and C are moving as shown in the figure below (Figure 1). Assume that vA = 12.0 m/s, VB = 9.0 m/s, and vc = 3.2 m/s. Part E %3D Find the x-component of the net momentum of the particles if we define the system to consist of all three objects. Express your answer in kilogram meters per second. ? Px = kg · m/s Submit Request Answer Part F Figure 1 of 1 Find the y-component of the net momentum of the particles if we define the system to consist of all three objects. Express your answer in kilogram meters per second. A ? 5.0 kg B 60° 6.0 kg 10.0 kg Ру kg m/s %3D Submit Request Answerarrow_forward
- Do as instructed:a. Simulate m1 = m2 with their respective velocities v1 = v2. Take a screenshot of the simulation. Explain the collision, reaction, and motion of the two masses.Here is the direct link to the simulator - https://ophysics.com/e2.htmlarrow_forwardPart A A package of mass m is released from rest at a warehouse loading dock and slides down a 3.0-m-high frictionless chute to a waiting truck. Unfortunately, the truck driver went on a break without having removed the previous package, of mass 2m, from the bottom of the chute as shown in (Figure 1) Suppose the packages stick together. What is their common speed after the collision? Express your answer in meters per second. ΑΣφ ? V = m/s Submit Request Answer redo Part B Suppose the collision between the packages is elastic. To what height does the package of mass m rebound? Express your answer in centimeters. ? h = cm Submit Request Answer Provide Feedback Next > Figure 1 of 1 3.0 m 2m P Pearson Copyright © 2022 Pearson Education Inc. All rights reserved. I Terms of Use Privacy Policy I Permissions Contact Usarrow_forwardA 750 kg car traveling at 10 m/s strikes a second car at rest. The two stick together and move off with a speed of 7.5 m/s. What is the mass of the second car? please show your work, including diagrams, algebraic equations, and enough written explanations that somebody who is not familiar with the problem could understand what you are doing.arrow_forward
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON





