
Concept explainers
a)
To determine: The daily production plan which would minimize the cost of meeting the daily demand of the company.
Introduction: In linear programming, the unbounded solution would occur when the objective function is infinite. If no solution satisfied the constraints, then it is said to be an unfeasible solution.
a)
Explanation of Solution
Determine the daily production plan which would minimize the cost of meeting the daily demand of the company using solver:
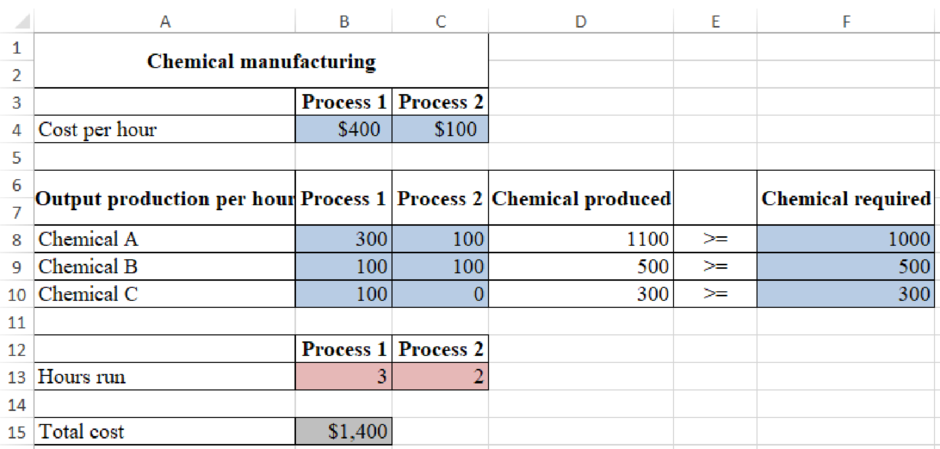
Figure (1)
Formulae to determine the total cost:
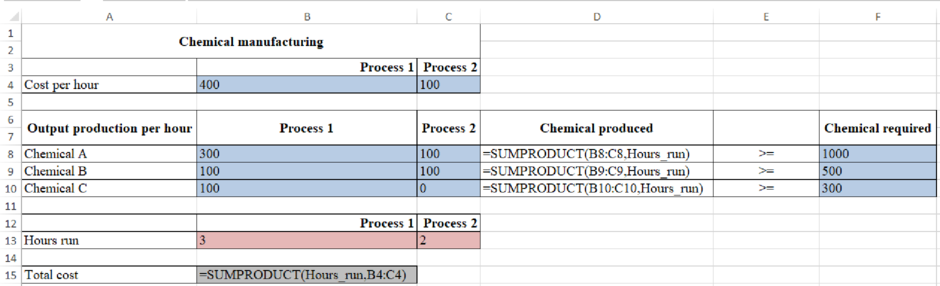
Figure (2)
Solver parameters are given as follows:
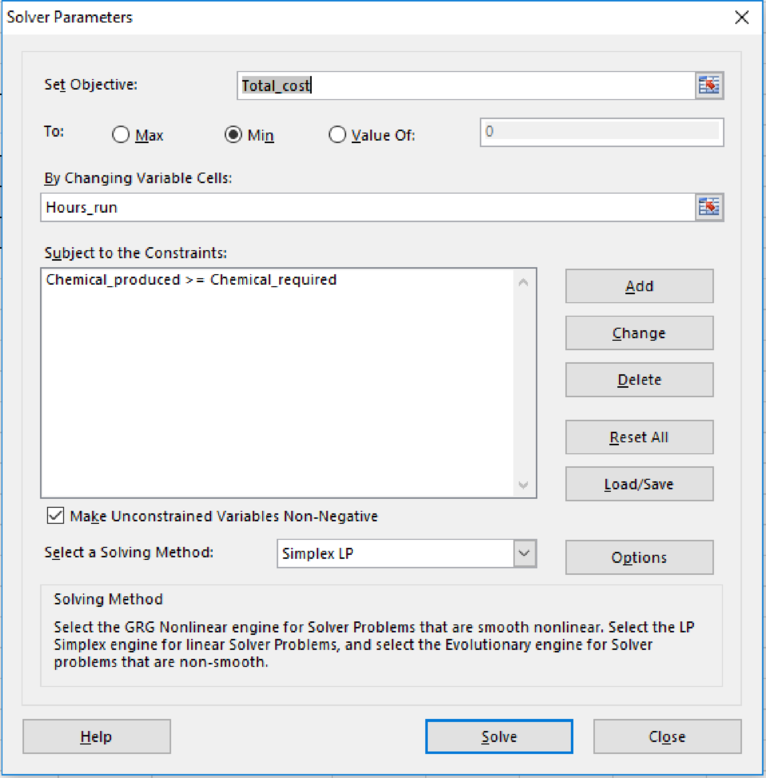
Figure (3)
b)
To draw: The daily production plan which would minimize the cost of meeting the daily demand of the company graphically.
Introduction: In linear programming, the unbounded solution would occur when the objective function is infinite. If no solution satisfied the constraints, then it is said to be an unfeasible solution.
b)
Explanation of Solution
Determine the daily production plan which would minimize the cost of meeting the daily demand of the company:
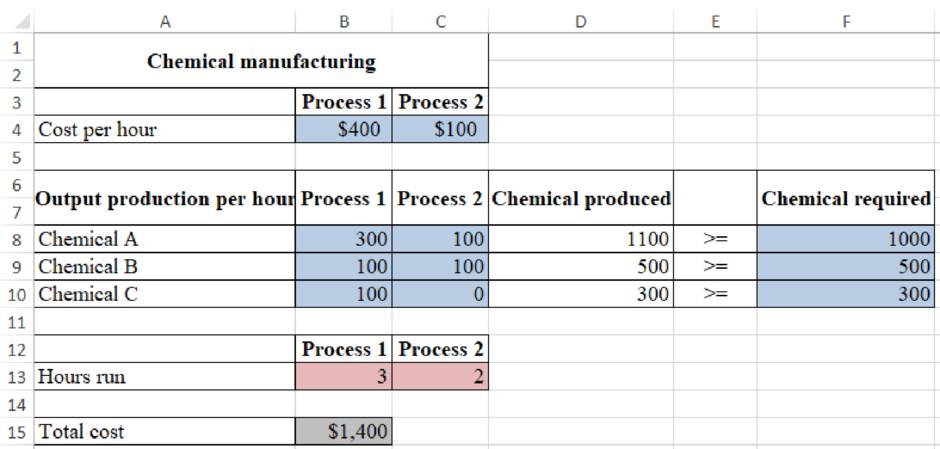
Figure (1)
Draw the graph:
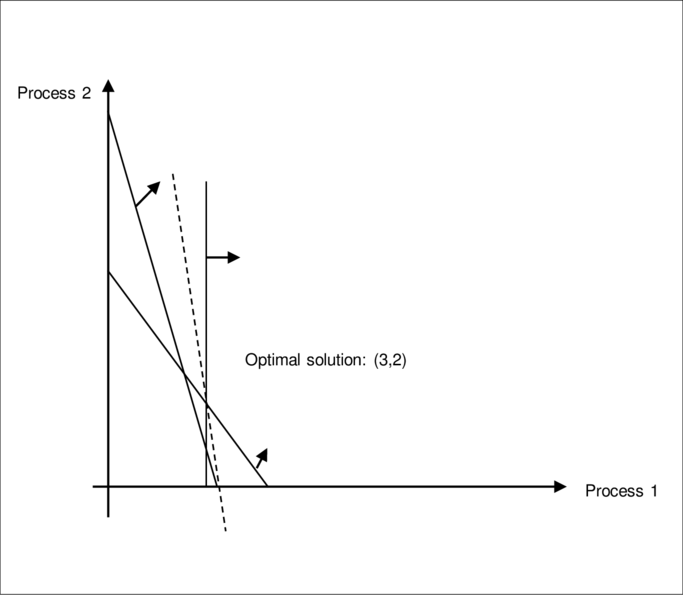
Figure (4)
c)
To determine: The increase in the total cost before the change in the decision variable.
Introduction: In linear programming, the unbounded solution would occur when the objective function is infinite. If no solution satisfied the constraints, then it is said to be an unfeasible solution.
c)
Explanation of Solution
Determine the daily production plan which would minimize the cost of meeting the daily demand of the company:
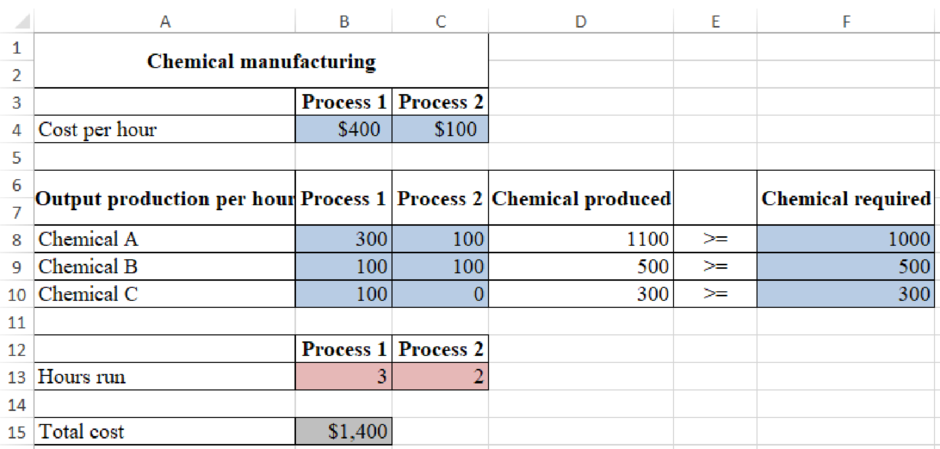
Figure (1)
Solver table:
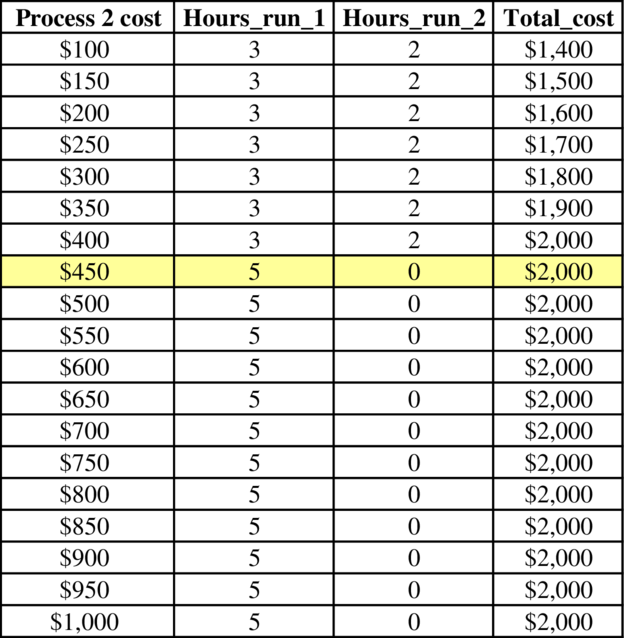
Figure (5)
In figure (1), the cost of process 2 should be increased from $100 to $1,000 to determine the total cost shown in above solver table (figure (5)).
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
Practical Management Science
 Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage,
Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage,
