
Concept explainers
Five loops of copper wire of same gauge (cross−sectional area). Loops 1−4 are identical; loop
5 has the same height as the others but is longer. At the instant shown, all the loops are moving at the same speed in the directions indicated.
There is a uniform magnetic field pointing out of the page in region I; in region II there is no magnetic field. Ignore any interactions between the loops.
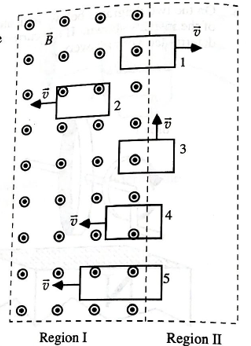
b. Rank the magnitudes of the emfs around the loops. Explain your reasoning.
Learn your wayIncludes step-by-step video

Chapter 22 Solutions
Tutorials in Introductory Physics
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
The Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals (2nd Edition)
Essential University Physics: Volume 2 (3rd Edition)
Applied Physics (11th Edition)
College Physics (10th Edition)
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern Physics
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
- The figure shows a circuit with an area of 0.060 m² containing a R=1.0 2 and a C = 250 μF uncharged capacitor. (Figure 1) Pointing into the plane of the circuit is a uniform magnetic field 0.25 T. In 0.010s the magnetic field reverses direction at a constant rate to become 0.25 T pointing out of the plane. Part A What maximum charge (sign and magnitude) accumulates on the upper plate of the capacitor in the diagram? Express your answer using two significant figures. V—| ΑΣΦ Q = 3 ? mCarrow_forwardFigure 3 shows a straight wire carrying a current in upwarddirection. The wire is placed near a wire loop. For each case described below, answer the following questions:a. What is the direction of the magnetic flux through theloop?b. Is the magnitude of the flux through the loop increasing ordecreasing with time?c. What is the direction of the magnetic field produced by theinduced current in the loop?d. What is the direction of the current induced in the loop?1. Case 1: The current is increasing.2. Case 2: The current is decreasing.3. Case 3: The current is constant but the loop is being pulledaway from the straight wire.arrow_forwarde br Direction: Solve as directed. Write your answers on the box provided. Find the unknown values of voltage and current in each resistor as shown in the given circuit diagram. 1. The magnetic field of a certain region has a magnitude of 1.50 T, and its direction is along the positive x-axis, as shown in the figure below. 30 сm b. 40 cm 30 сm a. What is the flux across the surface abcd? a b. What is the flux across the surface befc? 50 cm c. What is the flux across the surface aefd? С. d. d. What is the flux across the surface in the shaded volume?arrow_forward
- The circuit shown below is in a uniform magnetic field that is into the page. The current in the circuit is (1.2x10^-1) A. At what rate is the magnitude of the magnetic field changing? Use T/s for your answer. Note: Use a positive sign if the rate is increasing or a negative sign if the rate is decreasing. 12 cm ↑ 12 cm 100 4Varrow_forwardIn the figure (Figure 1) the top wire is 1.2 mm -diameter copper wire and is suspended in air due to the two magnetic forces from the bottom two wires. The current flow through the two bottom wires is 79 A in each. Figure 1 of 1 N -3.8 cm -3.8 cm -3.8 cm Part A Calculate the required current flow in the suspended wire. Express your answer using two significant figures. —| ΑΣΦ ? Icu = Submit Provide Feedback Request Answer A Next >arrow_forwardThe diagram below represents an electron being fired at right angles towards a uniform magnetic field acting out of the page. a Copy the diagram and mark on it the continued path you would expect the electron to follow. b Which factors would alter the path radius of the electron as it travels? A stream of electrons travels in a straight line through a uniform magnetic field and between a pair of charged parallel plates, as shown in the diagram. 3.5 cm 500 V Calculate the: a magnitude of the electric field strength between the plates b speed of the electrons, given that the magnetic field is of strength 1.5 x 10 T.arrow_forward
- In a physics laboratory experiment, a coil with 230 turns enclosing an area of 10 cm? is rotated in a time interval of 0.050 s from a position where its plane is perpendicular to the earth's magnetic field to a position where its plane is parallel to the field. The earth's magnetic field at the lab location is 6.0x10-5 T. Part A What is the magnetic flux through each turn of the coil before it is rotated? Express your answer with the appropriate units. ? Value Units Part B What is the magnetic flux through each turn of the coil after it is rotated? Express your answer with the appropriate units. ? 2 = Value Unitsarrow_forwardA long pair of insulated wires serves to conduct 33.0 A of dc current to and from an instrument. If the wires are of negligible diameter but are 2.8 mm apart, what is the magnetic field 10.0 cm from their midpoint, in their plane (see the figure(Eigure 1))? Express your answer using two significant figures. ? Buet = T Submit Request Answer Part B Figure < 1 of 1 Compare to the magnetic field of the Earth (5.0 × 10-5 T). Express your answer using two significant figures. ? 10.0 cm Buet/ BEarth = Submit Request Answer 2.8 mmarrow_forwardB INSTRUCTION Solve the following problems. ANSWER ONLY TWO OUT OF THREE QUESTIONS. Show your complete solutions. NOT FOLLOWING OF INSTRUCTIONS will be a deduction of 10 POINTS from the total score. 1.A proton enters a magnetic tield of flux density 1.5 Wb/m² with a vetocity of 2.0 x 107 m/s at an angle of 30° with the field. Compute the force on the proton. 2.A steady current of 2 A in a coil of 400 turns causes a flux of 104 wb to link (pass through) the loops of the coil. Compute the average back emf induced in the coit it the current is stopped in 0.08 seconds. 3. A coil of 50 loops is pulled in 0.020 seconds from between the poles of a magnet, where its area intercepts a flux of 3.1 x 10-4 Wb, to a place where the intercepted flux is 0.10 x 10-4 Wb. Determine the average emf induced.arrow_forward
- The element niobium, which is a metal, is a superconductor (ie, no electrical resistance) at temperatures below 9 K. However, the superconductivity is destroyed if the magnetic field at the surface of the metal reaches or exceeds 0.10 T. Part A What is the maximum current in a straight, 3.40-mm-diameter superconducting niobium wire? Express your answer with the appropriate units. Value submit Units Request Answer ?arrow_forwarda) Observe Figure 1a below. If a current, I, flows in an infinitely long conducting wire, the magnetic flux density, B, is defined as a function of distance r, from the wire. It is assumed that r is much greater than the radius of the wire. Derive the expression for the flux density, B, at a point r from an infinitesimally thin wire that is infinitely long. Show all of your workings. Electric current В Magnetic field Figure 1a.arrow_forwardA circular loop of wire with radius 0.0430 m and resistance 0.152 N is in a region of spatially uniform magnetic field, as shown in the following figure (Figure 1). The magnetic field is directed out of the plane of the figure. The magnetic field has an initial value of 8.48 T and is decreasing at a rate of -0.622 T/s. Part A Part B What is the rate at which electrical energy is being dissipated by the resistance of the loop? Express your answer with the appropriate units. HA ? P = Value Units Submit Request Answerarrow_forward
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON





