
Tutorials in Introductory Physics
1st Edition
ISBN: 9780130970695
Author: Peter S. Shaffer, Lillian C. McDermott
Publisher: Addison Wesley
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 12.1, Problem 4cT
A syringe is used to remove some water from the left side of the U-tube. The water level on the left side is seen to be lowered, butthe water level on the right does not change.
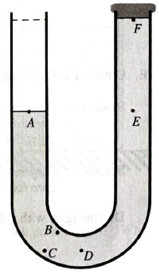
Consider the following student dialogue:
| Student 1: | “The pressure at point F must now be higher than atmospheric pressure because the water there is being pushed up against the stopper.” |
| Student 2: | “I think that the pressure at point E must be the same as at point A because they are at the same level. These points are both at atmospheric pressure. So the pressure at point F is lower than atmospheric pressure because know that pressure gets less as you go up.” |
| Student 3: | “But water is more dense than air so the pressure at F cannot be less than atmospheric pressure.” |
With which student(s), if any, do you agree?
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
please answer the following
A bicycle tire pump has a piston with area 0.31 in2. If a person exerts a force of 18 lb on the piston while inflating a tire, what pressure does this produce on the air in the pump?
A large truck tire is inflated to a gauge pressure of 86 psi. The total area of one sidewall of the tire is 1,220 in2. What is the net outward force (in lb) on the sidewall because of the air pressure? (Enter the magnitude.)
A pitot tube (the figure) is used to determine the airspeed of an airplane. It consists of an
outer tube with a number of small holes B (four are shown) that allow air into the tube; that
tube is connected to one arm of a U-tube. The other arm of the U-tube is connected to hole A
at the front end of the device, which points in the direction the plane is headed. At A the air
becomes stagnant so that và = 0. At B, however, the speed of the air presumably equals the
airspeed B of the plane.
A pitot tube on a high-altitude aircraft measures a differential pressure of 240 Pa. What is
the aircraft's airspeed if the density of the air is 0.0330 kg/m³?
Number
Pair-
Hole A
B
B
Units
Liquid
Air
h
A pitot tube (the figure) is used to determine the airspeed of an airplane. It consists of an outer tube with a number of small holes B (four are shown) that allow air into the tube; that tube is connected to one arm of a U-tube. The other arm of the U-tube is connected to hole A at the front end of the device, which points in the direction the plane is headed. At A the air becomes stagnant so that vA = 0. At B, however, the speed of the air presumably equals the airspeed B of the plane.A pitot tube on a high-altitude aircraft measures a differential pressure of 230 Pa. What is the aircraft's airspeed if the density of the air is 0.0320 kg/m3?
Chapter 12 Solutions
Tutorials in Introductory Physics
Ch. 12.1 - For each layer, draw a free-body diagram in the...Ch. 12.1 - Imagine that a small hole is opened in the...Ch. 12.1 - Prob. 2aTCh. 12.1 - Suppose you wanted to determine the pressure at...Ch. 12.1 - Prob. 2cTCh. 12.1 - Prob. 2dTCh. 12.1 - Draw a freebody diagram for the small voulme of...Ch. 12.1 - Prob. 3bTCh. 12.1 - Use your answer to part B to compare the pressures...Ch. 12.1 - Prob. 3dT
Ch. 12.1 - Consider the following student dialogue: Student...Ch. 12.1 - Prob. 4aTCh. 12.1 - The right end of the tube is now scaled with a...Ch. 12.1 - A syringe is used to remove some water from the...Ch. 12.2 - A cubical block is observed to float in a beaker...Ch. 12.2 - Prob. 1bTCh. 12.2 - Imagine that you were to release the block from...Ch. 12.2 - In general, does the buoyant force on an object...Ch. 12.2 - By how much does the volume reading increase when...Ch. 12.2 - Does the volume of water displaced by a completely...Ch. 12.2 - Consider the following statement made by a...Ch. 12.2 - A rectangular block, A, is released from rest at...Ch. 12.2 - A second block, B,of the same size and shape as A...Ch. 12.2 - A third block, C, of the same size and shape as A...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
65. * Daring Darless wishes to cross the Grand Canyon of the Snake River by being shot from a cannon. She wishe...
College Physics
3. What is free-fall, and why does it make you weightless? Briefly describe why astronauts are weightless in th...
The Cosmic Perspective (8th Edition)
The pV-diagram of the Carnot cycle.
Sears And Zemansky's University Physics With Modern Physics
Which of the three orbits shown below (A, B, or C) would you say most closely matches the shape of Earth's orbi...
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Choose the best answer to each of the following. Explain your reasoning. To determine a planets average density...
The Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals (2nd Edition)
1.84 Two vectors and have magnitudes A = 3.00 and B = 3.00. Their vector product is . What is the angle betwe...
University Physics with Modern Physics (14th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- CO-3,4,5 SITUATION 4. (Flow in Pipes - a) A circular pipe has a diameter of 750 millimeters is flowing full of water. Diameter = D NOTES: For "Manning's Formula" Velocity V = 1/n x R S 2/3 1/2 d) WS O NOTES: Manning's Roughness Coef. n = 0.012 Consider pipe is flowing full. Pipe Invert Slope is S=1.55% Hydraulic Radius R= D/4 Flow Rate Q = A x V Figure 1. FLOW IN PIPES H +D Note: Volume = 1.0 m³ = 1,000 liters Calculate its hydraulic radius, R = ? in meters Calculate the mean velocity V = ? in meters per sec. Determine the flow rate Q = ? in cubic meters per sec. ? Determine the flow rate Q = ? in liters per sec. ?arrow_forwardA horizontal bend of constant cross-sectional area (A) pipe is shown below (you are looking down on the bend from above). Water flows through the bend at steady flow conditions and the pressure is the same at points 1 and 2 (P1 = P2 = P). The mass flowrate (m_dot) and velocity (V) in the pipe are also constant. What is the magnitude of the force required to keep the bend from moving? V, in Force to keep the bend from moving V, m - 2 O2PA O2m_dotV O2m_dotV + 2PA Om_dotv + 2PA O2m_dotV + PAarrow_forwardAt 20 ° C, the surface tension of water is 0.073 N/m. A soap film is holding up the entire weight of a horizontal slide wire, as shown in the figure below. 2yl Part A If the wire has a length of 2.2 cm and a diameter of 0.10 cm , what is its density? Express your answer in kilograms per meter cubed. ? kg/m? Submit Request Answerarrow_forward
- INSTRUCTION: Please show your solution especially the raw value and rounded off value of your final answer PROBLEM: The water pipe below contains water that passes through A to C. What is the pressure at point C with a cross-sectional area of 0.1 m2 and is elevated 5.0 m from the ground if at point A, the pressure is 2.0 ATM, cross-sectional area of 0.2m2, velocity is 4 m/s, and is placed at the ground level?arrow_forwardSeawater has a density of 1024 kg/m3. If a submersible machine which is at a pressure of 8.00 x 104 Pa on the inside needs to be lowered from the sea surface 375 m to the ocean floor, what is the pressure differential that its hull needs to be able to withstand? Show your work.arrow_forwardFind the gauge pressure in torr at point a, the bottom of the right arm. what is the pressure in torr of the gass in the tank?arrow_forward
- Looking at the figure below, a small parallelepiped of fluid centered on the point, explain why the pressure will be independent of x and z? And what will you need to know to determine the pressure in y?arrow_forwardQI. Solve the following: (Compulsory question) a) Pressure on the quay Weight of the container. Length of the reachstacker: Length of the arm 32 tons 4 meters 14 meters. Pls calculate the pressure on the quay. What is the pressure on the quay 32 tons Discover your scO ?? Quay www.nhtv: What is the axle pressure on the front axle (which is standing on the quay)?arrow_forwardPlease answer part A. Sho all work and circle your answer What if you changed the fluid? Calculate the pressure of a fluid (vat of rum) at the given depth h: Where, Po = 101 kPa and r = 948 kg/m3 (density of high proof alcohol) Part A: How does these pressures compare to those of water? Explain.arrow_forward
- Compute for the surface tension of a force of 3.65 x 10⁷ dyne acting on 7 m². Determine all of your answers in the MKS unit. What is the radius of the capillary tube? What is the diameter of the capillary tube?arrow_forwardA cube of wood with density of 0.780g/cm3 is 10.0cm3 on each side. When the cube is placed in sea water, what buoyant force acts on the wood? Show your solutions. A tank 14.0m deep is filled with water. The top of the tank is open to the air. What is the absolute pressure at the bottom of the tank? What is the gauge pressure?arrow_forwardIf water is flowing half-full in a circular pipe containing a gas at a constant pressure (as shown in the figure below), how does the pressure at the free water surface change in relation to the pressure of the gas? R= 2 m 0 = a/2arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON
The Laws of Thermodynamics, Entropy, and Gibbs Free Energy; Author: Professor Dave Explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8N1BxHgsoOw;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY