
1.
Provide a multi-step income statement for the year 2016.
1.
Explanation of Solution
Multi step income statement: A multiple step income statement refers to the income statement that shows the operating and non-operating activities of the business under separate head. In different steps of the multi-step income statement, principal operating activities are reported that starts from the record of sales revenue with all contra sales revenue account like sales returns, allowances and sales discounts.
Provide a multi-step income statement for the year 2016.
| Company R | ||
| Multi-Step Income Statement | ||
| For the Year Ended December 31, 2016 | ||
| Particulars | Amount | Amount |
| ($) | ($) | |
| Sales revenue | $200,000 | |
| Less: Cost of goods sold | ($121,120) | |
| Gross profit | $78,880 | |
| Less: Operating expenses | ||
| Selling expenses | ($26,000) | |
| Administrative expenses | ($16,000) | |
| ($7,000) | ||
| Operating expenses | ($49,000) | |
| Operating income | $29,880 | |
| Other revenues and expenses: | ||
| Interest revenue | $1,000 | |
| Interest expense | ($4,880) | |
| Loss due to flood | ($8,000) | ($11,880) |
| Income before taxes | $18,000 | |
| Less: Income taxes @30% | ($5,400) | |
| Net income | $12,600 | |
| Components of income | Earnings per common share | |
| Net income | $2.52 | |
Table (1)
2.
Provide a schedule that discloses the revenues, profits, and assets of divisions 1 and 2 and the remaining operating segments.
2.
Explanation of Solution
Provide a schedule that discloses the revenues, profits, and assets of divisions 1 and 2 and the remaining operating segments.
| Company R | ||||
| Industry Segment Financial Results | ||||
| For the Year Ended December 31, 2016 | ||||
| Particulars | Reportable Operating Segments | All Other Segments | Totals | |
| 1 | 2 | |||
| Total revenues (Sales) | 98,000 | 60,000 | 42,000 | 200,000 |
| Segment profit (Pretax) | 17,100 | 10,830 | 9,750 | 37,680 |
| General corporate expenses | -7,800 | |||
| Interest revenue | 1,000 | |||
| Interest expense | -4,880 | |||
| Loss due to flood | -8,000 | |||
| Income before taxes | 18,000 | |||
| Identifiable asset | 135,000 | 87,000 | 54,000 | 276,000 |
| General corporate assets | 24,000 | |||
Table (2)
Working note (1):
Prepare a working paper for segment reporting:
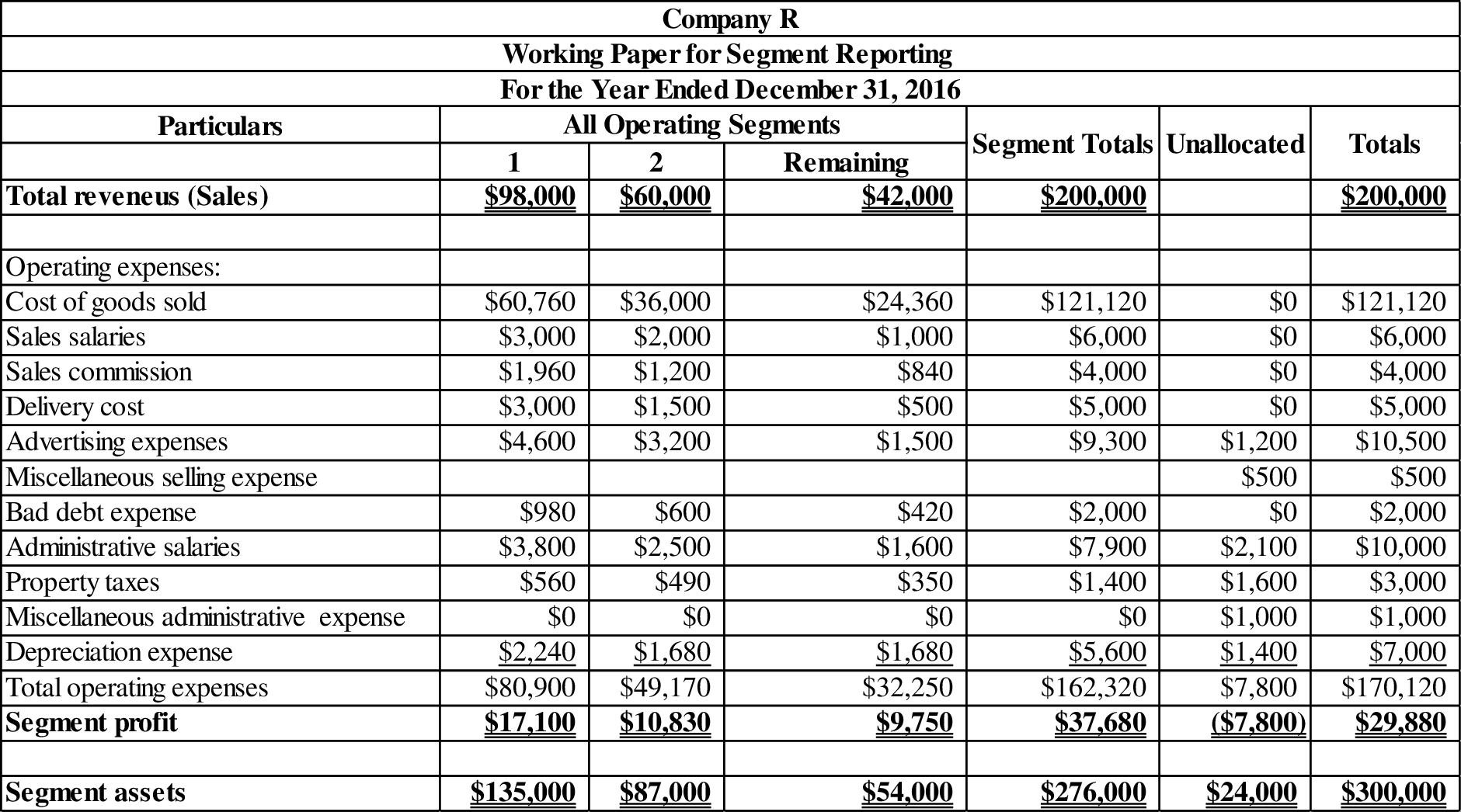
Table (3)
3.
Provide a suitable segment notes related to depreciation, profit, and capital expenditures.
3.
Explanation of Solution
In the calculation of segment profit none on the following item has been added or subtracted. Formula for segment profit is as follows:
Depreciation expenses for Division 1 and 2 are $2,240 and $1,680 respectively.
In the year of 2016, capital expenditure amount of $25,000 placed in Division 1 and $6,000 placed in Division 2.
4.
Compute the profit margin before income taxes and pretax return on identifiable assets for Divisions 1 and 2 and for other divisions and evaluate the ratios.
4.
Explanation of Solution
Compute the profit margin before income taxes for Division 1:
Calculate profit margin before income taxes for Division 2:
Calculate profit margin before income taxes for other division:
Hence, the profit margin before income taxes for Division 1, 2 and other division is
Calculate pretax return on identifiable assets for Division 1:
Calculate pretax return on identifiable assets for Division 2:
Calculate pretax return on identifiable assets for other division:
Hence, the pretax return on identifiable assets Division 1, 2 and other division is
These ratios expose that the profit margin before income taxes for other division has higher margin of 23.21%.
This ratio expose that the other operating divisions have a higher pretax profit margin and pretax return on identifiable assets than the two reportable divisions. This reveals that the economic resources are used lesser in the reportable divisions.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Cengagenowv2, 1 Term Printed Access Card For Wahlen/jones/pagach’s Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And Analysis, 2017 Update, 2nd
- Melville Corporation provided the following partial-trial balance for the current year Prepare a single-step income statement for the year ended December 31. Melville is subject to a 40% income tax rate. (Round all amounts to the nearest whole dollar.) Melville Corporation Trial Balance (Selected Accounts) For the Year Ended December 31 Account Debit Credit Dividends $1,400 Sales $120,000 Dividend Income 590 Interest Income 900 Gain on Disposal of Plant Assets 1,100 Unrealized Gain on Trading Investments 1,700 Cost of Goods Sold 45,000 Office Supplies Expense 4,100 Sales Salaries Expense 3,300 Selling Expenses 15,000 Accounting and Legal Fees—General Expense 830 Advertising Expense 3,800 Office Salaries Expense 6,600 Depreciation Expense—General Expense 9,400 Interest Expense 2,200 Loss on Asset Impairment 2,400arrow_forwardThe following information pertains to Corsig Corp. and its divisions for the year ended December 31, 2017. Sales to unaffiliated customers $2,125,000 Intersegment sales of products similar to those sold to unaffiliated customers 1,250,000 Interest earned on loans to other operating segments 56,000 Corsig and all of its divisions are engaged solely in manufacturing operations. Corsig has a reportable segment if that segment's revenue exceeds $212,500. $337,500. $331,900. $343,100.arrow_forwardThe following are the statements of comprehensive income and financial positions of Green Limited: Green Limited Statement of Comprehensive Income for the Year Ended 31st December 2018 GH₵ GH₵ Sales 86,000 Less: Cost of goods sold Opening stock 16,500 Purchases 48,000 64,500 Less closing stock (24,000) (40,500) Gross profit 45,500 Less operating expenses Administrative expenses (9,000) Depreciation (4,000) Selling & distribution expenses (10,000) (23,000) Profit before interest and tax 22,500 Interest (5,000) Profit before tax 17,500 Corporate tax 6,000 Profit after interest & tax 11,500 Green Limited Statement of Financial Position as at 31st December 2018 31/1/2018 31/12/017 Non-current assets Plant & machinery 20,000 15,000 Motor…arrow_forward
- Waller Company does business in two regional segments: North and South. The following annual revenue information was determined from the accounting system's invoice data: Current Year Prior Year Segment North South $ 80,000 260,000 $100,000 200,000 Total revenues $340,000 $300,000 Using horizontal analysis, determine the percentage change in revenues for the North region. Round to one decimal place. Oa. (20.0)% Ob. (22.4)% Oc. 22.4% Od. 20.0%arrow_forwardThe following information pertains to Xavier Corp. and its divisions for the year ended 12/31/20: Sales to unaffiliated customers $4,000,000 Intersegment sales of products similar to those sold to unaffiliated customers 900,000 60,000 Interest earned on loans to other operating segments Xavier and all of its divisions are engaged solely in manufacturing operations. Xavier has a reportable segment if that segment's revenue exceeds a. $496,000. b. $490,000. $406,000. $400,000. C. d.arrow_forwardABC Corporation's accounting records include the following items, listed in no particular order, at December 31, 2024: Other Income and (Expenses) $7,200 Cost of Goods Sold $30,000 Net Sales $81,000 Operating Expenses $25,000 Gain on Discontinued Operations $3,600 The income tax rate for ABC Corporation is 21%. Prepare ABC's income statement for the year ended December 31, 2024. Omit earnings per share. Prepare the income statement through the income before taxes, then complete the income statement through the net income. ABC Corporation Income Statement Year Ended December 31, 2024 Costs of Goods Sold $___________ Discontinued Operations (less applicable tax) $___________ Income Tax Expense $___________ Operating Expenses $___________ Other Income and (Expenses) $___________ Net Sales $___________ Income Before Income Taxes $___________arrow_forward
- The most recent financial statements for Bello Co. are shown here: Income Statement Balance Sheet Sales $ 20,500 Current assets $ 12,020 Debt $ 16,660 Costs 14,100 Fixed assets 33,300 Equity 28,660 Taxable income $ 6,400 Total $ 45,320 Total $ 45,320 Taxes (21%) 1,344 Net income $ 5,056 Assets and costs are proportional to sales. Debt and equity are not. The company maintains a constant 30 percent dividend payout ratio. What is the internal growth rate? (Do not round intermediate calculations and enter your answer as a percent rounded 2 decimal places, e.g., 32.16.)arrow_forwardSnelling Company does business in two regional segments: North and South. The following annual revenue information was determined from the accounting system's invoice data: Segment Current Year Prior Year North $ 75,000 $100,000 South 260,000 220,000 Total revenues $335,000 $320,000 Using horizontal analysis, determine the percentage change in revenues for the South region. Round to one decimal place. Oa. (18.2)% Ob. 84.6% Oc. 15.4% Od. 18.2%arrow_forwardThe following are the details from the income statements of division S and division C for the year ending March 2014. Figures in TZS "000" Sales revenue 100,000 64,000 6,000 120,000 75,000 10,000 150,000 Operating cost Interest cost Capital invested 122,000 Capital invested include debt WACC 10% 12.5% Rate of corporate tax 40% 44% Required: Calculate NOPAT as adjusted for EVA and also calculate EVA for both the divisions. Which Division performed better?arrow_forward
- MEXICO Company and all its divisions are engaged in a merchandising business. The 2021 income statement of MEXICO showed the following: Sales to unaffiliated customers P 20,000,000 Gain on sale of machinery 1,500,000 Operating expenses 15.000.000) Net income P 6,500,000 In the process of determining the consolidated net income, intersegment sales of P3,000,000 were eliminated. What is the minimum amount of segment revenue to be reported by a division in order for it to be considered as a reportable segment under IFRS 8, Operating Segments?arrow_forwardThe following Income Statement information has been obtained from the books of Unlimited Liquors Corporation for the year ended March 31, 2022. The Income tax rate is 40% and the company has 50,000 shares of common stock outstanding. Sales Revenue $890,000 Cost of Goods sold 300,000 Operating expenses 220,000 Income from discontinued operations 140,000 Loss on disposal of discontinued operations 60,000 Determine the net income or loss from the discontinued segment of the company as reported on the Income Statement:arrow_forwardThe following Income Statement information has been obtained from the books of Unlimited Liquors Corporation for the year ended March 31, 2022. The Income tax rate is 40% and the company has 50,000 shares of common stock outstanding. Sales Revenue S890,000 Cost of Goods sold 300,000 Operating expenses 220,000 Income from discontinued operations 140,000 Loss on disposal of discontinued operations 60,000 Determine the income or loss from the discontinued segment of the company as shown on the income statement: Answer:arrow_forward
 Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning
