
Concept explainers
Part (a) To Determine:
The acceleration of the system of crates.
Answer to Problem 47P
Solution:
The acceleration of the system is 1.7 m/s2.
Explanation of Solution
Both the crates A and B are in contact with each other. Therefore, both the crates experience the same acceleration due to the force F acting on them.
The free body diagram of the crates is shown below.
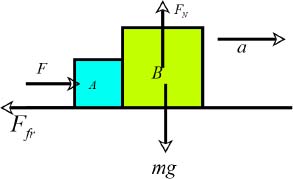
The mass m is the sum of the masses mA and mB of the crates. The weight mg of the system acts downwards, while the surface on which they rest exerts a normal force on the crates. Since the crates are accelerating, the
For vertical equilibrium,
…………(1)
In the horizontal direction, the crates accelerate with an acceleration of a.
…………(2)
The force of kinetic friction is related to the normal force as,
…………(3)
Equations (1), (2)and (3)can be simplified to give the expression for a.
Given:
The mass of crate A
The mass of crate B
The coefficient of kinetic friction
Formula used:
Calculation:
Calculate the acceleration of the system by substituting the given values of mass, force, and coefficient of kinetic friction. Use 9.8 m/s2 for g.
The mass of the system is the sum of the masses of the bodies A and B.
Calculate the acceleration of the system.
Part (b) To Determine:
The force exerted by each crate on the other.
Answer to Problem 47P
Solution:
The force the crates exert on each other is 430 N.
Explanation of Solution
To calculate the force exerted by one body on the other, draw free body diagrams for A and B.
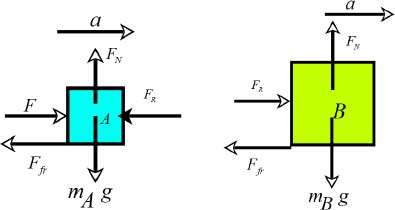
The crates exert a reaction force on each other.
For the crate B, the equation for horizontal motion can be written as,
The force of kinetic friction for B is given by,
The reaction force can be written as,
Given:
The mass of crate A
The mass of crate B
The coefficient of kinetic friction
Formula used:
Calculation:
Use the given values in the equation to determine the force exerted by one crate on the other.
Part (c) To Determine:
The acceleration of the system and the force they exert on each other when the crates are reversed.
Answer to Problem 47P
Solution:
When the position of the crates is reversed, the acceleration is 1.7 m/s2 and the force they exert on each other is 220 N.
Explanation of Solution
When the positions of the crates are reversed, the acceleration remains the same, since acceleration depends on the mass of the system.
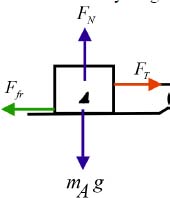
Draw the free body diagram for A.

For the crate A, the equation for horizontal motion can be written as,
The force of kinetic friction for A is given by,
The reaction force can be written as,
Given:
The mass of crate A
The mass of crate B
The coefficient of kinetic friction
Formula used:
Calculation:
If the crates are reversed, the acceleration remains the same at 1.7 m/s2.
The force exerted by one crate on the other when the position of the crates is reversed is calculated using the formula .
Substitute the given quantities in the equation.
Chapter 4 Solutions
Physics: Principles with Applications
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics (5th Edition)
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol. 1 (Chs 1-21) (4th Edition)
College Physics
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach with Modern Physics (4th Edition)
Conceptual Physical Science (6th Edition)
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON





