
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)
4th Edition
ISBN: 9781305389892
Author: Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillan
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 30, Problem 14TYK
Design an Experiment Experiments on the orange bread mold Neurosporacrassa, an ascomycete, were pivotal in elucidating the concept that each gene encodes a single enzyme. As N. crassa ascospores arise through meiosis and then mitosis in an ascus, each ascospore occupies a particular position in the final string of eight spores the ascus contains:
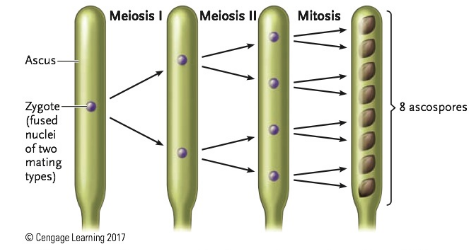
This quirk of ascospore development was extremely useful to early geneticists, because it vastly simplified the task of figuring out which alleles ended up in particular ascospores following meiosis. Recalling genetics topics discussed in Chapter 11, why was the analysis easier?
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
The figure below shows the life cycle of the fungus Neurospora. The adult stage of the Neurospora is a multicellular haploid:
a. Between which two stages of the Neurospora life cycle do most mitotic cell divisions occur?
b. Neurospora has an arginine amino acid synthesis pathway shown below:
Suppose I have a neurospora strain that has a mutation such that it will not grow unless I supplement the media (food) with arginine (but not with citrulline or ornithine). What gene is mutated? Explain your reasoning.
c. Suppose I take the strain above that only grows with arginine supplements and cross it to a different mutant Neurospora strain that grows with arginine and citrulline supplements but not ornithine supplements. Assming genes A, B and C are unlinked and there is only one mutation per strain:
i) What percentage of the progeny will grow on ornithine?
ii) What percentage on citrulline?
iii) What percentage on arginine?
Show your work for i), ii) and iii). [Can be answered in less…
Alternation of generations means
-One phase of the life cycle is photosynthetic and the other is heterotrophic.
-One phase of the life cycle is unicellular and the other is multicellular.
-One phase of the life cycle takes place on land and the other in water.
-One phase of the life cycle is multicellular diploid and the other is multicellular haploid.
-One phase of the life cycle is motile and the other is stationary.
Experiment:
Saccharomyces cerevisiae can exist stably in either a haploid or a diploid state. A haploid S. cerevisiae
cell has 16 chromosomes. When certain haploids come into contact, they fuse their cell walls and
membranes, followed by the fusion of their nuclear membranes. The single nucleus now has 32
chromosomes, 16 from each parent strain, and is thus a diploid.
Haploid yeast strains divide mitotically to give rise to haploid progeny, and diploid strains divide
mitotically to give rise to diploid progeny. Certain haploids can fuse to form diploids. Haploid S.
cerevisiae exists in two "mating types," called a and a. Mating occurs only between a and a cells; no
mating occurs between cells of identical mating type.
We have a collection of eight a haploid mutant strains and eight a haploid mutant strains of yeast
unable to synthesize tryptophan (trp). These will be combined (mated) in all possible combinations
to yield diploid strains. If the diploids can grow on minimal medium,…
Chapter 30 Solutions
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)
Ch. 30.1 - Prob. 1SBCh. 30.1 - Prob. 2SBCh. 30.1 - Prob. 3SBCh. 30.2 - Prob. 1SBCh. 30.2 - Prob. 2SBCh. 30.3 - Prob. 1SBCh. 30.3 - Prob. 2SBCh. 30.4 - Prob. 1SBCh. 30.4 - Prob. 2SBCh. 30 - Prob. 1TYK
Ch. 30 - Prob. 2TYKCh. 30 - Prob. 3TYKCh. 30 - Prob. 4TYKCh. 30 - Prob. 5TYKCh. 30 - A mushroom is: a. the food-absorbing region of an...Ch. 30 - Prob. 7TYKCh. 30 - Prob. 8TYKCh. 30 - Prob. 9TYKCh. 30 - In a college greenhouse, a new employee observes...Ch. 30 - Prob. 11TYKCh. 30 - Prob. 12TYKCh. 30 - Prob. 13TYKCh. 30 - Design an Experiment Experiments on the orange...Ch. 30 - Prob. 15TYKCh. 30 - Prob. 1ITDCh. 30 - Prob. 2ITD
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- When the Ascomycetes fungus reproduces sexually, mating type A fungi cross fertilize mating type a fungi. The resulting zygotes undergo meiotic and then mitotic division to produce asci with eight ascospores. The ascospores in the asci are ordered and reflect the position of the parental nuclei in the zygote. Use the passage to answer the question. Based on the diagram, how many unique ascospores are produced in each ascus resulting from the cross fertilization of two Ascomycetes fungi? A. 1 B. 2 C. 4 D. 8arrow_forwardDiscus the important finding which could be obtained from a linear tetrad analysis that can not be learned from an unordered tetrad analysis in fungi validate your answer by diagrammatic representationarrow_forwardWhen the Ascomycetes fungus reproduces sexually, mating type A fungi cross fertilize mating type a fungi. The resulting zygotes undergo meiotic and then mitotic division to produce asci with eight ascospores. The ascospores in the asci are ordered and reflect the position of the parental nuclei in the zygote. Use the passage to answer the question. How is the life cycle of Ascomycetes different from that of humans? A. Haploid cells undergo meiosis. B. Haploid cells undergo mitosis. C. Diploid cells undergo meiosis. D. Diploid cells undergo mitosis.arrow_forward
- Yeast are unicellular fungi that reproduce by budding (Fig. 8.4.). Identify individual yeast cells and locate a budding cellarrow_forward8) The diagram below represents a yeast cell that is in the process of budding, a form of asexual reproduction. Nucleus -Bud "Nucleus Which of the following statements describes the outcome of this process? A) The two cells that result will each contain half the species number of chromosomes. B) The two cells that result will have identical DNA. C) The bud will develop into a zygote. D) The bud will start to divide by the process of meiotic cell division.arrow_forwardAlthough ascospores are produced by mitotic division, none of the spores develop into fungi that are identical to either parental hyphae. What is the BEST explanation for this observation? A. The spores inherit half their genes from each parent. B. The spores inherit haploid nuclei from their parents. C. The spores inherit mutations as a result of meiosis. D. The spores inherit mutations as a result of mitosis. Photo Attatchedarrow_forward
- Does structure "A" produce haploid or diploid spores? Is structure "B" coenocytic or septate? A MacBook Proarrow_forwardAlthough ascospores are produced by mitotic division, none of the spores develop into fungi that are identical to either parental hyphae. What is the BEST explanation for this observation? A. The spores inherit half their genes from each parent. B. The spores inherit haploid nuclei from their parents. C. The spores inherit mutations as a result of meiosis. D. The spores inherit mutations as a result of mitosis.arrow_forwardThe figure below shows the life cycle of the fungus Neurospora. The adult stage of the Neurospora is a multicellular haploid. a) Between which two stages of the Neurospora life cycle (shown above) do most mitotic cell division oarrow_forward
- e. The 5' to 3' DNA template will be converted to mRNA. CLEAR MY CHOICE The growth of spores to mycelium is known as .. ... .. Answer: A berry plant uses the sun's energy to provide fruit, which is then consumed by a bird. Which characterist best represent? meet.google.com is sharing your screen. Sto a. All living things carry out the process of reproduction pe here to searcharrow_forwardTHIS IS A THREE PART QUESTION! PLEASE COMPLETE EACH OF THE PARTS (2a) For picture A Type a) Type 1) 4 dark spores 4 light spores.....in that order 4:4= 4 Type 2) 4 light spores 4 dark spores.....in that order 4:4= 3 Total sum of parental types =7 Type b) Type 1) 2 dark 2 light 2dark 2 light spores 2:2:2:2= 1 Type 2) 2 light 2 dark 2 light 2dark spores 2:2:2:2 = 4 Total sum of recombinat type A = 5 Type c) Type 1) 2 light spores 4 dark spores 2 light spores 2:4:2 = 1 Type 2) 2 dark spores. 4 light spores 2 dark spores= 5 Total sum of type B recombinats= 6 (2B) Type a) 4 dark spores 4 light spores.....in that order 4:4 (type 1) ---->8 4 light spores and 4 dark spores in that order...... 4:4 (type 2). ---->5 Total Sum of Parental Types =13 Type b) 2 dark 2 light 2dark 2 light spores 2:2:2:2 (type 1). ---->4 2 light 2 dark 2 light 2dark spores 2:2:2:2 (type 2). ---6 Total Sum Recombinant Type A =10 Type c) 2 light spores 4 dark spores 2 light spores 2:4:2 (type 1).…arrow_forwardIn a particular plant species, 2n=12. For this organism, how many chromosomes, and how many DNA molecules will be present per cell for each of the following? e) root meristem cell in telophase of mitosis (cytokinesis complete) f) microspore mother cell (in anther) in prophase 1 of meiosis g) microspore mother cell in metaphase II of meiosis h) pollen grain ( after meiosis is and cytokinesis complete)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning

Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:9781305389892
Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanisms of Genetic Change or Evolution; Author: Scientist Cindy;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5FE8WvGzS4Q;License: Standard Youtube License