
Organic Chemistry
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781305080485
Author: John E. McMurry
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 2.SE, Problem 60AP
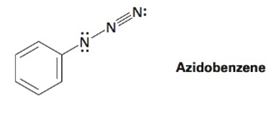
The azide
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
The two compounds nitrogen dioxide and dinitrogen tetraoxide are introduced in Section 3.13.
(a) NO2 is an odd-electron compound. Draw the best Lewis diagrams possible for it, recognizing that one atom cannot achieve an octet configuration. Use formal charges to decide whether that should be the (central) nitrogen atom or one of the oxygen atoms.
(b) Draw resonance forms for N2O4 that obey the octet rule. The two N atoms are bonded in this molecule.
The two compounds nitrogen dioxide and dinitrogentetraoxide are introduced in Section 3.13.(a) NO2 is an odd-electron compound. Draw the bestLewis diagrams possible for it, recognizing that oneatom cannot achieve an octet configuration. Use formal charges to decide whether that should be the(central) nitrogen atom or one of the oxygen atoms.(b) Draw resonance forms for N2O4 that obey the octetrule. The two N atoms are bonded in this molecule.
A stable triatomic molecule can be formed that contains one atom each of nitrogen, sulfur, and fluorine. Three bonding structures are possible, depending on which is the central atom: NSF, SNF, and SFN.
(a) Write a Lewis diagram for each of these molecules, indicating the formal charge on each atom.
(b) Often, the structure with the least separation of formal charge is the most stable. Is this statement consistent with the observed structure for this molecule— namely, NSF, which has a central sulfur atom?
(c) Does consideration of the electronegativities of N, S, and F from Figure 3.18 help rationalize this observed structure? Explain. 100. The gas
Chapter 2 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
Ch. 2.1 - Prob. 1PCh. 2.1 - Prob. 2PCh. 2.1 - Use the electronegativity values shown in Figure...Ch. 2.1 - Look at the following electrostatic potential map...Ch. 2.2 - Ethylene glycol, HOCH2CH2OH, may look nonpolar...Ch. 2.2 - Make three-dimensional drawings of the following...Ch. 2.3 - Calculate formal charges for the nonhydrogen atoms...Ch. 2.3 - Organic phosphate groups occur commonly in...Ch. 2.6 - Which of the following pairs of structures...Ch. 2.6 - Draw the indicated number of resonance forms for...
Ch. 2.7 - Nitric acid (HNO3) reacts with ammonia (NH3) to...Ch. 2.8 - Prob. 12PCh. 2.8 - Amide ion, H2N-, is a much stronger base than...Ch. 2.9 - Prob. 14PCh. 2.9 - Prob. 15PCh. 2.9 - Prob. 16PCh. 2.11 - Using curved arrows, show how the species in part...Ch. 2.11 - Prob. 18PCh. 2.12 - Of the two vitamins A and C, one is hydrophilic...Ch. 2.SE - Prob. 20VCCh. 2.SE - The following model is a representation of...Ch. 2.SE - cis-l, 2-Dichloroethylene and trans-1,...Ch. 2.SE - The following molecular models are representations...Ch. 2.SE - Predict the product(s) of the acid/base reactions...Ch. 2.SE - Use curved arrows to draw the protonated form of...Ch. 2.SE - Prob. 26MPCh. 2.SE - Double bonds can also act like Lewis bases,...Ch. 2.SE - Prob. 28APCh. 2.SE - Use the electronegativity table given in Figure...Ch. 2.SE - Which of the following molecules has a dipole...Ch. 2.SE - Prob. 31APCh. 2.SE - Phosgene, C12C=O, has a smaller dipole moment than...Ch. 2.SE - Prob. 33APCh. 2.SE - Methanethiol, CH3SH, has a substantial dipole...Ch. 2.SE - Calculate the formal charges on the atoms shown in...Ch. 2.SE - Assign formal charges to the atoms in each of the...Ch. 2.SE - Which of the following pairs of structures...Ch. 2.SE - Prob. 38APCh. 2.SE - 1, 3-Cyclobutadiene is a rectangular molecule with...Ch. 2.SE - Alcohols can act either as weak acids or as weak...Ch. 2.SE - The O-H hydrogen in acetic acid is more acidic...Ch. 2.SE - Draw electron-dot structures for the following...Ch. 2.SE - Write the products of the following acid-base...Ch. 2.SE - Rank the following substances in order of...Ch. 2.SE - Which, if any, of the substances in Problem 2-44...Ch. 2.SE - The ammonium ion (NH4+, pKa = 9.25) has a lower...Ch. 2.SE - Prob. 47APCh. 2.SE - Prob. 48APCh. 2.SE - Calculate Ka values from the following pka’s:...Ch. 2.SE - Calculate pKa values from the following Ka’s:...Ch. 2.SE - What is the pH of a 0.050 M solution of formic...Ch. 2.SE - Prob. 52APCh. 2.SE - Maleic acid has a dipole moment, but the closely...Ch. 2.SE - Assume that you have two unlabeled bottles, one of...Ch. 2.SE - Identify the acids and bases in the following...Ch. 2.SE - Which of the following pairs represent resonance...Ch. 2.SE - Draw as many resonance structures as you can for...Ch. 2.SE - Carbocations, which contain a trivalent,...Ch. 2.SE - We’ll see in the next chapter that organic...Ch. 2.SE - The azide functional group, which occurs in...Ch. 2.SE - Phenol, C6H5OH, is a stronger acid than methanol,...Ch. 2.SE - Thiamin diphosphate (TPP), a derivative of vitamin...Ch. 2.SE - Determine if each compound or ion below has a...Ch. 2.SE - Prob. 64APCh. 2.SE - Prob. 65APCh. 2.SE - Draw the conjugate base for each compound below...Ch. 2.SE - 1, 1, 1-Trichloroethanol is an acid more than 1000...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Although I3- is a known ion, F3- is not. (a) Draw the Lewis structure for I3- (it is linear, not a triangle). (b) One of your classmates says that F3 - does not exist because F is too electronegative to make bonds with another atom. Give an example that proves your classmate is wrong. (c) Another classmate says F3- does not exist because it would violate the octet rule.Is this classmate possibly correct? (d) Yet another classmatesays F3- does not exist because F is too small to make bonds tomore than one atom. Is this classmate possibly correct?arrow_forwardDraw the two resonance structures of CINO, with N as the central atom. Give the formal charges of all of the atoms.arrow_forward(a) Determine the formal charge of oxygen in the following structure. If the atom is formally neutral, indicate a charge of zero. (b) Draw an alternative Lewis (resonance) structure for the compound given in part (a). Show the unshared pairs and nonzero formal charges in your structure. Don't use radicals. Formal charge on O 0arrow_forward
- Some chemists believe that satisfaction of the octet rule should be the top criterion for choosing the dominant Lewis structure of a molecule or ion. Other chemists believe that achieving the best formal charges should be the top criterion. Consider the dihydrogen phosphate ion, HaPO, , in which the H atoms are bonded to O atoms. (a) What is the predicted dominant Lewis structure if satisfying the octet rule is the top eriterion? (b) What is the predicted dominant Lewis structure if achieving the best formal charges is the top criterion?arrow_forwardA stable triatomic molecule can be formed that containsone atom each of nitrogen, sulfur, and fluorine. Threebonding structures are possible, depending on which is thecentral atom: NSF, SNF, and SFN.(a) Write a Lewis diagram for each of these molecules,indicating the formal charge on each atom.(b) Often, the structure with the least separation of formal charge is the most stable. Is this statement consistent with the observed structure for this molecule—namely, NSF, which has a central sulfur atom?(c) Does consideration of the electronegativities of N, S,and F from Figure 3.18 help rationalize this observedstructure? Explain.arrow_forwardCompare the electron dot structures of the carbonate</o:p> (CO32- ) and borate (BO33- ) ions.</o:p> (a) Are these ions isoelectronic?</o:p> (b) How many resonance structures does each ion have?</o:p> (c) What are the formal charges of each atom in these ions?</o:p> (d) If an H+ ion attaches to CO32- to form the bicarbonate ion, HCO3- , does it attach to an O atom or to the C atom?</o:p> </o:p>arrow_forward
- For the next compounds/ions, draw two (2) appropriate Lewis structures. One structure must obey the octet rule and the other structure must be a non-octet obeying structure (octet deficient or octet expansion). Be sure to indicate which structure is the “best” structure and explain your choice formal charge arguments and any other points you deem important. (a) BeCl2 (b) POF3 (c) SO42−arrow_forwardDraw resonance structures for the bicarbonate ion, HCO3-. (a) Does HCO3- have the same number of resonance structures as the CO32- ion? Are any less likely than others? (b) What are the formal charges on the O and C atoms in HCO3- ? What is the average formal charge on the O atoms? Compare this with the O atoms in CO32- . (c) Protonation of HCO3- gives H2CO3. How do formal charges predict where the H+ ion will be attached?arrow_forwardDraw Lewis structures for each of the following compounds. In each case, specify the number of valence electrons surrounding the central atom. (Assign lone pairs and radical electrons where appropriate.) (Assume the central atom does not contain an expanded octet.) (a) bromine dioxide (BrO2) (b) beryllium bromide (BeBr2) (c) phosphorus pentafluoride (PF5)arrow_forward
- Carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen form two different polyatomic ions: cyanate ion (NCO) and fulminate ion (CNO). Write Lewis structures for each anion, including near-equivalent resonance structures (do not add any arrows between structures) and indicating formal charges. The isocyanate ion also has two near-equivalent structures, but the formal charge on the nitrogen attom cannot be reduced to zero: Cyanate ion (NCO)arrow_forwardWrite a Lewis electron dot diagram for phosphoryl chloride,POCl3 (Fig. 3.29). Assign formal charges to all the atoms.arrow_forwardThe Lewis structure for the chlorate ion is :0: Calculate the formal charge on the chlorine (Cl ) atom. Express your answer as an integer. • View Available Hint(s) formal charge on Cl = Submit Part B Calculate the formal charge on each of the oxygen (O) atoms labeled a, b, and c in the following Lewis structure. :0: Express your answers as integers separated by commas. • View Available Hint(s) formal charge on Oa , Ob , Oc = Submit ormal charges to predict the most stable structure he interactive activity shows how to calculate the formal charge of atoms in a structure. These formal charges can be used to predict the resonance structure that contributes most to the stability of a molecule or ion. The struc enerally the most stable. Part C What are the formal charges on the sulfur (S), carbon (C ), and nitrogen (N ) atoms, respectively, in the resonance structure that contributes most to the stability of the thiocyanate ion, SCN¯ ? The possible resonance structures for the thiocyanate…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285199047
Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Stoichiometry - Chemistry for Massive Creatures: Crash Course Chemistry #6; Author: Crash Course;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UL1jmJaUkaQ;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
Bonding (Ionic, Covalent & Metallic) - GCSE Chemistry; Author: Science Shorts;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=p9MA6Od-zBA;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
General Chemistry 1A. Lecture 12. Two Theories of Bonding.; Author: UCI Open;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dLTlL9Z1bh0;License: CC-BY