
(a)
Interpretation:
The structural formula for the given compound has to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Nomenclature of esters of carboxylic acids:
The acyl group bonded to
The naming of an ester of a
(a)
Explanation of Solution
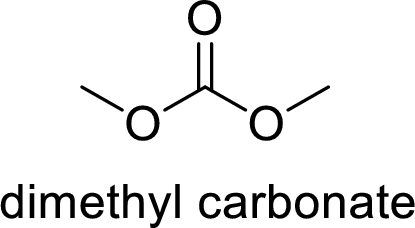
The name of the compound is given below:
Dimethyl carbonate
From the name, it is clear that two methyl groups are attached to oxygen atoms in the compound and the parent ester group is carbonate.
Thus, the structure of the compound is given below:
(b)
Interpretation:
The structural formula for the given compound has to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Nomenclature of nitriles:
The numbering 1 can be given to the nitrile carbon atom and add nitrile to end of the
(b)
Explanation of Solution
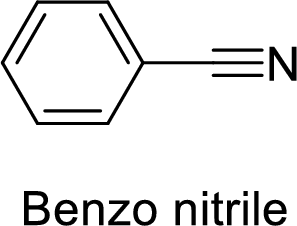
The name of the compound is given below:
The functional group is nitrile and benzene ring is attached to it.
Thus, the structure of the compound is given below:
Benzo nitrile
(c)
Interpretation:
The structural formula for the given compound has to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Nomenclature of esters of carboxylic acids:
The acyl group bonded to
The naming of an ester of a carboxylic acid is done by naming alkyl or aryl group bonded to oxygen first followed by the name of the acid in which the suffix –ic acid is replaced by the suffix –ate.
(c)
Explanation of Solution
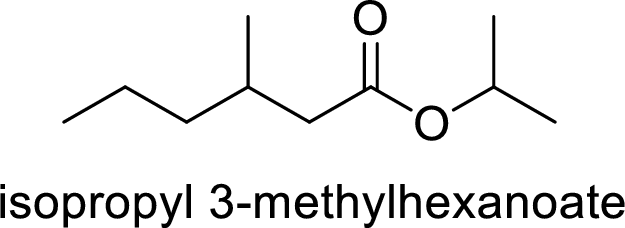
The name of the compound is given below:
Isopropyl-3-methylhexanoate
The alkyl group attached on oxygen atom is the isopropyl group and the parent chain is the methylhexanoate.
Thus, the structure of the compound is given below:
(d)
Interpretation:
The structural formula for the given compound has to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Nomenclature of esters of carboxylic acids:
The acyl group bonded to
The naming of an ester of a carboxylic acid is done by naming alkyl or aryl group bonded to oxygen first followed by the name of the acid in which the suffix –ic acid is replaced by the suffix –ate.
(d)
Explanation of Solution
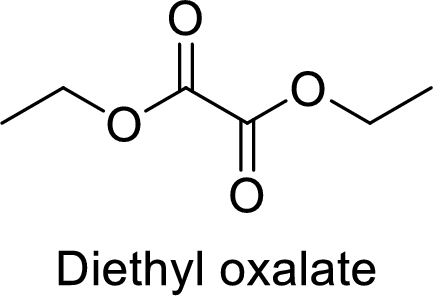
The name of the compound is given below:
Diethyl oxalate
From the name, it is clear that two ethyl groups are attached to oxygen atoms in the compound and the parent ester group is oxalate.
Thus, the structure of the compound is given below:
(e)
The structural formula for the given compound has to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Nomenclature of esters of carboxylic acids:
The acyl group bonded to
The naming of an ester of a carboxylic acid is done by naming alkyl or aryl group bonded to oxygen first followed by the name of the acid in which the suffix –ic acid is replaced by the suffix –ate.
(e)
Explanation of Solution
The name of the compound is given below:
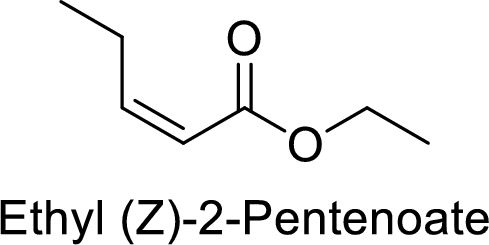
Ethyl (Z)-2-pentenoate
The alkyl group attached on oxygen atom is the ethyl group and the parent chain is the pentenoate. The double bond is having E configuration.
Thus, the structure of the compound is given below:
(f)
Interpretation:
The structural formula for the given compound has to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Nomenclature of anhydrides:
The nomenclature of anhydride involves replacement of the word acid with anhydride. In the case of mixed anhydrides, both acids should be named.
(f)
Explanation of Solution
The name of the compound is given below:
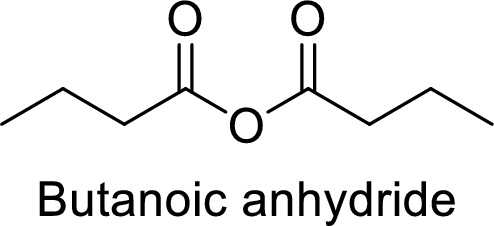
Butanoic anhydride
From the butanoic acid, acid part can be replaced with an anhydride group.
(g)
Interpretation:
The structural formula for the given compound has to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Nomenclature of amides and imides:
The acyl group bonded to a nitrogen atom is the functional group of an amide.
The naming of an amide can be done by giving the suffix –oic acid from the IUPAC name of the parent acid and adding –amide.
The location of the alkyl or aryl group attached on nitrogen atom in an amide is indicated by ‘N-‘
The indication “ N,N-di-“ is used for two identical alkyl or aryl groups on nitrogen atom
(g)
Explanation of Solution
The name of the compound is given below:
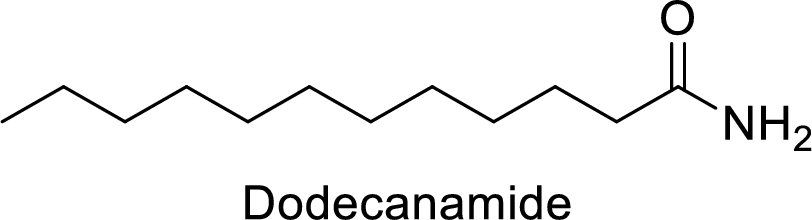
Dodecanamide:
The functional group is amide and the acyl group attached is the dodecane group.
Thus, the structure of the compound is given below:
(h)
The structural formula for the given compound has to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Nomenclature of esters of carboxylic acids:
The acyl group bonded to
The naming of an ester of a carboxylic acid is done by naming alkyl or aryl group bonded to oxygen first followed by the name of the acid in which the suffix –ic acid is replaced by the suffix –ate.
(h)
Explanation of Solution
The name of the compound is given below:
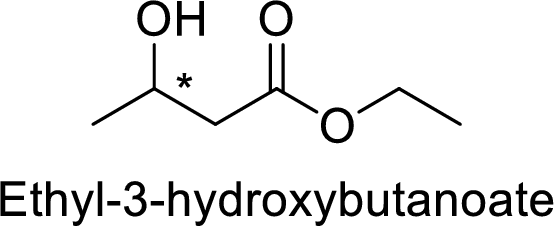
Ethyl-3-hydroxybutanoate
The alkyl group attached on oxygen atom is the ethyl group and the parent chain is the butanoate and a hydroxyl group is present in the third position.
Thus, the structure of the compound is given below:
(i)
The structural formula for the given compound has to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Nomenclature of acid chlorides:
The nomenclture of acid chlorides can be done by replacing –oic acid with –oyl chloride.
(i)
Explanation of Solution
The name of the compound is given below:
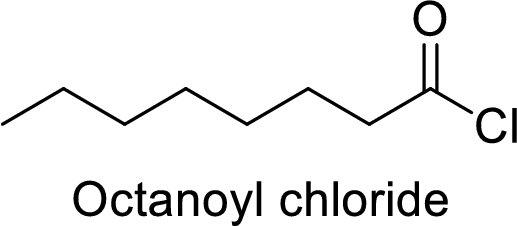
Octanoyl chloride
The acid group from the octanoic acid will be replaced by acid chloride group.
Thus, the structure of the compound is given below:
(j)
The structural formula for the given compound has to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Nomenclature of esters of carboxylic acids:
The acyl group bonded to
The naming of an ester of a carboxylic acid is done by naming alkyl or aryl group bonded to oxygen first followed by the name of the acid in which the suffix –ic acid is replaced by the suffix –ate.
(j)
Explanation of Solution
The name of the compound is given below:
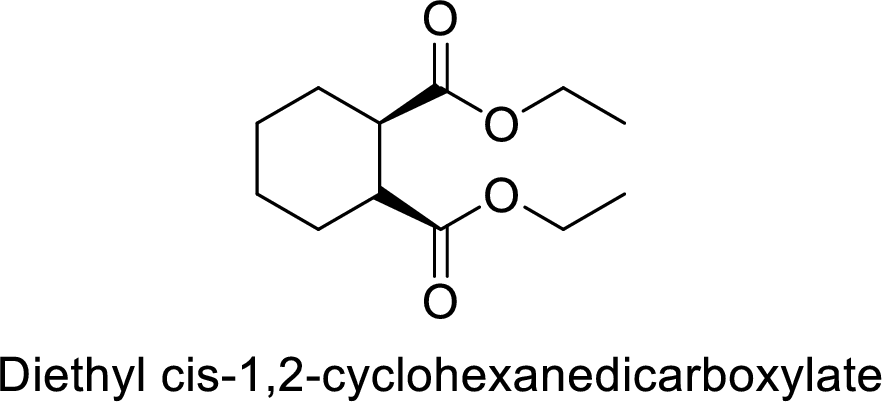
Diethyl cis-1,2-cyclohexanedicarboxylate
The alkyl group attached on oxygen atom are two ethyl groups and the parent chain is the dicarboxylate and a cyclohecxane group is present in the 1,2 position.
Thus, the structure of the compound is given below:
(k)
The structural formula for the given compound has to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Nomenclature of acid chlorides:
The nomenclture of acid chlorides can be done by replacing –oic acid with –oyl chloride.
(k)
Explanation of Solution
The name of the compound is given below:
Methanesulfonyl chloride
The acid group from the methanesulfonic acid will be replaced by acid chloride group.
Thus, the structure of the compound is given below:
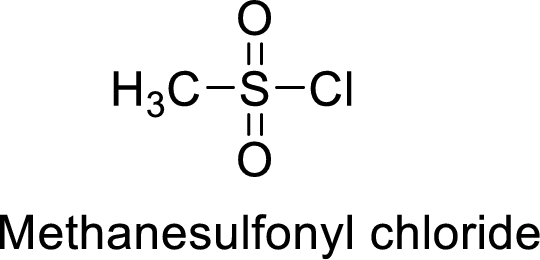
(l)
The structural formula for the given compound has to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Nomenclature of acid chlorides:
The nomenclture of acid chlorides can be done by replacing –oic acid with –oyl chloride.
(l)
Explanation of Solution
The name of the compound is given below:
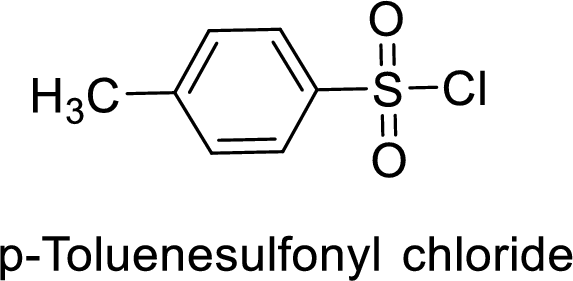
p-Toluenesulfonyl chloride
The acid group from the p-toluenesulfonic acid will be replaced by acid chloride group.
Thus, the structure of the compound is given below:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 18 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- Draw the structure of each compound.(a) o-nitroanisole (b) 2,4-dimethoxyphenol (c) p-aminobenzoic acid(d) 4-nitroanilinearrow_forwardThe odor of ripe bananas and many other fruits is due to the presence of esters. For example: Banana oil (isopentyl acetate) (a) Write the name (common or IUPAC) of the ester responsible for the fragrance of the following: pineapple, orange, apple, peach, & lavender (b) Choose one fragrant from (a) and name the alcohol and the carboxylic acid needed to synthesize this ester. (c) Show the detailed mechanism of the Fischer Esterification reaction that will be involved in the synthesis of the fragrant you have chosen in part (a).arrow_forwardDraw a structural formula for each carboxylic acid. (a) 4-Nitrophenylacetic acid (b) 4-Aminobutanoic acid (c) 4-Phenylbutanoic acid (d) cis-3-Hexenedioic acidarrow_forward
- (a) Draw the structure of the following :(i) p-Methylbenzaldehyde (ii) 4-Methylpent-3-en-2-one(b) Give chemical tests to distinguish between the following pairs of compounds :(i) Benzoic acid and Ethyl benzoate, (ii) Benzaldehyde and Acetophenone.(iii) Phenol and Benzoic acid.arrow_forward1. Draw structures corresponding to the following IUPAC names: (a) 4-Methylpentanoic acid (b) o-Hydroxybenzoic acid (c) 2,2-Dimethylpropanoyl chloride (d) trans-2-Methylcyclohexanecarboxamide (e) p-Methylbenzoic anhydride (f) p-Bromobenzonitrilearrow_forwardGive the chemical tests to distinguish between following pair of compounds : (i) Propanol and propanone (ii) Ethyl acetate and methyl acetate (iii) Benzaldehyde and benzoic acid (iv) Benzaldehyde and acetaldehyde (v) Formic acid and acetic acid (vi) Propanal and propanol (vii) Ethanoic acid and ethylethanoatearrow_forward
- How could you convert butanenitrile into the following compounds? Write each step showing the reagents needed. (a) 1-Butanol (b) Butylaminearrow_forwardCompounds that contain an N-H group associate by hydrogen bonding. (a) Do you expect this association to be stronger or weaker than that of compounds containing an O-H group? (b) Based on your answer to part (a), which would you predict to have the higher boiling point, 1-butanol or 1-butanamine?arrow_forwardPlease draw the skeletal formula of the following compounds: (A) Isobutyraldehyde (B) α-Ethyl-γ-methoxycaproaldehyde (C) 6-Hydroxyhexanal (D) 2,4-Pentanedione (E)3-Cyano-7-oxoheptanoic acidarrow_forward
- Draw a structural formula for each amine. (a) 2-Butanamine (b) 1-Octanamine (c) 2,2-Dimethyl-1-propanamine (d) 1,5-Pentanediamine (e) 2-Bromoaniline (f) Tributylaminearrow_forwardGive reasons for the following :(i) Phenol is more acidic than methanol.(ii) The C—O—H bond angle in alcohols is slightly less than the tetrahedral angle (190°28′).(iii) (CH3)3C—O—CH3 on reaction with HI gives (CH3)3C—I and CH3—OH as the main products and not (CH3)3C—OH and CH3—I.arrow_forwardPredict the major products formed when benzoyl chloride (PhCOCl) reacts with the following reagents.(a) ethanol (b) sodium acetate (c) anilinearrow_forward
 Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
