
Concept explainers
(a)
The base and the collector current in each of the transistor. Also, the power dissipation in the gate.
(a)
Answer to Problem 17.12EP
The currents in the transistors are,
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
The given diagram is shown in Figure 1
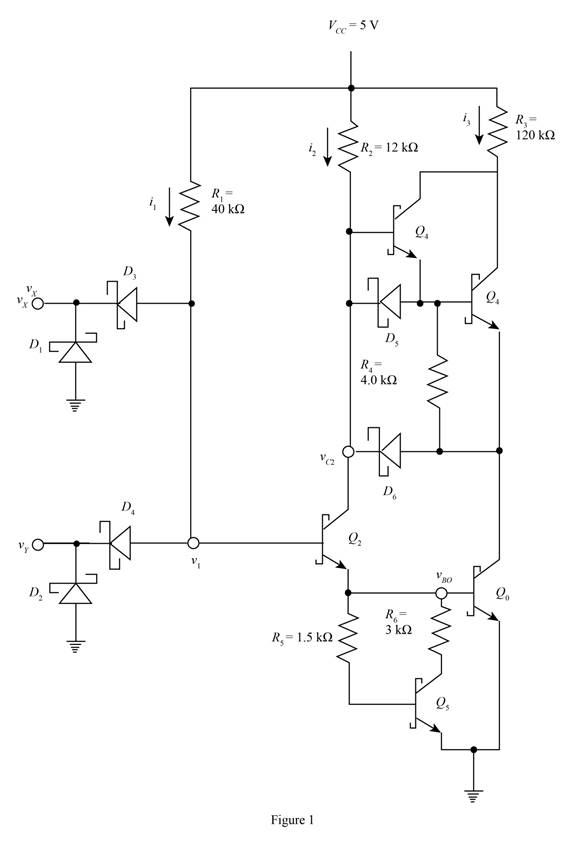
The expression to determine the value of the voltage
Substitute
The expression to determine the value of the current
Substitute
The conversion from
The conversion from
The second transistor and the output transistor are in cut off region and the current in the circuit are given by,
The expression for the value of the collector current and the base current of the output transistor is given by,
The expression for the base and the collector current of the third and the fourth transistor are given by,
The expression for the power dissipated in the circuit is given by,
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the currents in the transistors are,
(b)
The base and the collector current in each of the transistor. Also, the power dissipation in the gate.
(b)
Answer to Problem 17.12EP
The currents in the transistors are,
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
The expression to determine the value of the voltage
Substitute
The expression for the voltage
Substitute
The expression to determine the value of the current
Substitute
The expression to determine the value of the current
Substitute
The conversion from
The conversion from
The expression for the base current of the second transistor is given by,
Substitute
The expression for the collector current of the second transistor is given by,
Substitute
The fifth transistor is in the cut off region and the current in the circuit are given by,
The expression for the value of the collector current of output transistor is given by,
Substitute
The expression for the base and the collector current of the third and the fourth transistor are given by,
The expression for the power dissipated in the circuit is given by,
Substitute
The conversion from
The conversion from
Conclusion:
Therefore, the currents in the transistors are,
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 17 Solutions
Microelectronics: Circuit Analysis and Design
- 1. A SCR has a forward breakover voltage of 175V when a gate pulse of 2 mA is made to flow. Find the conduction angle if a sinusoidal voltage of 350 V peak is applied.arrow_forwardOutput voltage of an inverter is controlled by multiple pulse modulation technique. If the peak value of reference voltage is 4 V and peak value of carrier voltage is 6 V. Then the total pulse width in each half cycle is V = 6 V V₁ = 4 V T 2π otarrow_forwardi need the answer quicklyarrow_forward
- Please answer the question 1 a, b, and c with details on why it is true or false. Please make handwriting legible. Thank you.arrow_forwardintegrated circuit families (RTL, DTL, TTL, CMOS) 4. Let vx = vy = 0.1V (Logic 0), B = 25 Determine all the currents and voltages in the circuit below: 11, 12, iR, IRC, iB, v1 & vo. Vcc=5 V 84 48 = 4 ΚΩ VI Dx vx H Vy O KH Dy RB = 10 ΚΩ Figure 17.20 Basic diode-transistor logic gate D₁ D2₂ DA IRC VB ≤RC= 14 ΚΩ -OVO loarrow_forwardThe analog input channel voltage range for a PIC16 Microcontroller is limited to the positive range 0-Vref. Many situations require a digitized mapping from bipolar analog signals to unipolar signals. A simple resistive network has been designed to translate a bipolar voltage range of ±10V to a unipolar range of 0-6.6 V, assuming Vref is +6.6 V. A reasonable resistor combination is: a. None of them b. 2.212, 2.70, and 5 Kohms c. 2.212, 2.70, and 2.70 Kohms d. 1.122, 1.70, and 3.30 Kohmsarrow_forward
- Inverter.arrow_forward(a) Draw a 3-bit flash converter with Vref = 9.6V. (b) What is the digital output for Vn = 6.2V? (c) Draw the input versus output transfer curve for this converter and determine the following: 1. full scale range 2. transition voltages 3. code center for each code 4. LSB 5. resolution 6. quantization level 7. quantization interval 8. code widtharrow_forwardA 4bits Analog-digital converter with an input voltage signal ranging from (-2V to 2V). Determine the following. 1. Number of Quantization levels with their values 2. Step size. 3. SNR of Quantization 4. Quantization error. 5. Quantization level for the following values of the analog voltage (v=1.4V, -1.3V, 2V)arrow_forward
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,





