
Concept explainers
1.
Prepare the necessary
1.
Explanation of Solution
Straight-line depreciation method: The depreciation method which assumes that the consumption of economic benefits of long-term asset could be distributed equally throughout the useful life of the asset is referred to as straight-line method.
Prepare the necessary journal entries to record the given transactions as follows:
| Date | Account Title & Explanation | Debit ($) | Credit($) |
| January 2, 2016 | Trucks (1) | 160,000 | |
| Cash | 160,000 | ||
| (To record the purchase of trucks for cash) | |||
| December 31, 2016 | Depreciation expense (2) | 30,400 | |
| | 30,400 | ||
| (To record the depreciation expense incurred at the end of the accounting year) | |||
| January 1, 2017 | Cash | 4,000 | |
|
Accumulated depreciation-Trucks | 4,000 | ||
| Trucks | 8,000 | ||
| (To record the retirement of trucks ( truck retired at 2017)) | |||
| December 31, 2017 | Depreciation expense (4) | 28,880 | |
| Accumulated depreciation-Trucks | 28,880 | ||
| (To record the depreciation expense incurred at the end of the accounting year) | |||
| January 1, 2018 | Cash | 11,000 | |
|
Accumulated depreciation-Trucks | 13,000 | ||
| Trucks | 24,000 | ||
| (To record the retirement of trucks (3 trucks retired at 2018)) | |||
| December 31, 2018 | Depreciation expense (4) | 24,320 | |
| Accumulated depreciation-Trucks | 24,320 | ||
| (To record the depreciation expense incurred at the end of the accounting year) | |||
| January 1, 2019 | Cash | 19,000 | |
|
Accumulated depreciation-Trucks | 29,000 | ||
| Trucks | 48,000 | ||
| (To record the retirement of trucks (6 trucks retired at 2019)) | |||
| December 31, 2019 | Depreciation expense (4) | 15,200 | |
| Accumulated depreciation-Trucks | 15,200 | ||
| (To record the depreciation expense incurred at the end of the accounting year) | |||
| January 1, 2020 | Cash | 6,000 | |
|
Accumulated depreciation-Trucks | 34,000 | ||
| Trucks | 40,000 | ||
| (To record the retirement of trucks (5 trucks retired at 2020)) | |||
| December 31, 2020 | Depreciation expense (4) | 7,600 | |
| Accumulated depreciation-Trucks | 7,600 | ||
| (To record the depreciation expense incurred at the end of the accounting year) | |||
| January 1, 2021 | Cash | 4,000 | |
|
Accumulated depreciation-Trucks | 20,000 | ||
| Trucks | 24,000 | ||
| (To record the retirement of trucks (3 trucks retired at 2021)) | |||
| December 31, 2021 | Depreciation expense (4) | 3,040 | |
| Accumulated depreciation-Trucks | 3,040 | ||
| (To record the depreciation expense incurred at the end of the accounting year) | |||
| January 1, 2022 | Cash | 1,000 | |
|
Accumulated depreciation-Trucks | 15,000 | ||
| Trucks | 16,000 | ||
| (To record the retirement of trucks (2 trucks retired at 2022)) | |||
| December 31, 2022 | Loss on disposal of property, plant and equipment (6) | 5,560 | |
| Accumulated depreciation-Trucks | 5,560 | ||
| (To record the loss on disposal of property, plant and equipment) |
Table (1)
Working note (1):
Calculate the total cost of trucks.
Working note (2):
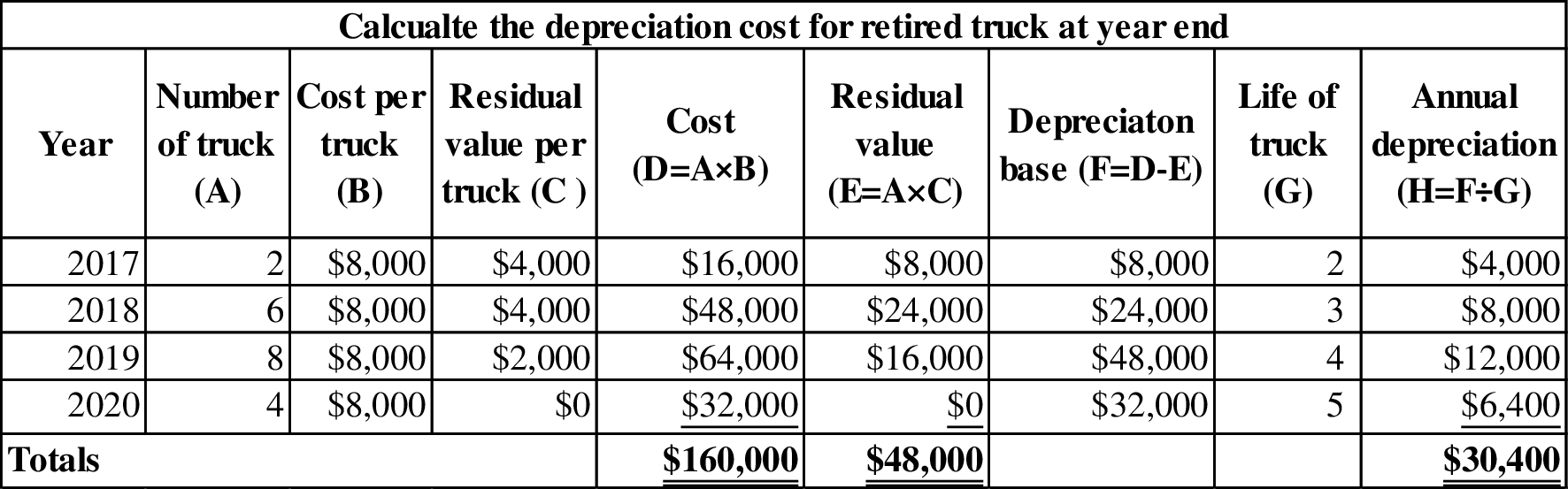
Figure (1)
Working note (3):
Calculate the depreciation rate.
Working note (4):
Calculate the depreciation expense after retirement of truck for each year.
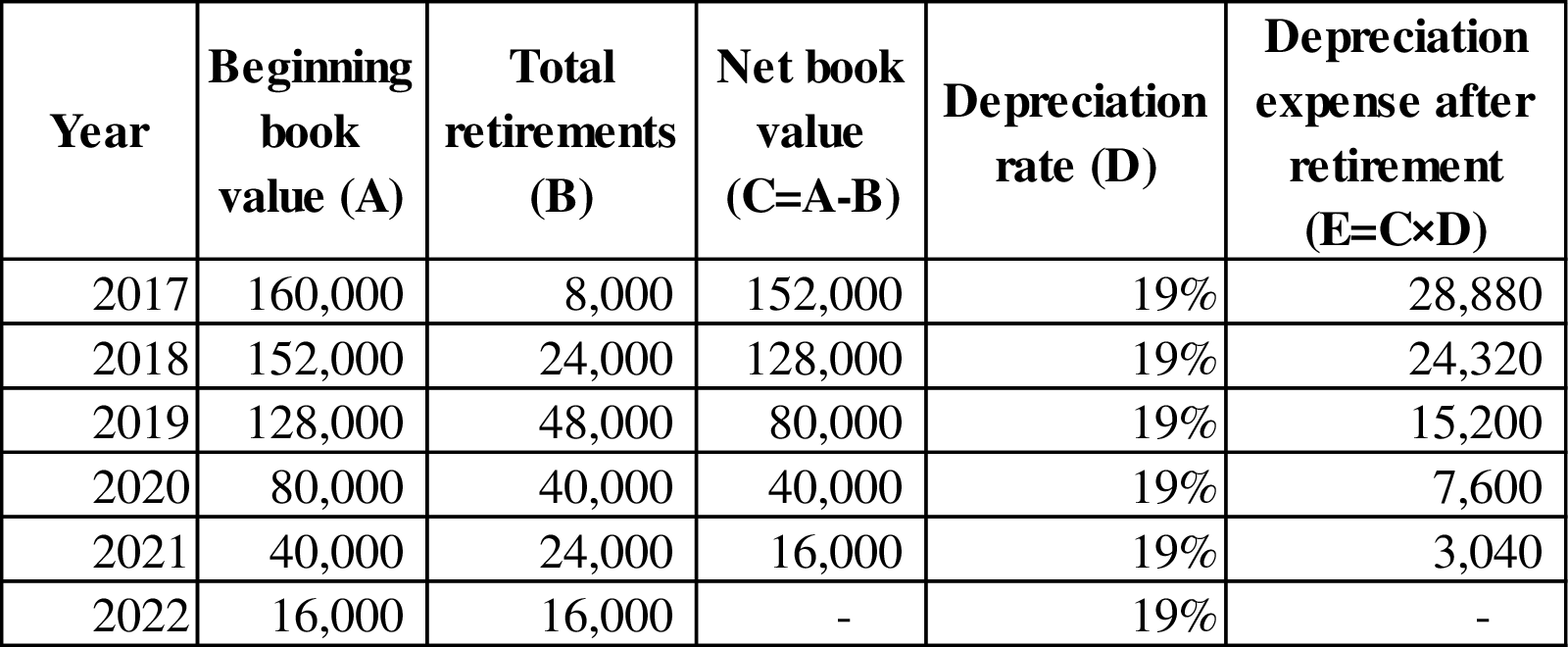
Figure (2)
Working note (5):
Calculate the total accumulated depreciation incurred at the time of retirement of truck and total depreciation expense after retirement of truck.
| Year | Accumulated depreciation incurred at the time of retirement of truck ($) | Depreciation expense for each year ($) |
| 2016 | $0 | $30,400 (2) |
| 2017 | $4,000 | $28,880 (4) |
| 2018 | $13,000 | $24,320 (4) |
| 2019 | $29,000 | $15,200 (4) |
| 2020 | $34,000 | $7,600 (4) |
| 2021 | $20,000 | $3,040 (4) |
| 2022 | $15,000 | $0 |
| Total depreciation | $115,000 | $109,440 |
Table (2)
Working note (6):
Calculate the loss on disposal of property, plant and equipment.
2.
Prepare necessary journal entries for all 6 years, if trucks are retired at $1,600 each.
2.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare necessary journal entries for all 6 years, if trucks are retired at $1,600 each as follows:
| Date | Account Title & Explanation | Debit ($) | Credit($) |
| January 2, 2016 | Trucks (1) | 1,60,000 | |
| Cash | 1,60,000 | ||
| (To record the purchase of trucks for cash) | |||
| December 31, 2016 | Depreciation expense (7) | 32,000 | |
| Accumulated depreciation-Trucks | 32,000 | ||
| (To record the depreciation expense incurred at the end of the accounting year) | |||
| January 1, 2017 | Cash | 4,000 | |
|
Accumulated depreciation-Trucks | 4,000 | ||
| Trucks | 8,000 | ||
| (To record the retirement of trucks ( truck retired at 2017)) | |||
| December 31, 2017 | Depreciation expense (8) | 30,400 | |
| Accumulated depreciation-Trucks | 30,400 | ||
| (To record the depreciation expense incurred at the end of the accounting year) | |||
| January 1, 2018 | Cash | 11,000 | |
|
Accumulated depreciation-Trucks | 13,000 | ||
| Trucks | 24,000 | ||
| (To record the retirement of trucks (3 trucks retired at 2018)) | |||
| December 31, 2018 | Depreciation expense (8) | 25,600 | |
| Accumulated depreciation-Trucks | 25,600 | ||
| (To record the depreciation expense incurred at the end of the accounting year) | |||
| January 1, 2019 | Cash | 19,000 | |
|
Accumulated depreciation-Trucks | 29,000 | ||
| Trucks | 48,000 | ||
| (To record the retirement of trucks (6 trucks retired at 2019)) | |||
| December 31, 2019 | Depreciation expense (8) | 16,000 | |
| Accumulated depreciation-Trucks | 16,000 | ||
| (To record the depreciation expense incurred at the end of the accounting year) | |||
| January 1, 2020 | Cash | 6,000 | |
|
Accumulated depreciation-Trucks | 34,000 | ||
| Trucks | 40,000 | ||
| (To record the retirement of trucks (5 trucks retired at 2020)) | |||
| December 31, 2020 | Depreciation expense (8) | 8,000 | |
| Accumulated depreciation-Trucks | 8,000 | ||
| (To record the depreciation expense incurred at the end of the accounting year) | |||
| January 1, 2021 | Cash | 4,000 | |
|
Accumulated depreciation-Trucks | 20,000 | ||
| Trucks | 24,000 | ||
| (To record the retirement of trucks (3 trucks retired at 2021)) | |||
| December 31, 2021 | Depreciation expense (8) | 800 | |
| Accumulated depreciation-Trucks | 800 | ||
| (To record the depreciation expense incurred at the end of the accounting year) | |||
| January 1, 2022 | Cash | 1,000 | |
|
Accumulated depreciation-Trucks | 15,000 | ||
| Trucks | 16,000 | ||
| (To record the retirement of trucks (2 trucks retired at 2022)) | |||
| December 31, 2022 | Loss on disposal of property, plant and equipment (12) | 2,200 | |
| Accumulated depreciation-Trucks | 2,200 | ||
| (To record the loss on disposal of property, plant and equipment) |
Table (3)
Working note (7):
Calculate the group depreciation cost under straight line method:
Working note (8):
Calculate the depreciation rate.
Working note (9):
Calculate the depreciation expense after retirement of truck for each year.
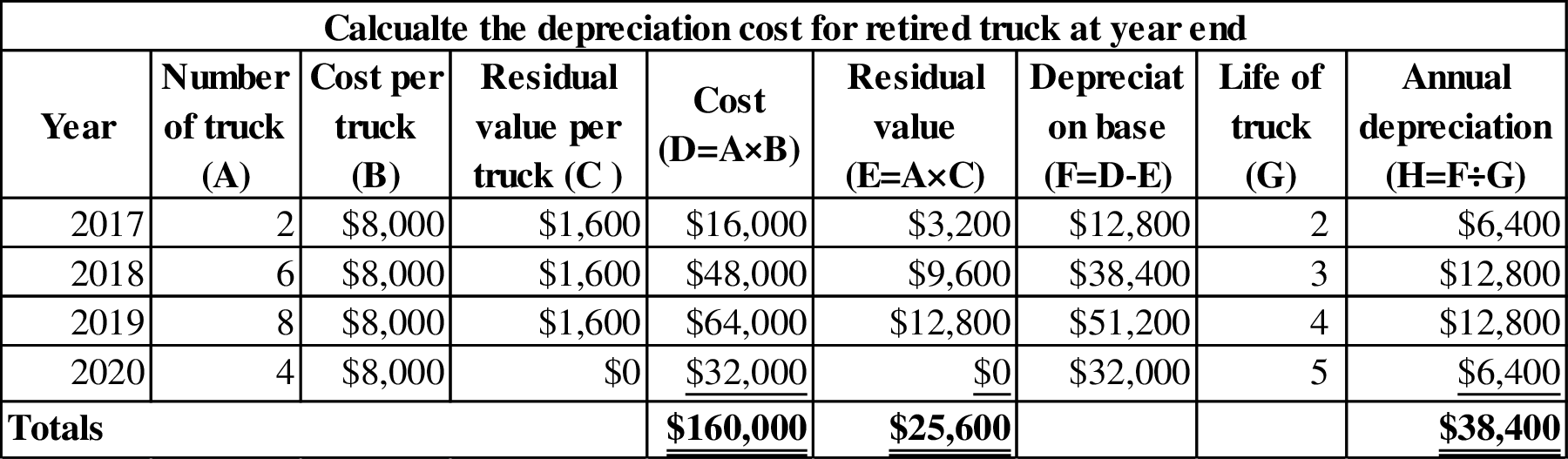
Figure (3)
Note: Depreciation expense after retirement for the year 2021 is $800, because the amount of $3,200 would reduce the book value of remaining two trucks (2 trucks) in the year 2022. Hence, the depreciation expense for 2021 is 800
Working note (10):
Calculate the depreciation expense after retirement of truck for each year.
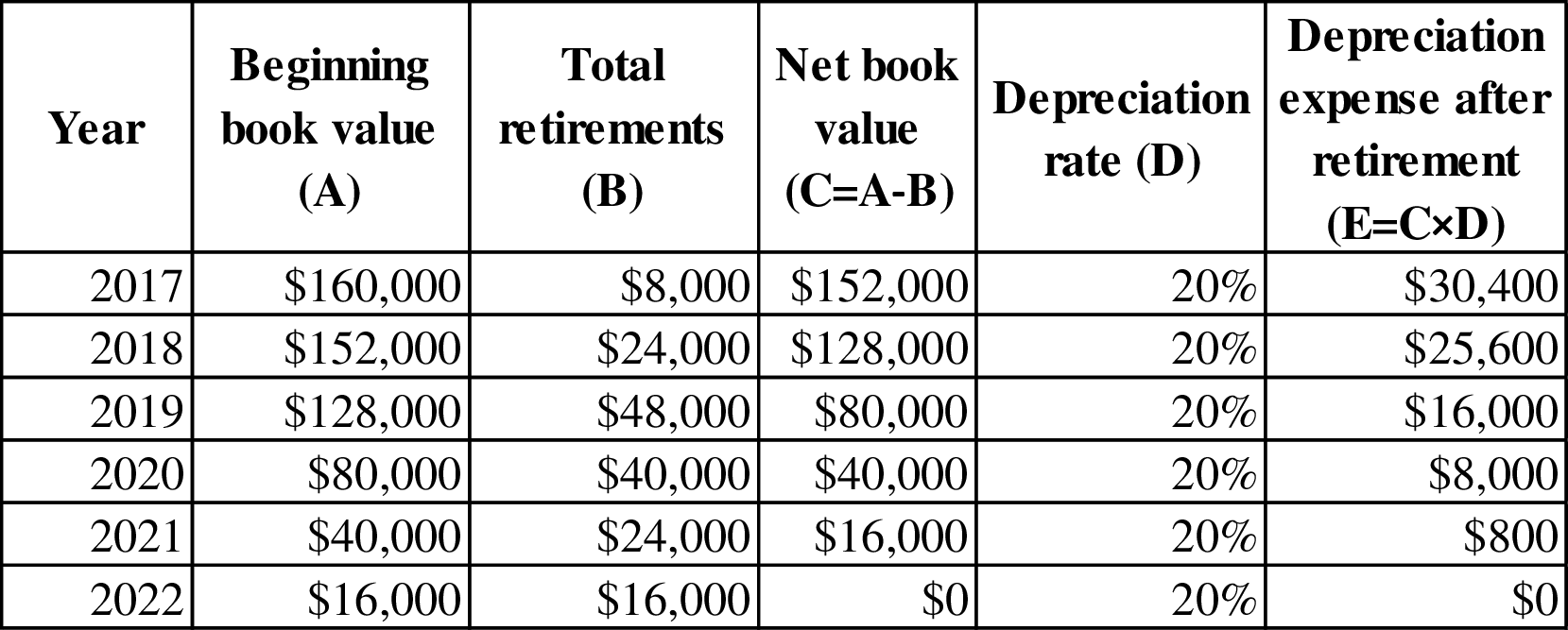
Figure (4)
Working note (11):
Calculate the total accumulated depreciation incurred at the time of retirement of truck and total depreciation expense after retirement of truck.
| Year | Accumulated depreciation incurred at the time of retirement of truck ($) | Depreciation expense for each year ($) |
| 2016 | $0 | $32,000 (7) |
| 2017 | $4,000 | $30,400 (10) |
| 2018 | $13,000 | $25,600 (10) |
| 2019 | $29,000 | $16,000 (10) |
| 2020 | $34,000 | $8,000 (10) |
| 2021 | $20,000 | $800 (10) |
| 2022 | $15,000 | $0 |
| Total depreciation | $115,000 | $112,800 |
Table (4)
Working note (12):
Calculate the loss on disposal of property, plant and equipment.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
Cengagenowv2, 1 Term Printed Access Card For Wahlen/jones/pagach’s Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And Analysis, 2017 Update, 2nd
- On January 2, 2016, the Jackson Company purchased equipment to be used in its manufacturing process. The equipment has an estimated life of eight years and an estimated residual value of $30,625. The expenditures made to acquire the asset were as follows: Purchase price $154,000 Freight charges 2,000 Installation charges 4,000 Jackson’s policy is to use the double-declining-balance (DDB) method of depreciation in the early years of the equipment’s life and then switch to straight line halfway through the equipment’s life. Required: 1. Calculate depreciation for each year of the asset’s eight-year life. 2. Discuss the accounting treatment of the depreciation on the equipment.arrow_forwardWardell Company purchased a minicomputer on January 1, 2013, at a cost of $50,000. The computer was depreciated using the straight-line method over an estimated seven-year life with an estimated residual value of $4,000. On January 1, 2016, the estimate of useful life was changed to a total of 11 years, and the estimate of residual value was changed to $800. Question Journal entries to record depreciation for 2016 would include: Debit to Depreciation Expense - Computers of $7,143 Credit to Accumulated Depreciation - Computers of $3,686 Debit to Accumulated Depreciation - Computers of $6,571 Debit to Depreciation Expense - Computers of $4,707arrow_forwardThe Peridot Company purchased machinery on January 2, 2014, for $800,000. A five-year life was estimated and no residual value was anticipated. Peridot decided to use the straight-line depreciation method and recorded $160,000 in depreciation in 2014 and 2015. Early in 2016, the company revised the total estimated life of the machinery to eight years. Required: 1. What type of change is this? 2. Briefly describe the accounting treatment for this change. 3. Determine depreciation for 2016.arrow_forward
- Rottino Company purchased a new cutting machine on January 1, 2017, at $17,000, paid in cash. It has been depreciated using the double-declining-balance method based on an estimated salvage value of $0 and an estimated useful life of 5 years. Prepare Rottino Company's journal entries to record the disposal of the machine on October 31, 2018, in these two independent situations (show your calculations to prove the result): Requirement: (i) Sold the machine for $7.600 cash. (ii) Exchange the old cutting machine with cash of $1,000 for a new cutting machine. The old machine had a fair value of $7,000.arrow_forwardHowarth Manufacturing Company purchased a lathe on June 30, 2014, at a cost of $80,000. The residual valueof the lathe was estimated to be $5,000 at the end of a five-year life. The lathe was sold on March 31, 2018, for$17,000. Howarth uses the straight-line depreciation method for all of its plant and equipment. Partial-year depreciation is calculated based on the number of months the asset is in service.Required:1. Prepare a schedule to calculate the gain or loss on the sale.2. Prepare the journal entry to record the sale.arrow_forwardLinton Company purchased a delivery truck for $S34,000 on January 1, 2014. The truck has an expected salvage value of $2,000, and is expected to be driven 100,000 miles over its estimated useful life of 10 years. Actual miles driven were 19,000 in 2014 and 16,000 in 2015. Instructions a) Compute depreciation expense for 2014 and 2015 using (1) the straight-line method and (2) the units-of-activity method (b) Assume that Linton uses the straight-line method, Prepare the journal entry to record 2014 depreciation.arrow_forward
- The Peridot Company purchased machinery on January 2, 2016, for $800,000. A five-year life was estimatedand no residual value was anticipated. Peridot decided to use the straight-line depreciation method and recorded$160,000 in depreciation in 2016 and 2017. Early in 2018, the company revised the total estimated life of themachinery to eight years.Required:1. What type of change is this?2. Briefly describe the accounting treatment for this change.3. Determine depreciation for 2018.arrow_forwardWhippet Bus Lines uses the units-of-activity method in depreciating its buses. One bus was purchased on January 1, 2017, at a cost of $117,000. Over its 4-year useful life, the bus is expected to be driven 210,000 miles. Salvage value is expected to be $7,800. (a) Compute the depreciation cost per unit. (Round answer to 3 declmal places, e.g. 6.251) Depreciation cost per unit 24 eTextbook and Media Attempts: 0 of 3 used Submit Answer Save for Laterarrow_forwardOn January 1, 2009, Neal Corporation acquired equipment at a cost of $540,000. Neal adopted the sum-of-the-years’-digits method of depreciation for this equipment and had been recording depreciation over an estimated life of eight years, with no residual value. At the beginning of 2012, a decision was made to change to the straight-line method of depreciation for this equipment. The depreciation expense for 2012 would be Select one: a. $108,000 b. $28,125. c. $67,500 d. $45,000.arrow_forward
- Howarth Manufacturing Company purchased a lathe on June 30, 2012, at a cost of $80,000. The residual value of the lathe was estimated to be $5,000 at the end of a five-year life. The lathe was sold on March 31, 2016, for $17,000. Howarth uses the straight-line depreciation method for all of its plant and equipment. Partial-year depreciation is calculated based on the number of months the asset is in service. Required: 1. Prepare the journal entry to record the sale. 2. Assuming that Howarth had instead used the sum-of-the-years’-digits depreciation method, prepare the journal entry to record the sale.arrow_forwardOn January 1, 2018, World Inc. purchased five machines at a cost of $14,000 each. The company adopted the group (straight-line) depreciation method, using an eight-year life with a $2,800 salvage value per machine. Correct depreciation was recorded in 2016 and 2017. On January 1, 2020, one of the machines was sold for $6,500. On January 3, 2020, a new unrelated piece of equipment was purchased for $15,000 with no salvage value and a six-year life. It will be depreciated using the straight-line method. Required: Prepare appropriate journal entries for a. January 1, 2020 b. December 31, 2020, to record depreciation expensearrow_forwardThe Snack Stop had the following long-term asset balances as of January 1, 2015: All of the assets were purchased at the beginning of 2013. The building is depreciated over a 20-year service life using the straight-line method and estimating no residual value. The equipment is depreciated over a 10-year useful life using the double-declining-balance method with an estimated residual value of $10,000. The patent is estimated to have an 8-year service life with no residual value and is amortized using the straight-line method. Depreciation and amortization has already been calculated for the first two years.Required:1. For the year ended December 31, 2015, record depreciation expense for buildings and equipment. Land is not depreciated.2. For the year ended December 31, 2015, record amortization expense for the patent.3. Calculate the book value for each of the four long-term assets at December 31,2015.arrow_forward
