
Concept explainers
Two creates, A and B, are in an elevator as shown. The mass of crate A is greater than the mass of create B.
- The elevator moves downward at constant speed.
i. How does the acceleration of crate A compare to that of crate B? Explain.
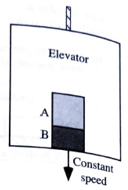
ii. In the spaces provided below, draw and label separate free-body diagrams for the crates.

iii. Rank the forces on the crates according to magnitude, from largest to smallest. Explain your reasoning, including how you used
iv. In the spaces provided at right, draw arrows to indicate the direction of the net force on each crate. If the net force on either crate is zero crate is zero, state so explicitly. Explain.

Is the magnitude of the net force on crate Agreater than, less than, or equal to that on crate B? Explain.
Learn your wayIncludes step-by-step video

Chapter 16 Solutions
Tutorials in Introductory Physics
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol. 1 (Chs 1-21) (4th Edition)
College Physics (10th Edition)
University Physics Volume 1
Modern Physics
Life in the Universe (4th Edition)
Conceptual Physics (12th Edition)
- The figure below shows a massless string wound around a spool of radius r. The mass falls with a constant acceleration, a. What is the equation for y in terms of θ and r? What is the equation for v in terms of ω and r? What is the equation for a in terms of α and r? Start from the expression for uniform acceleration in the y-direction for the falling mass and clearly show any steps or substitutions you make.arrow_forwardFor the given several questions, consider the dot diagram below for the motion of an object along a horizontal surface. The motion is divided into several time intervals, each labeled with a letter. 1. During which time interval(s), if any, are there no forces acting upon the object? List all that apply. 2. During which time interval(s), if any, are the forces acting upon the object balanced? List all that apply. 3. During which time interval(s), if any, is there a net force acting upon the object? List all that apply. 4. During which time interval(s), if any, is the net force acting upon the object directed toward the right? List all that apply. 5. During which time interval(s), if any, is the net force acting upon the object directed toward the left? List all that apply.arrow_forwardDirections: Write TRUE is the statement is correct but if it is false, change the underlined words with the correct answer. 1. A force is a push or pull 2. Force is a galar quantity 3. The unit of force is Newton (N) 4. In general, a body can have several forces acting on it at the same time 5. Inertial frame of reference are reference frame where Newton's First law are observable. 6. Another effect of a balanced force, equilibrium, is that a body accelerates. 7. The heavier the object, the lesser the inertia. 8. Forces acting on a body are unbalanced if the resultant force is not zero 9. In an inertial reference frame, No forces should be exerted within the frame. 10. Normal force is lateral in nature. П. Identify Action Reaction Pairs A student in hot air balloon ascends vertically at a constant speed. Consider the four forces in this situation: Fl= the weight of the baloon F2= the weight of the student F3= the force of the student pulling on the earth F4= the support force of the…arrow_forward
- PROBLEM SET # 8: PARTICLE UNDER A NET FORCE On the space provided, present correct and organized solutions to the following answered problems. Box the final answers. Detach each page neatly and submit to your instructor. A 2.5-kg concrete block sliding on a vertical wall is being acted upon by a force P as shown in the figure below. Assume that the coefficient of kinetic friction between the 2. concrete block and the wall is 0.88. 148° (a) Draw the free-body diagram of the concrete block. (b) If the normal force exerted by the wall to the concrete block is 20.0 N, what would be the magnitude of the external force P, and (Ans: 37.74 N) (c) The acceleration of the block? (Ans: -15.56 m/s)arrow_forwardthe problem, explain in words as much as you do know. 12. The inclined plane shown is tilted at an angle a = 20° with respect to the horizontal. Mass m, = 25 kg and m2 = 10 kg. A. If mass m2 is moving downward and the tension in the rope connecting the masses has magnitude 140 N, what is the coefficient of kinetic friction ug between mass m, and the ramp? B. If mass m, is moving down the ramp when the rope connecting the masses is cut, what is the acceleration of mass m, after the rope goes slack? Is the mass slowing down or speeding up? Assume that uy has the same value you calculated in part A. If you weren't able to solve part A, use uy = 0.5 to solve part B. 140N m2arrow_forwardConsider the cart on a frictionless track, shown below. For each question, one or more features of the setup have been changed. Assume that there is no friction. You are to indicate what effect the change will have on the acceleration compared to the original setup, which is shown below. (The picture is the original setup) 1. What happens to the acceleration if the mass of the cart is increased to 14kg, but the towing force remains the same? A. The acceleration will be greater than the original setup. B. The acceleration will be less than the original setup. C. The acceleration remains the same. D. It's not possible to tell.arrow_forward
- Your diagram from Knowledge Check: Static Friction, Part 1 should have looked like this: s,max 1. A block of mass 9.0 kg rests on a table with μ = 0.3. A force # applied pushes the block. = 26.49 (a) Calculate the maximum force of static friction. Enter to 2 significant figures Enter to 2 significant figures X fs 1. Drag and drop the heads and tails of the vectors to construct the free-body diagram. 2. Note that angles do not need to be exact and magnitudes are not considered. N; 90° + Fapplied; 0° N (b) If Fapplied = 5 N pulls the block, calculate the magnitude of force of friction f . Assume all quantities are correct to significant figures. = 26.49 fs; 180° N mg; 270°arrow_forwardBlocks A and B are held on the palm of your outstretched hand as you lift them straight up atconstant speed. Assume mB>mA and that mhand=0.a. Draw separated free-body diagrams for A, B and your hand. Show all vertical forces andmake sure the vector lengths indicate the relative sizes of the forces.b. Rank in order from largest to smallest all of the vertical forces. Explain your reasoning.Now the hand is lifting the blocks so they have an upward acceleration.c. Draw separated free-body diagrams for A, B and your hand. Show all vertical forces andmake sure the vector lengths indicate the relative sizes of the forces.d. Rank in order from largest to smallest all of the vertical forces for when the block isaccelerating. Explain your reasoning.arrow_forwardConsider the cart on a frictionless track, shown below. For each question, one or more features of the setup have been changed. Assume that there is no friction. You are to indicate what effect the change will have on the acceleration compared to the original setup, which is shown below. (The picture is the original setup) 4. What happens to the acceleration if both the mass of the cart is quadrupled and the towing force is doubled? A. The acceleration will be greater than the original setup. B. The acceleration will be less than the original setup. C. The acceleration remains the same. D. It's not possible to tell.arrow_forward
- You need to push the couch 4 m to the other side of the room. After the initial push to get it going you push on the 90 Kg couch with a steady horizontal force of 600 N. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the couch and the floor is 0.6. Calculate the answer for each of the following and explain/show your reasoning. What is the magnitude and direction of the frictional force on the couch? What is the magnitude and direction of the net force on the couch? What is the magnitude and direction of the acceleration of the couch? Advanced) How much time did it take to push the couch the 4 m?arrow_forwardA Box sits at rest on a rough 33 degrees inclined plane. Draw the free body diagram showing all the forces acting on the box using system of Coordinates x,y axis for each case. How would the diagram change if the box was sliding down the plane ? Draw the free body diagram for this case again. How would it change if it was sliding up the incline after given an initial speed ? Draw Free Body diagram for part D again. Calculate the acceleration for part A if m = 50kg and Uk = 0.25 _________arrow_forwardFor this question you may draw diagrams if necessary to explain your answer. 1. a. Explain clearly Newton's First Law, Second Law and Third Law of motion. b. Give two real life examples for each of the law. c. A rocket moving in space at uniform velocity explain why the net force on the ship is zero or E F = 0. d. Explain how the rocket can change direction.arrow_forward
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON





