
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
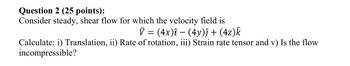
Transcribed Image Text:Question 2 (25 points):
Consider steady, shear flow for which the velocity field is
V = (4x)î − (4y)ĵ + (4z)k
Calculate: i) Translation, ii) Rate of rotation, iii) Strain rate tensor and v) Is the flow
incompressible?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- IRCIC Next Generat... A TASHRM The velocity field for a fluid flow is given by following expression: V (0.2x² +2y+2.5)i +(0.5x+2y -6)j+(0.15x +3y + z)k The strain tensor at (2,1,-1) will be: 0.8 1.25 0.30 a)-1.25 -4 0.30 -1 0.8 1.25 0.70) b) 1.25 4 2 0.30 -2 0.8 1.25 0.30 c) | 1.25 4 -2 0.30 -2 0.8 1.25 0.30 O Tvne aere to searcharrow_forwardTHREE DIMENSIONAL ( NEED NEAT HANDWRITTEN SOLUTION ONLY OTHERWISE DOWNVOTE).arrow_forwardConsider steady, incompressible, parallel, laminar flow of a film of oil falling slowly down an infinite vertical wall. The oil film thickness is h, and gravity acts in the negative z-direction. There is no applied (forced) pressure driving the flow. The oil falls by gravity alone.a) Simplify the continuity equation to show that w = w(x).b) Simplify the Navier-Stokes equations to model this flow field.c) Obtain expression for the liquid velocity profiled) Find the volume flow rate per unit widthe) What is the pressure in the oil film ?arrow_forward
- i didnt understand 3 fluid mechanics questions. please help me :) i will send of the three partarrow_forwardPLS SHOW ME FULL STEPS SIR PLS ANSWER WITHIN 30 MIN SIR SUBJECT (FLUID MECH 2)arrow_forwardAn incompressible velocity field is given by u=a(x°y²-y), v unknown, w=bxyz where a and b are constants. (a)What is the form of the velocity component for that the flow conserves mass? (b) Write Navier- Stokes's equation in 2-dimensional space with x-y coordinate system.arrow_forward
- C (C is a constant) 4xy)=xy-2y2+2x2+C (C is a constant) O C. O d. 4(xy)=xy3-2y2+2x2+C (C is a constant) Clear my choice The stream function for a two-dimensional incompressible flow field is y = - 2(x-y), what is the corresponding velocity potential equal? Oa. p = 2(x - y) + C O b. p = 2(x + y) + C p = (x + y) + C O d. p = (x - y) + C Clear my choice Consider a steady two-dimensional, incompressible flow of a Newtonian fluid with the veloc -x and v = y – x, Find the pressure field P(x, y) if the pressure at point O (x= 0, y = field: u = is equal to PO and the velocity field satisfies the Navier-Stokes equations.arrow_forwardConsider a 2-dimensional incompressible flow field. The vertical component of velocity forthe flow field is given by 2y. The pressure at (x, y) = 0,0 is given by 3 bar absolute. The densityof the fluid is 1.2 Kg/m3 . Find. a) x-component of velocity; b) acceleration at point (x, y) = 2,1;c) pressure gradient at the same point; d) pressure gradient along the x-axis; e) check whetherthe flow is irrotational; f) find the potential function; g) find the stream function; h) equationfor streamline and sketch few streamlines.arrow_forwardA Fluid Mechanics, Third Edition - Free PDF Reader E3 Thumbnails 138 FLUID KINEMATICS Fluid Mechanies Fundamenteis and Applicationu acceleration); this term can be nonzero even for steady flows. It accounts for the effect of the fluid particle moving (advecting or convecting) to a new location in the flow, where the velocity field is different. For example, nunan A Çengel | John M. Cinbala consider steady flow of water through a garden hose nozzle (Fig. 4-8). We define steady in the Eulerian frame of reference to be when properties at any point in the flow field do not change with respect to time. Since the velocity at the exit of the nozzle is larger than that at the nozzle entrance, fluid particles clearly accelerate, even though the flow is steady. The accel- eration is nonzero because of the advective acceleration terms in Eq. 4-9. FLUID MECHANICS FIGURE 4-8 Flow of water through the nozzle of a garden hose illustrates that fluid par- Note that while the flow is steady from the…arrow_forward
- a) Contsioer THE velbeine Fieb: V- xy i+ xyj (ij UNIT VECTORS AbNG X-, AND Y DIRECTTONS) IF THE FIUID DENSITY is CONOTANT, is CONSERVATION OF MASS SATİSFİED! CONSIDER THE FolbwiNG STREAM FUNCTION is THE Flow FielD IRROTATIONAL ? WHAT is THE VelocitY POTENTIAl ? C) CONSIDER THE STREAM FUNCTION DESCRIBING A Flow Field iN THE UPPER plaNE xy yoo. FOR THERE is A plATE @ y=0. ) i) is No-slip SATİS FIED @ PIATE (y=o) DRAW THE STREAMLINES FIND THE PRESSURE AS A FUNCTION OF THE PRESSURE O ORIGIN Po. (ASSOME NO GRAVitr).arrow_forwardQuestion 3 (a) A two-dimensional flow velocity field in the domain with non-dimensional coordinates x > 0 and y > 0 is defined as: v = -Upxy i+ Upxy j where i and j are the unit vectors in the x- and y-directions respectively and Uo is a constant with units m/s. (i) Determine the magnitude and direction of the velocity at the point (1,1). (ii) Find the equation of the streamlines.arrow_forwardA incompressible, steady, velocity field is given by the following components in the x-y plane: u = 0.205 + 0.97x + 0.851y ; v = v0 + 0.5953x - 0.97y How would I calculated the acceleration field (ax and ay), and the acceleration at the point, v0= -1.050 ? Any help would be greatly appreciated :)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY