
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
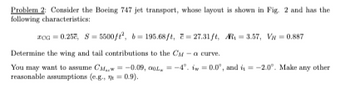
Transcribed Image Text:Problem 2: Consider the Boeing 747 jet transport, whose layout is shown in Fig. 2 and has the
following characteristics:
xoa 0.25, 8 5500/2, b 195.68ft, 27.31ft, AR, 3.57, V = 0.887
Determine the wing and tail contributions to the CM-a curve.
You may want to assume CM,
reasonable assumptions (e.g.,
-0.09, 0, -4°. i=0.0°, and i = -2.0°. Make any other
0.9).
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Consider a thin aerofoil, with mean camber line in the form of a circular arc, with mean camber given by the image provided. f is the maximum camber Find the lift coefficient, the zero lift AOA, the moment coefficient about the leading edge, the moment coefficient about the aerodynamic centre and the location of theaerodynamic centrearrow_forwardShow stepsarrow_forwardA 1:7 scale model simulates the operation of a large turbine that is to generate200 kW with a flow rate of 1.5 m3/s. What flow rate should be used in the model, andwhat power output is expected?(a) Water at the same temperature is used in both model and prototype.(b) The model water is at 25°C and the prototype water is at 10°C.arrow_forward
- Please do not rely too much on chatgpt, because its answer may be wrong. Please consider it carefully and give your own answer. You can borrow ideas from gpt, but please do not believe its answer.Very very grateful! Please do not copy other's work,i will be very very grateful!!arrow_forwardCornering force and drag force on tires. Consider a tire that has lateral force behavior like the one in the following figure. Assuming that the drift angle is 4 degrees and the normal force F = 5000N, calculate the cornering and drag forces on the tire.arrow_forwardParrow_forward
- 8. A spherical balloon is 40 ft in diameter and surrounded by air at 60°F and 29.92 in Hg abs. (a) If the balloon is filled with hydrogen at a temperature of 70°F and atmospheric pressure, what total load can it lift? (b) If it contains helium instead of hydrogen, other conditions remaining the same, what load can it lift? (c) Helium is nearly twice as heavy as hydrogen. Does it have half the lifting force? R for hydrogen is 766.54 and for helium is 386.04 ft.lb/lb.°R. Ans. (a) 2381 lb; (b) 2209 lbarrow_forwardParrow_forwardThis is a practice hw question not graded!!arrow_forward
- (5) A pickup truck has a five liter, V6, SI engine operating at 2400 r.p.m. the compression ratio rc = 10.2:1, the volumetric efficiency y = 0.91, and the bore and stroke related as stroke S = 0.92 B. calculate :- (a) stroke length. (cm) (b) Average piston speed. m sec (c) Clearance volume of one cylinder. kg (d) Air flow rate into engine. sec (cm³)arrow_forwardOO O0I 94) 8:50 EXAMPLE Given: A sports car has a mass of 2 Mg and an engine efficiency of ɛ = 0.65. Moving forward, the wind creates a drag resistance on the car of F, = 1.2v2 N, where v is the velocity in m/s. The car accelerates at 5 m/s?, starting from rest. Find: The engine's input power when t = 4 s. Plan: 1) Draw a free body diagram of the car. 2) Apply the equation of motion and kinematic equations to find the car's velocity at t = 4 s. 3) Determine the power required for this motion. 4) Use the engine's efficiency to determine input power. nashat N •..arrow_forward(b) A wind-tunnel experiment is performed on a small 1:5 linear-scale model of a car, in order to assess the drag force F on a new full-size car design. A dimensionless "drag coefficient" Ca is defined by C, =- pu'A where A is the maximum cross-sectional area of the car in the flow. With the model car, a force of 3 N was recorded at a flow velocity u of 6 m s. Assuming that flow conditions are comparable (i.e., at the same Reynolds number), calculate the expected drag force for the full-sized car when the flow velocity past it is 31 m s (equivalent to 70 miles per hour). [The density of air p= 1.2 kg m.]arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY