
Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course List)
13th Edition
ISBN: 9781337395083
Author: Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. Daves
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
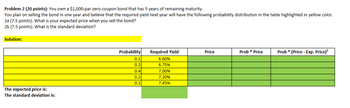
I must use formulas and cell references PV of Payments when computing all values in the green cells
You own a $1,000-par zero-coupon bond that has 5 years of remaining maturity.
You plan on selling the bond in one year and believe that the required yield next year will have the following probability distribution in the table highlighted in yellow color.
2a (7.5 points). What is your expected price when you sell the bond?
2b (7.5 points). What is the standard deviation?
Transcribed Image Text:Problem 2 (20 points): You own a $1,000-par zero-coupon bond that has 5 years of remaining maturity.
You plan on selling the bond in one year and believe that the required yield next year will have the following probability distribution in the table highlighted in yellow color.
2a (7.5 points). What is your expected price when you sell the bond?
2b (7.5 points). What is the standard deviation?
Solution:
The expected price is:
The standard deviation is:
Probability
Required Yield
Price
Prob * Price
Prob* (Price - Exp. Price)²
0.1
6.60%
0.2
6.75%
0.4
7.00%
0.2
7.20%
0.1
7.45%
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- You own a $1,000-par zero-coupon bond that has 5 years of remaining maturity.You plan on selling the bond in one year and believe that the required yield next year will have the following probability distribution in the table highlighted in yellow color.2a. What is your expected price when you sell the bond?2b. What is the standard deviation?arrow_forwardAssume that the yield curve is YT = 0.04 + 0.001 T. (a) What is the price of a par - $1,000 zero - coupon bond with a maturity of 10 years? (b) Suppose you buy this bond. If 1 year later the yield curve is YT = 0.042 + 0.001 T, then what will be the net return on the bond?arrow_forwardSuppose that a 1-year zero-coupon bond with face value $100 currently sells at $90.44, while a 2-year zero sells at $82.64. You are considering the purchase of a 2-year-maturity bond making annual coupon payments. The face value of the bond is $100, and the coupon rate is 12% per year. Required: a. What is the yield to maturity of the 2-year zero? b. What is the yield to maturity of the 2-year coupon bond? c. What is the forward rate for the second year? d. If the expectations hypothesis is accepted, what are (1) the expected price of the coupon bond at the end of the first year and (2) the expected holding-period return on the coupon bond over the first year? e. Will the expected rate of return be higher or lower if you accept the liquidity preference hypothesis? Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Required A Required B Required C Required D Required E Will the expected rate of return be higher or lower if you accept the liquidity preference hypothesis?…arrow_forward
- Suppose the yield on a one-year zero-coupon bond is 7%. The yield on a two-year zerocoupon bond is 8%. You expect the one-year yield next year to rise to 7.5%. Which ofthe following strategies would give you the highest expected HPR over one year?(a) Invest in the one-year bond(b) Invest in the two-year bond and sell after one year(c) The expected returns on a and b are equal(d) Impossible to tellarrow_forwardSuppose you buy a bond with 3 years to maturity. The face value is 1000 and the coupon rate is 12 %. Assume after holding the bond for one year the market interest rate falls to 8 % a. What will be the new price of your bond? b. What will be the annual rate of return on your bond? c. Discuss the interest rate risk on bonds using your results in parts (a) and (b)?arrow_forwardSuppose that a 1-year zero-coupon bond with face value $100 currently sells at $89.75, while a 2-year zero sells at $79.88. You are considering the purchase of a 2-year-maturity bond making annual coupon payments. The face value of the bond is $100, and the coupon rate is 10% per year. Required: What is the yield to maturity of the 2-year zero? What is the yield to maturity of the 2-year coupon bond? What is the forward rate for the second year? If the expectations hypothesis is accepted, what are (1) the expected price of the coupon bond at the end of the first year and (2) the expected holding-period return on the coupon bond over the first year? Will the expected rate of return be higher or lower if you accept the liquidity preference hypothesis?arrow_forward
- Correct Answerarrow_forwardThe YTM on a bond is the interest rate you earn on your investment if interest rates don’t change. If you actually sell the bond before it matures, your realized return is known as the holding period yield (HPY). a.Suppose that today you buy a bond with an annual coupon rate of 6 percent for $1,150. The bond has 20 years to maturity. What rate of return do you expect to earn on your investment? Assume a par value of $1,000. (Do not round intermediate calculations and enter your answer as a percent rounded to 2 decimal places, e.g., 32.16.)b-1.Two years from now, the YTM on your bond has declined by 1 percent, and you decide to sell. What price will your bond sell for? (Do not round intermediate calculations and round your answer to 2 decimal places, e.g., 32.16.)b-2.What is the HPY on your investment? (Do not round intermediate calculations and enter your answer as a percent rounded to 2 decimal places, e.g., 32.16.)arrow_forwardThe YTM on a bond is the interest rate you earn on your investment if interest rates don't change. If you actually sell the bond before it matures, your realized return is known as the holding period yield (HPY). a. Suppose that today you buy an annual coupon bond with a coupon rate of 8.3 percent for $785. The bond has 8 years to maturity and a par value of $1,000. What rate of return do you expect to earn on your investment? Note: Do not round intermediate calculations and enter your answer as a percent rounded to 2 decimal places, e.g., 32.16. b-1. Two years from now, the YTM on your bond has declined by 1 percent, and you decide to sell. What price will your bond sell for? Note: Do not round intermediate calculations and round your answer to 2 decimal places, e.g., 32.16. b-2. What is the HPY on your investment? Note: Do not round intermediate calculations and enter your answer as a percent rounded to 2 decimal places, e.g., 32.16. a. Rate of return b-1. Price b-2. Holding period…arrow_forward
- Suppose that you buy a TIPS (inflation-indexed) bond with a 1-year maturity and a coupon of 2% paid annually. Assume you buy the bond at its face value of $1,000, and the inflation rate is 10%. a. What will be your cash flow at the end of the year? (Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answer to 2 decimal places.) b. What will be your real return? c. What will be your nominal return? (Do not round intermediate calculations. Enter your answer as a percent rounded to 2 decimal places.)arrow_forward1. Suppose you buy an annual coupon bond with a coupon rate of 6% for $915. The bond has 10 years to maturity and a par value of $1000. What rate of return do you expect to ern on your investment? Two years from now the YTM on your bond has declined by one percentage point, and you decide to sell. What is the holding period yield on your investment? Compare this yield to the YTM when you first bought the bond. Why are they different?arrow_forwardAnswer this question using the Par Value formula and showing all work. You have been given the following information for an existing bond that provides coupon payments. Par Value: $2000 Coupon rate: 6% Maturity: 4 years Required rate of return: 6%. What is the Present Value (PV) of the bond? If the required rate of return by investors were 11% instead of 6%, what would the Present Value of the bond be? Look at the same Par Value $2,000 Same Coupon rate: 6% Maturity: 10 years Required rate of return: 7% What is the Present Value of the Bond now? Explain how the longer maturities and higher required rate of return by investors affects the bond valuation.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course...FinanceISBN:9781337395083Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. DavesPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course...FinanceISBN:9781337395083Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. DavesPublisher:Cengage Learning

Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course...
Finance
ISBN:9781337395083
Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. Daves
Publisher:Cengage Learning