What are joining processes?
It is the process of permanent or temporary joining of two metal pieces with the help of heat or pressure. Two metal parts are assembled by applying an energy source for the formation of a single unit. The obtained joined metals cannot be fragmented easily with the application of any force.
What are the types of metal joining processes?
Metal joining processes can be classified into two types which are as follows:
Permanent joining process
The common permanent joining process is welding, riveting (mechanical assembly), brazing, soldering.
Temporary joining process
The common temporary joining processes are adhesive bonding, crimping, shrink fitting, bolting or screwing (mechanical joining), clamping, fasteners like clutch, nut-bolt, zipper, button, nail hook, etc.
Welding
In this joining process, two or more parts of metals are coalesced or fused at their surface of contact by applying heat energy or pressure. This joining takes place when atoms of two metallic materials are joined to constitute a specific crystallographic structure. The joint can also be obtained with the temperature, metallurgical conditions or parameters, and pressure.
The welding can be represented as,
What are the types of welding processes?
There are three types of welding processes, namely solid-state (autogenous), liquid state (homogeneous), and solid liquid (heterogeneous).
Solid state welding
In solid-state, no filler material is used. There are four types of welding, namely cold, friction, diffusion, and forge. The cold welding types are pressure, exclusive, and ultrasonic welding.
Liquid state welding
The liquid state welding consists of arc welding, chemical reaction, and resistance welding. A liquid state welding is also known as fusion welding. The arc welding consists of flux cord which is further classified into alternating and direct current types. The arc welding also consists of shielding metal arc welding, which is further divided into tungsten and metal inert gas.
The other types of arc welding are submerged arc welding and plasma arc welding. The chemical reaction welding is classified into gas and resistance welding. The gas welding is divided into oxy-acetylene, oxy-hydrogen, air-acetylene, and pressure gas welding. The resistance welding is classified into spot, seam, projection, and resistance welding.
Solid liquid welding
Solid liquid welding is classified into soldering, brazing, and adhesive bonding. In this type of welding, filler material varies with the base material. Other types of welding are thermo-chemical welding and radiant energy welding. Thermochemical is divided into thermit and atomic hydrogen welding. Radiant energy is classified into electron beam and laser beam welding.
Common welding processes can be discussed as,
Friction welding
The joining of two materials takes place with the help of heat generated due to friction and non-elastic (plastic) deformation.
Diffusion welding
Two metal pieces are kept close at high temperature and pressure, and then the joint is formed due to solid-state diffusion.
Ultrasonic welding
When two parts oscillate with greater frequencies (ultrasonic frequencies) parallel with the contacting (meeting) surfaces, medium pressure is applied between them.
Arc welding
The arc welding can be shown as,
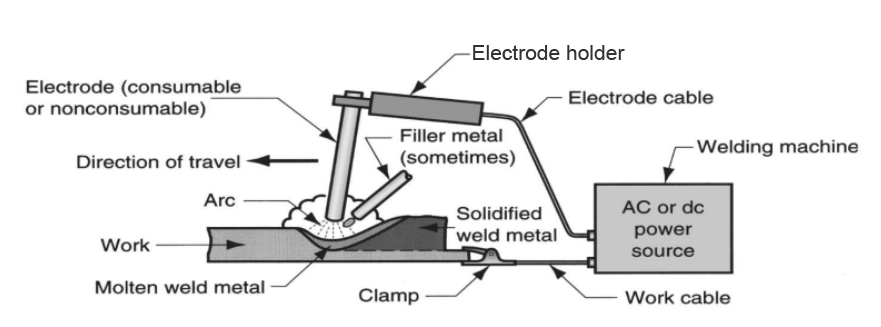
The potential difference establishes between electrodes for the generation of arc. Arc is produced when the electrodes contact the workpiece, and they quickly get separated by a small distance (gap). Sometimes, the filler metal is also added to the gap. Due to the arc, temperature which is of the range of 5500 degrees is obtained, and it is pretty enough to melt the base metal and filler metal. These molten metal then gets solidified. Thus, the welding is produced with this arc welding method.
Plasma arc welding
The plasma arc welding can be shown as,
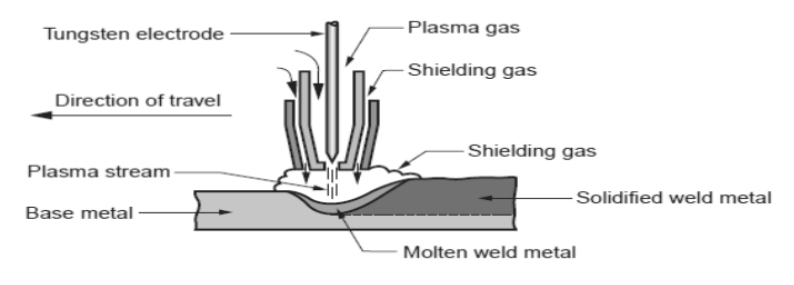
The arc is generated between the tungsten electrode and the metal workpiece. Here, the tungsten is placed in a vertical nozzle, and hot plasma steam of arc at the exit of the nozzle is produced. The plasma gas is provided between the gaps. The high temperature (nearly 17000 degrees Celsius) of the plasma is created. As a result, heat is released during this process, and welding takes place. This method is applicable for the welding of titanium, stainless steel, etc.
Spot Welding
The spot welding can be shown as,
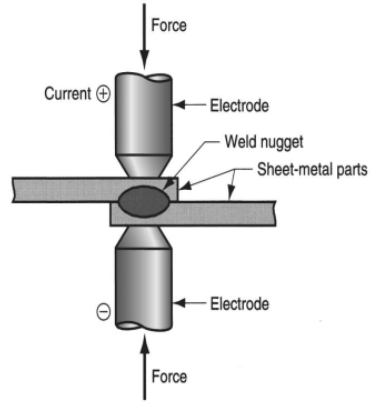
In this type of welding, two parallel metal sheets are held together between two vertical electrodes. Then high current is provided through the sheets, and maximum resistance and high pressure are created between them. Then, the materials between both the sheets liquefy, and spot welding occurs.
Submerged arc welding
The submerged arc welding can be shown as,
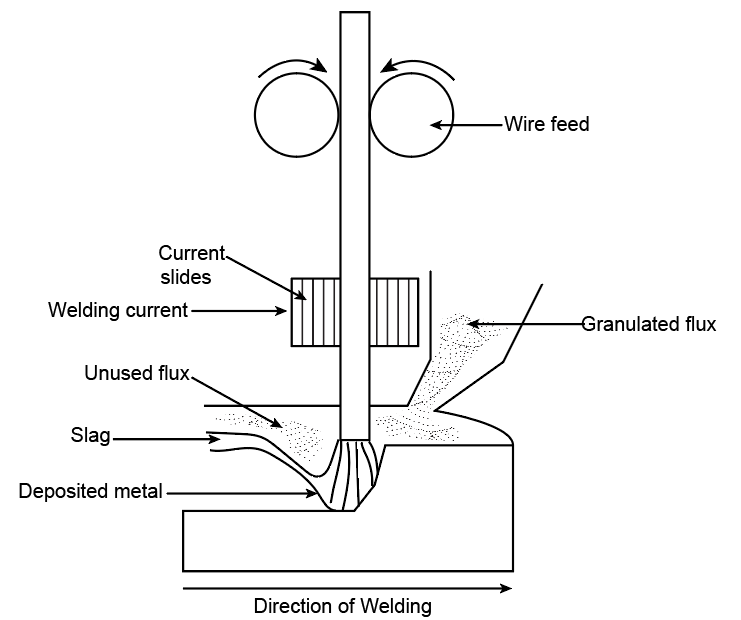
Here, the nozzle is fed with granulated flux (silica, calcium fluoride, etc.) which is fed into the weld space. The arc is created between the workpiece and the metal electrode. The shielding is done through the hopper.
Brazing
It is carried out when the filler material's melting point is above , but usually less than the melting temperature of the base metal. Here, the filler materials employed are copper, zinc, silver, etc. The strength of the braze joint is high. Braze joint is considered stronger than the solder joint. Braze joints are widely used in pipe fittings.
Soldering
Soldering is done where the melting temperature of filler material is lower than , but it is also lower than the melting temperature of the base material. It is highly used in electronic companies. Filler materials like lead alloys can be used here.
Common Mistakes
- It is a misconception that soldering is a more robust joining process than brazing. But brazing is stronger than soldering.
- Sometimes students get confused between the temperatures of soldering and brazing. Brazing is performed above 430 degrees centigrade filler metal's melting temperature, and soldering is done up to 430 degrees centigrade filler material's melting temperature.
- It is a misconception that heat treatment processes are required in the soldering process. But no heat treatment is required in this.
- It is a misconception that lap joints are also made by resistance welding. But lap joints are not formed by this welding.
- Sometimes students get confused in between filler materials of soldering and brazing processes. Filler materials of soldering are lead, but brazing consists of alloys of copper and silver.
Context and Application
The topic joining processes is generally studied in many technical and professional courses, graduation courses, post-graduation, Doctor of Philosophy, and others. For example:
- Bachelor of Technology in Mechanical Engineering
- Bachelor of Technology in Production Engineering
- Master of Technology in Mechanical Engineering
- Master of Technology in Production Engineering
- Doctor of Philosophy in Mechanical Engineering
- Doctor of Philosophy in Production Engineering
Related Concept
- Welding
- Types of welding
- Welding defects
- Brazing
- Riveting
- Soldering
- Arc welding
Practice Problems
Q1: Which of the following are not the applications of brazing processes?
- Jewelry making
- Wire joining
- Tube joining
- Printed circuit board production
Correct option: (d)
Explanation: Brazing process applications are radiators, axles, electrical parts, heat exchangers. This process is used in jewelry designing, wire joining, tube joining. The brazing process can be employed for the joining of two metal pieces.
Q2: Which of the following are the applications of the soldering processes?
- Shipbuilding
- Construction
- Printed circuit board making
- Machine structures
Correct option: (c)
Explanation: The application of the soldering process is in heating, air conditioners, fire sprinklers, etc. In the soldering process, the operator fatigue is much less than in the welding process. The other applications are in making a printed circuit board.
Q3: Which of the following are not the features of the brazing process?
- Done above 430 degrees centigrade melting temperature of the filler metal
- Filler material like copper, zinc
- Strength high
- Application in electronic industries
Correct option: (d)
Explanation: With the help of the brazing process, dimensional stability can be achieved. It is used to produce simple as well as complex objects. They are not used in the electronic industries. The filler materials can be employed as copper and zincs.
Q4: Which of the following are not the welding defects?
- Swaging
- Undercut
- Overlapping
- Cracks
Correct option: (a)
Explanation: Most common welding defects are spattered, undercuts, cracks, overlaps, porosity, slag inclusions, and many more. Swaging is considered the forging process. It is employed to reduce or increment the diameters of the tubes.
Q5: What are not the applications of resistance welding?
- Welding of automobiles bodies
- LPG cylinders
- Nuts and bolts welded to sheets
- Shopping carts
Correct option: (b)
Explanation: Resistance welding is used for the welding of sheet metals. They are employed in the aerospace industries. They are used in automobile industries, nut and bolts making, shopping carts, etc.
Want more help with your mechanical engineering homework?
*Response times may vary by subject and question complexity. Median response time is 34 minutes for paid subscribers and may be longer for promotional offers.
Search. Solve. Succeed!
Study smarter access to millions of step-by step textbook solutions, our Q&A library, and AI powered Math Solver. Plus, you get 30 questions to ask an expert each month.
Manufacturing Engineering and Technology
Manufacturing Processes
Joining Processes
Search. Solve. Succeed!
Study smarter access to millions of step-by step textbook solutions, our Q&A library, and AI powered Math Solver. Plus, you get 30 questions to ask an expert each month.