
Physics: Principles with Applications
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780321625922
Author: Douglas C. Giancoli
Publisher: Addison-Wesley
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 9, Problem 4P
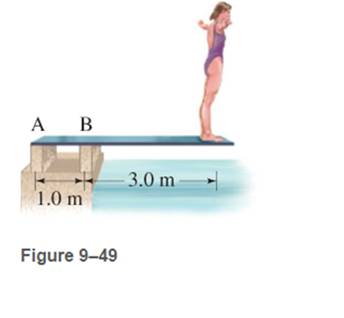
What is the mass of the diver in Fig. 9-49 if she exerts a torque of 1800m. N on the board, relative the left (A) support post?
Expert Solution & Answer
Learn your wayIncludes step-by-step video

schedule02:53
Students have asked these similar questions
(I) What is the mass of the diver in Fig. 9–49 if she
exerts a torque of 1800 m · N on the board, relative
to the left (A) support post?
А В
FIGURE 9–49
3.0 m –|
Problems 4 and 5.
1.0 m
9. In Figure 9-26 below, a crane is lifting a heavy concrete panel The force holding up
the panel is F = 2.00 x 104 N. Torque is respect to O below. a) What is the direction of
rotation? b) What is the torque?
Fig. 9-26
T=2.00 x 10°N
10.0 m
53.0
0
A ground retaining wall is shown in Fig. 9–36a. The ground,
particularly when wet, can exert a significant force F on the
wall. (a) What force produces the torque to keep the wall
upright? (b) Explain why the retaining wall in Fig. 9–36b
would be much less likely to overturn than that in Fig. 9–36a.
-F
(a)
(b)
FIGURE 9-36 Question 5.
Chapter 9 Solutions
Physics: Principles with Applications
Ch. 9 - Prob. 1OQCh. 9 - Describe several situations in which an object is...Ch. 9 - Prob. 2QCh. 9 - You can find the center of gravity of a meter...Ch. 9 - Prob. 4QCh. 9 - A ground retaining wall is shown in Fig. 9-36a...Ch. 9 - Can the sum of the torques on an object be zero...Ch. 9 - A ladder, leaning against a wall, makes a 60°...Ch. 9 - A uniform meter stick supported at the 25-cm mark...Ch. 9 - Why do you tend to lean backward when carrying a...
Ch. 9 - Figure 9-38 shows a cone. Explain how to lay it on...Ch. 9 - Prob. 11QCh. 9 - Why is it not possible to sit upright in a chair...Ch. 9 - Why is it more difficult to do sit-ups when your...Ch. 9 - Explain why touching your toes while you are...Ch. 9 - Prob. 15QCh. 9 - Name the type of equilibrium for each position of...Ch. 9 - (
17.
)
Is the Young's modulus for a bungee cord...Ch. 9 - Prob. 18QCh. 9 - Prob. 19QCh. 9 - A 60-kg woman stands on the very end of a uniform...Ch. 9 - Prob. 2MCQCh. 9 - Prob. 3MCQCh. 9 - Prob. 4MCQCh. 9 - Two children are balanced on opposite sides of a...Ch. 9 - Prob. 6MCQCh. 9 - Prob. 7MCQCh. 9 - Prob. 8MCQCh. 9 - Prob. 9MCQCh. 9 - Prob. 10MCQCh. 9 - Three forces are applied to a tree sapling, as...Ch. 9 - Prob. 2PCh. 9 - 3(I) A tower crane ( Fig. 9-48a) must always be...Ch. 9 - What is the mass of the diver in Fig. 9-49 if she...Ch. 9 - Prob. 5PCh. 9 - Figure 9-50 shows a pair of forceps used to hold a...Ch. 9 - Prob. 7PCh. 9 - The two trees in Fig. 9-51 are 6.6 m apart. A...Ch. 9 - Prob. 9PCh. 9 - Prob. 10PCh. 9 - Prob. 11PCh. 9 - Find the tension in the two cords shown in Fig....Ch. 9 - Prob. 13PCh. 9 - Prob. 14PCh. 9 - The force required to pull the cork out of the top...Ch. 9 - Prob. 16PCh. 9 - Three children are trying to balance on a seesaw,...Ch. 9 - A shop sign weighing 215 N hangs from the end of a...Ch. 9 - Prob. 19PCh. 9 - Prob. 20PCh. 9 - Prob. 21PCh. 9 - 22 (II) A 20.0-m-long uniform beam weighing 650 N...Ch. 9 - Prob. 23PCh. 9 - Prob. 24PCh. 9 - Prob. 25PCh. 9 - Prob. 26PCh. 9 - A uniform rod AB of length 5.0 m and mass M=3.S kg...Ch. 9 - You are on a pirate ship and being forced to walk...Ch. 9 - Prob. 29PCh. 9 - Prob. 30PCh. 9 - Prob. 31PCh. 9 - Prob. 32PCh. 9 - Prob. 33PCh. 9 - Prob. 34PCh. 9 - Prob. 35PCh. 9 - 36 (II) The Achilles tendon is attached to the...Ch. 9 - If 25 kg is the maximum mass m that a person can...Ch. 9 - Prob. 38PCh. 9 - Prob. 39PCh. 9 - Prob. 40PCh. 9 - A marble column of cross-sectional area 1.4 m2...Ch. 9 - Prob. 42PCh. 9 - A sign (mass 1700 kg) hangs from the bottom end of...Ch. 9 - Prob. 44PCh. 9 - Prob. 45PCh. 9 - Prob. 46PCh. 9 - A steel wire 2.3 mm in diameter stretches by...Ch. 9 - Prob. 48PCh. 9 - Prob. 49PCh. 9 - Prob. 50PCh. 9 - Prob. 51PCh. 9 - Prob. 52PCh. 9 - (a) What is the minimum cross-sectional area...Ch. 9 - Prob. 54PCh. 9 - Prob. 55PCh. 9 - Prob. 56PCh. 9 - Prob. 57PCh. 9 - Prob. 58GPCh. 9 - Prob. 59GPCh. 9 - Prob. 60GPCh. 9 - Prob. 61GPCh. 9 - Prob. 62GPCh. 9 - Prob. 63GPCh. 9 - Prob. 64GPCh. 9 - When a mass of 25 kg is hung from the middle of a...Ch. 9 - Prob. 66GPCh. 9 - Prob. 67GPCh. 9 - Prob. 68GPCh. 9 - Prob. 69GPCh. 9 - Prob. 70GPCh. 9 - Prob. 71GPCh. 9 - Prob. 72GPCh. 9 - Prob. 73GPCh. 9 - A 2.0-m-high box with a 1.0-m-square base is moved...Ch. 9 - Prob. 75GPCh. 9 - Prob. 76GPCh. 9 - Prob. 77GPCh. 9 - Prob. 78GPCh. 9 - In a mountain-climbing technique called the...Ch. 9 - Prob. 80GPCh. 9 - A cubic crate of side s=20m is top-heavy: its cgis...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
The Rankine temperature scale (abbreviatedR) uses the same size degrees as Fahrenheit, but measured up from abs...
An Introduction to Thermal Physics
Given the vectors in the preceding figure, find vector Rthat solves equations (a) D+R=Fand (b) D-2D+5R=3F . Ass...
University Physics Volume 1
A body is subject to three forces; F1=1i+2jN, applied at the point x = 2m, y = 0 m; F2=2i5jN, applied at x = 1 ...
Essential University Physics: Volume 1 (3rd Edition)
24. A copper wire is stretched so that its length increases and its diameter decreases. As a result,
A. The wir...
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Edition)
(a) Find an expression for the electric field on the y-axis due to the two charges q in Fig. 20.7. (b) At what ...
Essential University Physics (3rd Edition)
The electric field at the center of straw.
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- What force must be applied to end of a rod along the x-axis of length 2.0 m in order to produce a torque on the rod about the origin of 8.0k Nm ?arrow_forwardIn Figure 9.21, the cg of the pole held by the pole vaulter is 2.00 m from the left hand, and the hands are 0.700 m apart. Calculate the force exerted by (a) his right hand and (b) his left hand. (c) If each hand supports half the weight of the pole in Figure 9.19, show that the second condition for equilibrium (net =0 ) is satisfied for a pivot other than the one located at the center of gravity of the pole. Explicitly show how you follow the steps in the Problem-Solving Strategy for static equilibrium described above. Figure 9.21 A pole vaulter is holding a pole horizontally with both hands. The center of gravity is to the left side of the vaulter.arrow_forwardWhat three factors affect the torque created by a force relative to a specific pivot point?arrow_forward
- A body moving in a circle with a constant seed is in rotational equilibrium.arrow_forwardWhen tightening a bolt, you push perpendicularly on a wrench with a force of 165 N at a distance of 0.140 m from the center of the bolt. How much torque are you exerting in newton-meters (relative to the center of the bolt)?arrow_forwardCan a set of forces have a net force that is zero and a net torque that is not zero?arrow_forward
- (I) A tower crane (Fig. 9–48a) must always be carefully balanced so that there is no net torque tending to tip it. A particular crane at a building site is about to lift a 2800-kg air-conditioning unit. The crane's dimensions are shown in Fig. 9-48b. (a) Where must the crane's 9500-kg counterweight be placed when the load is lifted from the ground? (The counterweight is usually moved auto- matically via sensors and motors to precisely compensate for the load.) (b) Determine the maximum load that can be lifted with this counterweight when it is placed at its full extent. Ignore the mass of the beam. (a) Counterweight M = 9500 kg +3.4 m- 7.7 m m = 2800 kg FIGURE 9-48 (b) Problem 3.arrow_forwardCalculate the amount of torque generated at a joint when a muscle attaching to a bone 4 cmfrom the joint center exerts 100 N of tension at the following angles of attachment: (a) 30° (b)60° (c) 90° (d)150°arrow_forward10-75. The two shafts are made of A36 steel. Each has a diameter of 25 mm and they are connected using the gears fixed to their endk Their other ends are attached to fixed supports at A and B. They are also supported by journal bearings at Cand D, which alkow free rotation of the shafts along their axes. If a torque of S00 N-m is applied to the gear at E, determine the rotation of this gear. S0 mm 0.75 100 mm- S00N-marrow_forward
- 11 Figure 10-28a shows a meter stick, half wood and half steel, that is pivoted at the wood end at O.A force F is applied to the steel end at a. In Fig. 10-28b, the stick is reversed and pivoted at the steel end at O', and the same force is applied at the wood end at a'. Is the resulting angular acceleration of Fig. 10-28a greater than, less than, or the same as that of Fig. 10-28b? Figure 10-28 Question 11. (a) (b)arrow_forwardA uniform plank has a mass of 4.00 kg and a length of 10.0 m. A fulcrum is placed below the plank at a position 1.00 m to the left of its center of mass. -39,2N.m a) Find the net torque on the plank. Include direction with cw or ccw. b) A person has a set of masses handy: 1 kg, 2 kg, 3 kg, and 4 kg. Give at least two ways they could place a single mass on top of the plank to put the system in equilibrium. kg mass at a position kg mass at a position c) Find a way that they could place all four masses on top of the plank and have the system in rotational equilibrium. Explain your answer / show your work: Place a OR Place a meters to the meters to the of the fulcrum. of the fulcrum.arrow_forward(I) Suppose the point of insertion of the biceps muscle intothe lower arm shown in Fig. 9–13a (Example 9–8) is 6.0 cminstead of 5.0 cm; how much mass could the person holdwith a muscle exertion of 450 N?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax - Rice University

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...
Physics
ISBN:9780078807213
Author:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781938168000
Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:OpenStax College
Static Equilibrium: concept; Author: Jennifer Cash;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0BIgFKVnlBU;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY