
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Topic Video
Question

Transcribed Image Text:during its burn.
(a) She moves, just like the archer in Example 9.1.
(b) -(w v
(c) As she throws the gloves and
exerts a force on them, the gloves exert an equal and
gloves
opposite force on her that causes her to accelerate from
rest to reach the velocity v
girl"
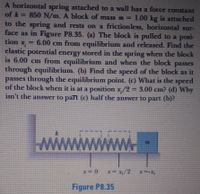
Transcribed Image Text:A horizontal spring attached to a wall has a force constant
of k= 850 N/m. A block of mass m = 1.00 kg is attached
to the spring and rests on a frictionless, horizontal sur-
face as in Figure P8.35. (a) The block is pulled to a posi-
tion x,
6.00 cm from cquilibrium and released. Find the
clastic potential energy stored in the spring when the block
is 6.00 cm from cquilibrium and when the block passes
through equilibrium. (b) Find the speed of the block as it
passes through the equilibrium point. (c) What is the speed
of the block when it is at a position x/2 = 3.00 cm? (d) Why
isn't the answer to part (c) half the answer to part (b)?
wwww
/2
Figure P8.35
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A7.1g marble is fired vertically upward using a spring gun. The spring must be compressed 5.7 cm if the marble is to just reach a target 11 m above the marble's position on the compressed spring. (a) What is the change AU, in the gravitational potential energy of the marble-Earth system during the 11 m ascent? (b) What is the change AU; in the elastic potential energy of the spring during its launch of the marble? (c) What is the spring constant of the spring? (a) Number Units (b) Number Units (c) Number i Units > > >arrow_forwardA 7.80-g bullet moving at 560 m/s penetrates a tree trunk to a depth of 4.80 cm. (a) Use work and energy considerations to find the average frictional force that stops the bullet. (b) Assuming the frictional force is constant, determine how much time elapses between the moment the bullet enters the tree and the moment it stops moving.arrow_forwardA 0.800-kg particle has a speed of 2.10 m/s at point and kinetic energy of 7.80 J at point . (a) What is its kinetic energy at ?(b) What is its speed at ?(c) What is the net work done on the particle by external forces as it moves from to ?arrow_forward
- A 7.80 g bullet is moving at 460 m/s just before it penetrates a tree trunk to a depth of 4.9 cm (ay What the magnitude of the average frletional force (In N) that is exerted on the bullet whille moving the tree trunk? Uso work considerations to o your answer. (b) Asturing the frictional force is constant, how much time elapses between the moment the bullet enters the tree trunk and the moment it moving?arrow_forwardFigure (a) applies to the spring in a cork gun (Figure (b)); it shows the spring force as a function of the stretch or compression of the spring. The spring is compressed by 7.00 cm and used to propel a 3.90 g cork from the gun. (a) What is the speed of the cork if it is released as the spring passes through its relaxed position? (b) Suppose, instead, that the cork sticks to the spring and stretches it 1.70 cm before separation occurs. What now is the speed of the cork at the time of release? Force (N) 0.4 0.2 -4-2 2 4 -0.2 -0.4 (a) x (cm) Compressed spring. 0 (b) Corkarrow_forwardA pendulum consists of a 1.2 kg stone swinging on a 4.2 m string of negligible mass. The stone has a speed of 8.3 m/s when it passes its lowest point. (a) What is the speed when the string is at 56" to the vertical? (b) What is the greatest angle with the vertical that the string will reach during the stone's motion? (c) If the potential energy of the pendulum-Earth system is taken to be zero at the stone's lowest point, what is the total mechanical energy of the system? (a) Number i Unit (b) Number i Unit (c) Number i Unitarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON