
College Physics
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781285737027
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
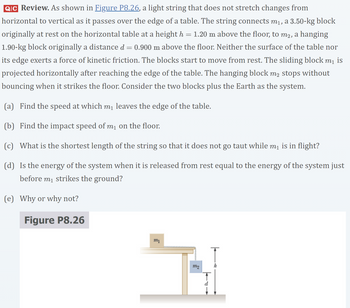
Transcribed Image Text:QIC Review. As shown in Figure P8.26, a light string that does not stretch changes from
horizontal to vertical as it passes over the edge of a table. The string connects m₁, a 3.50-kg block
originally at rest on the horizontal table at a height h = 1.20 m above the floor, to m2, a hanging
1.90-kg block originally a distance d = 0.900 m above the floor. Neither the surface of the table nor
its edge exerts a force of kinetic friction. The blocks start to move from rest. The sliding block m₁ is
projected horizontally after reaching the edge of the table. The hanging block m2 stops without
bouncing when it strikes the floor. Consider the two blocks plus the Earth as the system.
(a) Find the speed at which m₁ leaves the edge of the table.
(b) Find the impact speed of m₁ on the floor.
(c) What is the shortest length of the string so that it does not go taut while må is in flight?
(d) Is the energy of the system when it is released from rest equal to the energy of the system just
before m₁ strikes the ground?
(e) Why or why not?
Figure P8.26
m₁
m2
T
d
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- A 0.400-kg pendulum bob passes through the lowest part of its path at a speed of 3.00 m/s. (a) What is the tension in the pendulum cable at this point if the pendulum is 80.0 cm long? (b) When the pendulum reaches its highest point, what angle does the cable make with the vertical? (c) What is the tension in the pendulum cable when the pendulum reaches its highest point?arrow_forwardA makeshift sign hangs by a wire that is extended over an ideal pulley and is wrapped around a large potted plant on the roof as shown in Figure P6.10. When first set up by the shopkeeper on a sunny and dry day, the sign and the pot are in equilibrium. Is it possible that the sign falls to the ground during a rainstorm while still remaining connected to the pot? What would have to be true for that to be possible? FIGURE P6.10 Problems 10 and 11.arrow_forwardTo give a pet hamster exercise, some people put the hamster in a ventilated ball andallow it roam around the house(Fig. P13.66). When a hamsteris in such a ball, it can cross atypical room in a few minutes.Estimate the total kinetic energyin the ball-hamster system. FIGURE P13.66 Problems 66 and 67arrow_forward
- An object of mass m is suspended from the top of a cart by a string of length L as in Figure P5.88a. The cart and object are initially moving to the right at a constant speed 0. The cart comes to rest after colliding and sticking to a bumper, as in Figure P5.88b, and the suspended object swings through an angle . (a) Show that the initial speed is 0=2gL(1cos). (b) If L = 1.20 m and = 35.0, find the initial speed of the cart (Hint: The force exerted by the string on the object docs no work on the object.) Figure P5.88aarrow_forwardOn a horizontal air track, a glider of mass m carries a -shaped post. The post supports a small dense sphere, also of mass m, hanging just above the top of the glider on a cord of length L. The glider and sphere are initially at rest with the cord vertical. A constant horizontal force of magnitude F is applied to the glider, moving it through displacement x1; then the force is removed. During the time interval when the force is applied, the sphere moves through a displacement with horizontal component x2. (a) Find the horizontal component of the velocity of the center of mass of the glidersphere system when the force is removed. (b) After the force is removed, the glider continues to move on the track and the sphere swings back and forth, both without friction. Find an expression for the largest angle the cord makes with the vertical.arrow_forwardEach Voyager spacecraft was accelerated toward escape speed from the Sun by the gravitational force exerted by Jupiter on the spacecraft. (a) Is the gravitational force a conservative or a nonconservative force? (b) Does the interaction of the spacecraft with Jupiter meet the definition of an elastic collision? (c) How could the space-craft be moving faster after the collision?arrow_forward
- Figure P5.41 shows the speed of a persons body as he does a chin-up. Assume the motion is vertical and the mass of the persons both is 64.0 kg. Determine the force exerted by the chin-up bar on his body at (a) t = 0, (b) t = 0.5 s, (c) t = 1.1 s, and (d) t = 1.6 s.arrow_forwardA particle moves in a medium under the influence of a retarding force equal to mk(υ3+ a2υ), where k and a are constants. Show that for any value of the initial speed the particle will never move a distance greater than π/2kaand that the particle comes to rest only for t → ∞.arrow_forwardA 1.00-kg glider on a horizontal air track is pulled by a string at an angle . The taut string runs over a pulley and is attached to a hanging object of mass 0.500 kg as shown in Figure P5.40. (a) Show that the speed vx of the glider and the speed vy of the hanging object are related by vx = uvy, where u = z(z2 h02)1/2. (b) The glider is released from rest. Show that at that instant the acceleration ax of the glider and the acceleration ay of the hanging object are related by ax = uay. (c) Find the tension in the string at the instant the glider is released for h0 = 80.0 cm and = 30.0. Figure P5.40arrow_forward
- A car with a mass of 1453 kg is rolling along a flat stretch of road and eventually comes to a stop due to rolling friction. If the car begins with a speed of 10.0 m/s and the car comes to a stop in 6.88 s, what is the coefficient of rolling friction between the tires and the road?arrow_forwardTwo figure skaters are coasting in the same direction, with the leading skater moving at 5.5 m/s and the trailing skating moving at 6.2 m/s. When the trailing skater catches up with the leading skater, he picks her up without applying any horizontal forces on his skates. If the trailing skater is 50 heavier than the 50-kg leading skater, what is their speed after he picks her up?arrow_forwardTo get up on the roof, a person (mass 70.0 kg) places 6.00-m aluminum ladder (mass 10.0 kg) against the house on a concrete pad with the base of ladder 2.00 m from the house. The ladder rests against a plastic rain gutter, which we can assume to frictionless. The center of ladder is 2.00 m from the bottom. The person is standing 3.00 m from the bottom. Find the normal reaction and friction forces on the ladder at its base.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781285737027
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning