
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
thumb_up100%
The surface of an airplane wing is subjected to plane stress with normal stresses x and cr and shear stress tx y, as shown in the figure. At a counterclockwise angle 9 = 32° from the x axis, the normal stress is 29 MPa in tension, and at an angle 8 = 46°, it is 17 MPa in compression.
If the stress trx equals 105 MPa in tension, what are the stresses cr, and r,,,?
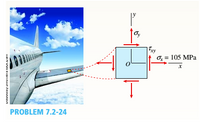
Transcribed Image Text:1Fry
o, = 105 MPa
PROBLEM 7.2-24
unnmeiaunue hennnen
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Q# 3 A rectangular plate in biaxial stress (see figure) is subjected to normal stresses 0,=100 MPa (tension) and 0,=20 MPa (compression). The plate has dimensions 200 x 400 x 10 mm 6 and is made of steel with E = 200 GPa and v = 0.30. (a) Determine the maximum in-plane shear strain Ymax in the plate. (b) Determine the change At in the thickness of the plate. (c) Determine the change AV in the volume of the plate.arrow_forwardstrength of materialsarrow_forwardIn the figure, the steel shaft with a diameter of 36 mm is 240 mm diameter pulley. Belts also formed under given angles If the tensile Forces are 2400N and 400N, the shaft at point K on the x-z plane Calculate the normal and shear stresses. Plotting the stress state for this point show me The shaft can carry safely if shear stress em=100 MPa Using the Greatest Transformation Energy (vonMises) hypotheses, the K point Show if it is safe.arrow_forward
- A plastic bar of diameter d = 32 mm is compressedin a testing device by a force P = 190 N thatis applied as shown in the figure.(a) Determine the normal and shear stresses actingon all faces of stress elements oriented at (1) anangle θ = 0°, (2) an angle θ = 22.5°, and (3) anangle θ = 45°. In each case, show the stresses ona sketch of a properly oriented element. Whatare σmax and τmax? (b) Find σmax and τmax in the plastic bar if a recenteringspring of stiffness k is inserted intothe testing device, as shown in the figure. Thespring stiffness is 1/6 of the axial stiffness of theplastic bar.arrow_forwardAn element in plane stress is subjectedto stresses σx = -8400 psi, σy =1100 psi , andτxy =-1700 psi (see figure). The material is aluminumwith modulus of elasticity E =10,000 ksi andPoisson’s ratio n = 0.33.Determine the following quantities: (a) the strainsfor an element oriented at an angle θ = 30°, (b) theprincipal strains, and (c) the maximum shear strains.Show the results on sketches of properly orientedelements.arrow_forwardprincipal stress is 10 kPa, then the normal stress stress, is shown in the figure below. If the minimum The state of stress at a point, for a body in place o (in kPa) is = 50 kPa 0,= 100 kPa %3D X,arrow_forward
- QUESTION 3 Two vertical forces are applied to a beam as in Figure Q3(a) with the cross section shown in Figure Q3(b). Determine the maximum tensile and compressive stresses in portion BC of the beam. 15 N 3 mm 3 mm 3 mm В 15 N 6 mm 40 mm 60 mm 2 mm A-B 40 mm 40 mm B-C 60 mm C-D 40 mm (b) (a) Figure Q3arrow_forwardThe figure above are two rods attached to a rigid bar AB with negligible mass . A MN kN load was applied at the end of this bar. The computed stresses for steel and bronze are Blank 1 mPa and Blank 2 mPa respectively. MN = 48arrow_forwardVertical load is applied to point B of a 10 mm radius cylindrical bar as shown in the figure. Calculate the normal stress at point A.arrow_forward
- 4- The cross-section of the ABCD element in the figure is a circle with a diameter of 6 cm. The force of P-500 N is in the x-z plane. The CD segment is parallel to the y-axis. In line with the information given, a- Find the most critical points in section A. b- Calculate the normal and shear stresses at the most critical points in section A. c- Calculate the principal stresses at the specified points. d- Check the section with the Tresca Hypothesis. em = 95 MPa 75 cm B A N 50 cm 10 40 cm Parrow_forwardThe cantilever beam with a rectangular cross-section is under the loading P as shown in the figure. P Part A At an arbitrary cross-section, a - a the state of stress is obtained at various points (point 1 - 5, where point 3 is the midpoint). Select all that describe the stress at the cross-section a - a correctly. O The cross-section a-a has three internal loadings, i.e., shear force, normal force, and bending moment. O The normal stress by bending moment at point 5 is zero. O The maximum shear stress by shear force occurs at the same point as the maximum normal stress by bending moment. O The maximum shear stress by shear force occurs at point 3. O Point 1 develops compressive normal stress by bending moment. O The shear stress by shear force at point 1 is zero. Submit Request Answerarrow_forwardA rectangular bar having width w = 6.50 in. and thickness t = 1.25 in. is subjected to a tension load P, as shown in the figure. The %3D magnitudes of the normal and shear stresses on plane AB must not exceed 16 ksi and 7 ksi, respectively. Determine the maximum load P that can be applied without exceeding either stress limit. Assume a = 3 and b = 4. A P a b B Answer: P = i kips %3Darrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY