
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Can the two blocks be in equilibrium in the position shown? Justify your answer. All surfaces are frictionless except the horizontal surface beneath block B.
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
Given Data:
- The weight of block A is WA = 120 lb.
- The weight of block B is WB = 80 lb.
- The coefficient of static friction is μs=0.2.
The free-body diagram of block A can be drawn as,
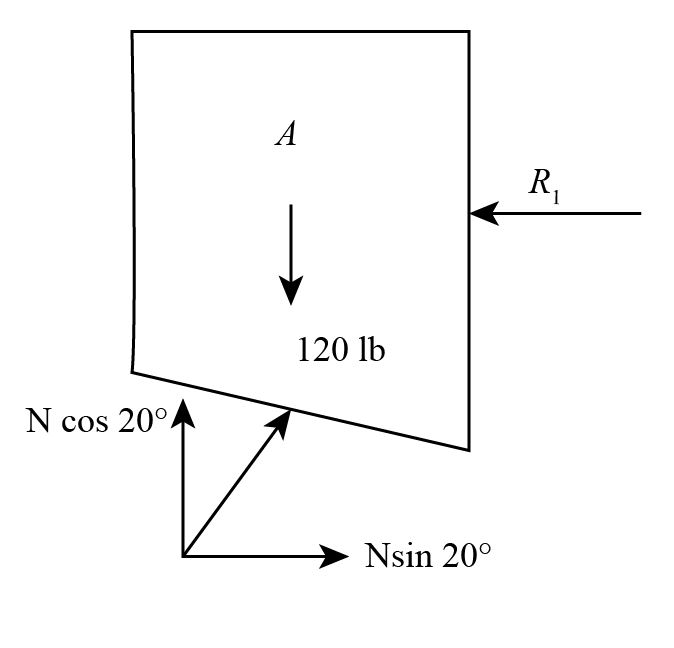
arrow_forward
Step 2
Assuming block A to be in the equilibrium, apply force balance in the vertical direction,
Ncos20°
The free-body diagram of the Block B can be drawn as,
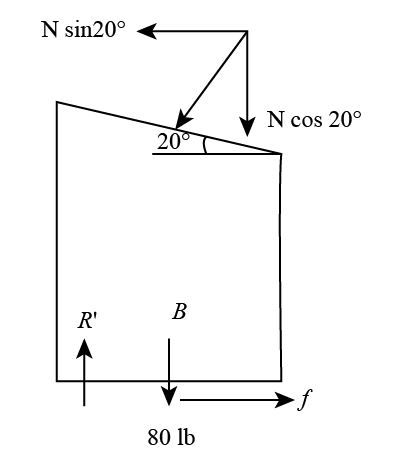
Applying force balance in the vertical direction,
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A 8.0 m long ladder AB leans against a smooth wall making an angle of 70º with the floor. The ladder is uniform and has a mass of 40.0 kg.(a) Determine the forces exerted on the ladder by the floor and the wall (i.e. at A and B respectively).(b) Determine the minimum value of the coefficient of static friction to prevent the ladder from slipping.arrow_forwardThe spring clamp of Fig. block Fagainst the floor. The force in the spring is F = k(e – lo), where e is the present length of the spring, lo = 3 in. is the unstretched length of the spring, and k = 240 lb/ft is the spring constant. Determine all forces acting on mem- ber ÁBC of the spring clamp and the force exerted by the spring clamp on the block E. is used to hold the 8 in. D E 8 in. 6 in -6 in.- 6 in.arrow_forwardDetermine the magnitude of the clamping forces (in pounds) exerted on the nut along line aa when two 78-lb forces are applied to the handles as shown. Assume that pins A and D slide freely in the slots in the jaws.arrow_forward
- Show complete and detailed solution. View Image.arrow_forwardA 200 lb rock is being lifted by a pry bar. Determine the force “P” required to lift the rock into the position show.arrow_forwardQ4: The uniform box shown in next figure, has a mass of 40 Kg. If the two forces T = 60 N and F =30 N are applied on the box, determine if it remains in equilibrium. The coefficient of static friction (H) = 0.24 F=30N T=60N 30 40 Kgarrow_forward
- Given the figure shown below, what is the mass of block B on the smooth incline if the system is in static equilibrium? A rope runs from block B up around the frictionless pulley at A down to a 10 kg counterweight. A 1 m B- 1m 10 kg 45°arrow_forwardA crate with dimensions l = 0.50 m and h = 0.75 m rests on a plane that is inclined by θ = 30◦ from thehorizontal. The crate is in equilibrium, but if the crate were too tall, it will fall over down the slope.Find the effective point of application of the normal force on the crate, i.e., where is the normal force actingon the crate, keeping the crate in equilibrium? Hint: choose the crate’s center of mass as the axis of rotation.arrow_forwardIf the value of P in the above figure is 180-lb,determine the angle θ at which it must beinclined with the smooth plane to hold 300-lbbox in equilibrium.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY