
What is the difference between the upstream velocity and the free-stream velocity? For what types of flow are these two velocities equal to each other?
Difference between"Upstream flow velocity" and "free stream velocity"and for which flow are they equal.
Answer to Problem 1CP
Upstream velocity represents approaching velocity while free stream velocity represents velocity of fluid relative to the immersed body(solid).
They are equal in uniform flow.
The difference between upstream flow velocity and free stream velocity is given in table below:
| Upstream flow velocity | Free stream velocity |
| The velocity(V) at which any fluid flow approaches an immersed body is known as upstream flow velocity. | The sufficiently far away velocity of the fluid which is relative to the immersed body(solid) is the free stream velocity. It is denoted by |
| It is the actual velocity of fluid flowing just before approaching the immersed body | It is the velocity which exists at end of the velocity boundary layer around the immersed body. |
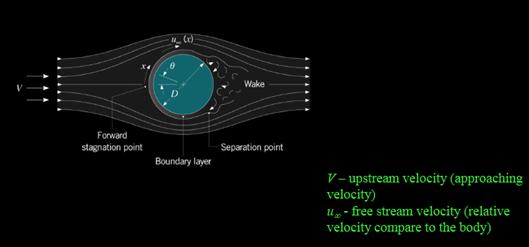
"Upstream flow velocity " and "free stream velocity" are same/equal when:
a. There is uniform fluid flow.
b. When the immersed body in fluid is relatively in comparison to uniform fluid flow rate, where it is immersed.
Explanation of Solution
The difference between upstream flow velocity and free stream velocity is given in table below:
| Upstream flow velocity | Free stream velocity |
| The velocity(V) at which any fluid flow approaches an immersed body is known as upstream flow velocity. | The sufficiently far away velocity of the fluid which is relative to the immersed body(solid) is the free stream velocity. It is denoted by |
| It is the actual velocity of fluid flowing just before approaching the immersed body | It is the velocity which exists at end of the velocity boundary layer around the immersed body. |

"Upstream flow velocity " and "free stream velocity" are same/equal when:
a. There is uniform fluid flow.
b. When the immersed body in fluid is relatively in comparison to uniform fluid flow rate, where it is immersed.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
Heat and Mass Transfer: Fundamentals and Applications
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Introduction to Heat Transfer
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics, 11th Edition
Fluid Mechanics Fundamentals And Applications
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
EBK FUNDAMENTALS OF THERMODYNAMICS, ENH
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics and Dynamics
- The weight of a thin flat plate 50 cm * 50 cmin size is balanced by a counterweight that has a mass of2 kg. Now a fan is turned on,and air at 1 atm and 25°C flows downward over bothsurfaces of the plate (front and back in the sketch) with afree-stream velocity of 10 m/s. Determine the mass of thecounterweight that needs to be added in order to balancethe plate in this case.arrow_forwardThe impeller of a centrifugal blower has a radius of 15 cm and a blade width of 6.1 cm at the inlet, and a radius of 30 cm and a blade width of 3.4 cm at the outlet. The blower delivers atmospheric air at 20°C and 95 kPa. Disre- garding any losses and assuming the tangential components of air velocity at the inlet and the outlet to be equal to the impeller velocity at respective locations, determine the volu- metric flow rate of air when the rotational speed of the shaft is 800 rpm and the power consumption of the blower is 120 W. Also determine the normal components of velocity at the inlet and outlet of the impeller.arrow_forwardWe derived the continuity equation in two ways: by using the divergence theorem and by summing mass flow rates through each face of an infinitesimal control volume. Explain why the former is so much less involved than the latter.arrow_forward
- Air lows past an object and exits as a free jet as shown in the figure. Because of the obstruction, the exit velocity is non-uniform with magnitude of 4 m/s from r = 0 to r = 0.5 m and 12 m/s from r = 0.5 m/s to r = 1.0 m. It is initially calculated that the average velocity is 10 m/s, Using a differential area, dA = 2rdr, what is the value of the kinetic energy correction factor, a? Air -4 m/s 2-m-dia. Wake 1-m dia. -12 m/s Exit Answer:arrow_forwardWater enters a 10-cm-diameter pipe steadily with a uniform velocity of 3 m/s and exits with the turbulent flow velocity distribution given by u = umax (1 - r/R)1/7. If the pressure drop along the pipe is 10 kPa, determine the drag force exerted on the pipe by water flow.arrow_forwardExpress the angular momentum equation in scalar form about a specified axis of rotation for a fixed control volume for steady and uniform flow.arrow_forward
- A garden hose attached witha nozzle is used to fill a 20 Liters bucket. The inner diameter of the hose is d =8 cm, and it reduces to d = 3.74 cm at the nozzle exit. If it takes 50 seconds to fill the bucket with hose nozzle water, determine average velocity (m/s) of water at the nozzle exit. Nozzle Garden Bucket hose cao-la ENG 100 US 07/05 DELL F8 F9 F10 F11 F12 PrtScr Insert Delete PgUp PgDn & Num Daliarrow_forwardConsider two different flows over geometrically similar airfoil shapes,one airfoil being twice the size of the other. The flow over the smallerairfoil has freestream properties given by T∞ = 200 K, ρ∞ = 1.23 kg/m3,and V∞ = 100 m/s. The flow over the larger airfoil is described byT∞ = 800 K, ρ∞ = 1.739 kg/m3, and V∞ = 200 m/s. Assume thatboth μ and a are proportional to T 1/2. Are the two flows dynamicallysimilar?arrow_forwardThe fluid condition at the inlet and exit of a horizontal convergent nozzle is analysed. The nozzle is operating steadily. and heat loss is assumed negligible. If the specific enthalpy of fluid and velocity of fluid at the inlet are 3,089 kJ/kg and 229 km/hr respectively. At the exit the specific enthalpy, of fluid is 2,569 J/kg. Calculate the exit area (in mm2)of the nozzle when the specific volume at the 3 nozzle exit is 0.63 m/kg at the inlet area of 0.2 m2 and the specific volume at the inlet is 0.31 m3/kg. You do not need to include the unit for this question.arrow_forward
- Consider the flow of an incompressible Newtonian fluid between two parallel plates that are 4 mm apart. If the upper plate moves to right with u1 = 5 m/s while the bottom one moves to the left with u2 = 1.5 m/s, what would be the net flow rate at a cross-section between two plates? Take the plate width to be 5 cm.arrow_forwardThe fluid condition at the inlet and exit of a horizontal convergent nozzle is analysed. The nozzle is operating steadily and heat loss is assumed negligible. If the specific enthalpy of fluid and velocity of fluid at the inlet are 3,314 kJ/kg and 226 km/hr respectively. At the exit the specific enthalpy of fluid is 2,563 J/kg. Calculate the exit area (in mm-)of the nozzle when the specific volume at the nozzle exit is 0.61 m3/kg at the inlet area of 0.23 m2 and the specific volume at the inlet is 0.3 m3/kg.arrow_forwardAt what distance r from the centre of a tube of radius r0 does the angular velocity occur in laminar flow?arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





